INTRODUCTION
Sickle cell disease (SCD), an autosomal recessive hemoglobinopathy, is associated with a high morbidity and mortality rate, especially in low income countries. In Africa, 5% of deaths among children under five are attributable to SCD [59th World Health Assembly, WHO 2006]. This chronic disease greatly alters the quality of life of affected children.
However, according to several published studies, SCD clinical course can be improved with the administration of hydroxyurea, an antimetabolite drug. [Nkashama, Pan African Medical Journal,2015]
Saint-Damien, a pediatric hospital in Haiti, has a current cohort of 1248 sickle cell children. Forty of them (3 %) benefit from hydroxyurea administration since November 2015. In this hospital, data on how hydroxyurea modifies SCD clinical course are lacking, despite the advantage of this drug described in literature [Charache,New England Journal of Medicine,1995]. This study aims to compare the evolution of children treated at Saint Damien Hospital, before and after receiving hydroxyurea.
METHODS
A retrospective analytic study was conducted from November 2013 to June 2018 in the Sickle Cell Clinic at Saint-Damien Hospital. We included 40 children aged 2 to 15 years old treated with hydroxyurea. All of them benefit of the same treatment protocol: Initial dose of 10 mg per kg per day increase to maintenance dose of 25 mg per kg per day. Any child whose treatment has been permanently discontinued regardless of the cause was excluded. Epidemiological and clinical data were collected using Excel 2010.
We compared children clinical evolution two years before and two years after hydroxyurea administration using these parameters: frequency and duration of hospitalizations, hospitalization frequency for specific complications (pain crisis, stroke and acute chest syndrome), and frequency of blood transfusions. We calculated frequencies, ratios and means using Epi Info. We realized statistical analysis to compare quantitative variables with a p value significant when less than 5%.
RESULTS
Gender ratio was 1:1. The mean age of children at enrollment on hydroxyurea was 8 years. Thirty-eight children of 40 (95 %) experienced at least one hospitalization before receiving the drug, compared with 17 (42.5%) after, p=0.025. The mean duration of hospitalization was 9 days before and 6 days after, p=0.0319. The average number of hospitalizations per child was decreased by 30 %.
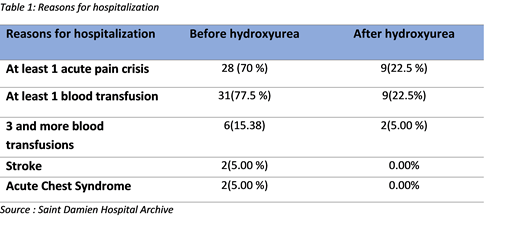
Seventy percent of children were hospitalized at least once due to painful crisis 2 years before receiving hydroxyurea, compare to 22.5 % after. Thirty-one children (77.5%) were transfused at least once before receiving the drug and 9 (22.5%) after receiving it. There was no cases of acute chest syndrome or stroke reported after hydroxyurea, unlike before the introduction of the drug. (Table 1)
CONCLUSION
The percentage of hospitalized children and the average length of hospitalization stay decreased significantly with hydroxyurea intake; as well as the frequency of painful crisis and blood transfusions.
Hydroxyurea acts directly on the two main causes of hospitalization in the sickle cell, reducing the morbidity related to this pathology; and demonstrating the direct benefit of this drug at Saint Damien Hospital.
Since our cohort is young, we have not been able to follow his evolution over a longer period of time. We plan to continue to observe this cohort. But these first results already allow us to recommend a broader use of hydroxyurea for pediatric patients with SCD in Haiti.
Alvarez:Forma Therapeutics: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.