Multiple Myeloma (MM) maintenance therapy is a low intensive, prolonged treatment, commonly administered to newly diagnosed patients (pts) at the end of fixed-time, front-line regimens. Lenalidomide (LEN) is considered the best available maintenance option for MM able to prolong pts survival. However, the actual benefits or disadvantages of a LEN-based continuous maintenance and its potential role as selective pressure able to induce genomic changes are still unclear. The identification of specific therapy-driven modifications has been so far prevented by the scarce number of homogeneously-treated cohorts of pts with paired samples (diagnosis, D and relapse, R).
In this study we estimated the role of LEN maintenance therapy in eliciting genomic changes in a cohort of MM pts homogeneously up-front treated with PI-based regimens.
Whole genome Copy Number Aberrations (CNAs) landscape was obtained by SNPs array in 54 pts whose BM-CD138+ were collected both at D and at first R. Pts had an high-risk (HR) disease, as defined both by the presence of HR cytogenetic aberration at baseline in 81% of pts and by the 29 m median TTP.
RawCopy 1.10 was used for the segmentation of SNPs array signals; samples' purity was adjusted by using manually reviewed ASCAT solutions. A custom gene-level CN calling approach was set up, to match every gene's CN value at D and R, thus generating genomic evolutive patterns based on changes of these values. Finally, high-risk genomic loci were computed using GISTIC 2.0_v7 to derive focal regions with oncogene and/or tumor suppressor genes relevant for MM biology.
After induction therapy, 31/54 pts were treated with HD chemotherapy followed by either single or double ASCT; LEN maintenance therapy was then offered both to 20/31 auto-transplanted and to 6/23 not auto-transplanted pts.
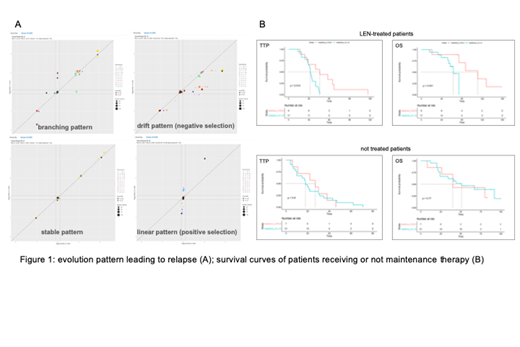
Three main evolutive trajectories (linear L, drift D, and branching B) were defined according to the CN changes' direction, reflecting a putative positive, negative, or both positive and negative selective pressure, respectively. A fourth, stable (S) trajectory was also observed, characterized by the absence of CN changes between D and R. Overall, 29, 15 and 10 pts relapsed with B/D, L and S pattern, respectively; at R, all LEN-treated pts quantitively and qualitatively changed their sub-clonal architecture: a B/D evolutive pattern characterized 70% of pts. By contrast, genome remained mostly stable in 61% of not-treated pts.
We then focused on CN changes of specific chromosomal regions and/or genomic loci, whose prognostic role has been already established in MM (i.e. CN losses of TP53 on chr17p, RB1 on chr13q, CYLD on chr16q, CDKN2C and FAM46C on chr1p; CN gain of CKS1B on chr1q). When present at D these CNAs tended to persist throughout the disease course regardless of whether pts received or not maintenance. The emersion of any of these CNAs at R was widely observed both in pts receiving or not maintenance, whereas a negative selective pressure over them was more likely to occur in pts receiving maintenance, as compared to the others (50% vs 11% of B/D trajectories in LEN-treated vs not-treated pts, respectively). Strikingly, in LEN-treated pts, the extension of both TTP and OS was favored by the extinction and/or negative selection of the HR CNAs (B/D patterns), and shortened by their stability or positive selection (L/S patterns) (median TTP 46 vs 32 m HR=3,6 CI 1,2-10,6, p=0.01; median OS 111 vs 63 m HR 5,7 CI 1,1-32,4, p=0.04 in B/D vs L/S pts, respectively). On the contrary, the absence of maintenance selective pressure seemed to affect neither the evolution trajectory, nor the clinical course of not-treated pts (fig 1).
The extinction of sub-clones carrying HR lesions in pts receiving maintenance therapy is likely to be associated to the negative selection exerted by the therapy itself. This might explain the extended survival of pts receiving maintenance and relapsing with B/D evolution patterns, as compared to that of pts whose genomic landscape either tended to remain stable or let the prevalent emersion of HR genomic features. On the contrary, the sub-clonal architecture of pts not receiving maintenance seemed to randomly evolve, due to the absence of a specific therapy-related selective pressure. Overall, information on the genomic changes occurring throughout the disease course might be relevant for the recognition of pts most benefitting from a continuous therapy.
Thanks to AIRC_IG2014-15839, RF-2016-02362532
Zamagni:Takeda: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Sanofi: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Honoraria, Other: Advisory board, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Honoraria, Other: Advisory board, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board, Speakers Bureau; Celgene Corporation: Honoraria, Other: Advisory board, Speakers Bureau. Tacchetti:BMS: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Honoraria; Oncopeptides: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Mancuso:Celgene: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria. Petrucci:Janssen-Cilag: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sanofi: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Liberati:Incyte: Consultancy; Servier: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol & Mayer: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria. Rossi:Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Daiichi-Sankyo: Consultancy; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sanofi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Jazz: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria; Mundipharma: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria; Sandoz: Honoraria. Boccadoro:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Research Funding; Mundipharma: Research Funding; Sanofi: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria. Cavo:amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; novartis: Honoraria; sanofi: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; bms: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: travel accommodations, Speakers Bureau; celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: travel accommodations, Speakers Bureau; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.