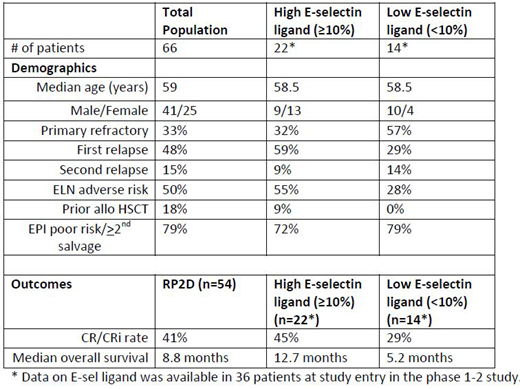
Leukemic myeloblasts expressing E-selectin ligand (E-sel ligand) adhere to E-selectin on bone marrow endothelium resulting in environment-mediated drug resistance (EMDR). Uproleselan, a potent E-selectin inhibitor, disrupts the adhesion of AML cells in the bone marrow, re-sensitizing blasts to the cytotoxic effects of chemotherapy. Retrospective data demonstrated that E-sel ligand expression in AML patients is higher in relapsed disease compared to newly diagnosed AML, is more commonly seen in biologically adverse risk patients, and is present on leukemic stem cells (Chien et al ASH 2018). Preliminary data from a phase 1-2 trial of uproleselan combined with mitoxantrone, etoposide, cytarabine (MEC) chemotherapy in R/R AML demonstrated enhanced survival in patients with E-sel ligand expression on AML cells of > 10% compared to lower levels (DeAngelo et al ASH 2018). In order to more fully understand the relationship of E-sel ligand to the activity of uproleselan, we examined the clinical variables of patients with both high (> 10%) and low E-sel ligand levels in comparison to the total population of patients treated on the phase 1-2 trial. Uproleselan, combined with MEC chemotherapy was studied in 66 patients with relapsed and/or refractory AML. The expression level of E-sel ligand on the surface of AML cells (blasts/leukemic stem cells (LSCs)) in the bone marrow was measured by a flow cytometric assay using the HECA 452 antibody that recognizes a functional trisaccharide domain shared by sialyl Lea and sialyl Lex and known to bind to E-selectin. Data on E-sel ligand was available in 36 patients at study entry in the phase 1-2 study and E-sel ligand was detectable on blasts in all patients. E-sel ligand on LSCs was demonstrated at levels ≥ 10% in 22 patients (61%) and at levels < 10 % in 14 patients (39%). Overall, the clinical characteristics confirmed a highly resistant population of R/R AML patients (see table) with 79% categorized as either poor risk by the European Prognostic Index (EPI) for first salvage therapy or ≥ second salvage, with an expected 1 year survival of less than 20% (Breems et al JCO 2005, Giles et al Cancer 2005). Although the sample size was small (n=36), substantially more patients with high E-sel ligand had achieved an initial remission and were in relapse (68%) whereas low E-sel ligand patients were more likely to be primary refractory (57%) (p=0.17). Patients with high E-sel ligand were more likely to have adverse ELN risk disease (55%) compared to low E-sel ligand patients (28%) (p=0.053). These data are consistent with previous findings demonstrating that higher E-sel ligand expression contributes to clinical chemotherapy resistance, particularly increasing the risk of relapse, whereas alternative resistance mechanisms may more commonly contribute to primary resistance. Importantly, the 45% response rate and 12.7 months median overall survival (OS) in the high E-sel ligand patients suggests that E-selectin inhibition by uproleselan contributed to their significantly improved outcomes when compared to the historically dismal outcomes with standard of care alone in these poor risk R/R AML patients.
DeAngelo:Incyte Corporation: Consultancy; Celgene Corporation: Consultancy; Pfizer, Inc.: Consultancy; GlycoMimetics: Research Funding; AbbVie, Inc.: Research Funding; Takeda Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Shire: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Blue Print Medicines: Consultancy, Research Funding; Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Consultancy, Research Funding. Jonas:AbbVie, Accelerated Medical Diagnostics, AROG, Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo, Esanex, Forma, Genentech/Roche, GlycoMimetics, Incyte, LP Therapeutics, Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, GlycoMimetics, Jazz, Pharmacyclics, Tolero: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie, Amgen, GlycoMimetics: Other: Travel expenses. Liesveld:Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Onconova: Other: Data safety monitoring board. Advani:Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding; Glycomimetics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Kite Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Abbvie: Research Funding; Macrogenics: Research Funding. Marlton:Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. O'Dwyer:Onkimmune: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; GlycoMimetics Inc: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding. Fogler:GlycoMimetics Inc: Employment, Equity Ownership. Magnani:GlycoMimetics Inc: Employment, Equity Ownership. Chen:GlycoMimetics: Employment. Feldman:GlycoMimetics Inc: Employment. Thackray:GlycoMimetics Inc: Employment. Becker:AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Glycomimetics, Invivoscribe, JW Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Trovagene: Research Funding; Accordant Health Services/Caremark: Consultancy; The France Foundation: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.