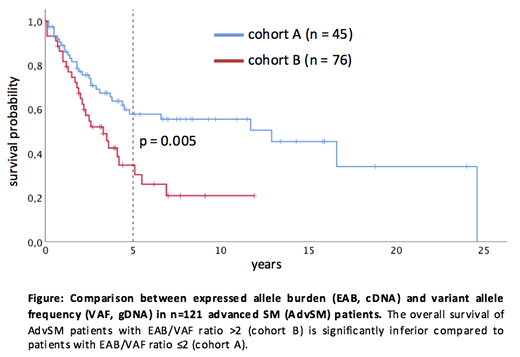
Systemic mastocytosis (SM) is characterized by activating mutations in KIT, usually KIT D816V in >90% of patients. According to the WHO classification, detection of KIT D816V is a minor diagnostic criterion. Moreover, a reduction of the RNA-based KIT D816V expressed allele burden (EAB) of ≥25% at month 6 is a favorable marker for improved survival in midostaurin-treated advanced SM (AdvSM) patients. However, only limited data exist upon the comparison between RNA-based and DNA-based quantitative KIT D816V mutation analyses. We therefore collected peripheral blood samples from 161 SM patients (indolent SM [ISM], n=40; AdvSM, n=121) at time of referral. We applied a real time reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) assay for assessment of the KIT D816V EAB and a chip-based digital PCR (dPCR) for the quantification of the DNA-based KIT D816V variant allele frequency (VAF, QuantStudio 3D dPCR System, ThermoFisher Scientific, Massachusetts, USA). The limit of detection (LOD) was assessed through serial dilution experiments with DNA from healthy individuals and DNA from a SM patient with a KIT D816V VAF of approximately 50%. All samples were analyzed in two independent dPCR runs. In an inital round-robin test for an inter-laboratory (n=4) comparison on 30 DNA samples (ISM, n=7; AdvSM, n=19), we found a very good correlation between 3 different chip-based digital PCR systems (dPCR; droplet-based dPCR, ddPCR, BioRad Laboratories, California, USA; quantitative real-time PCR, qPCR, California, USA; dPCR vs. ddPCR r=0.99, R2=0.99; dPCR vs. qPCR r=0.99, R2=0.98). In ISM patients, the comparison between EAB and VAF revealed a strong linear relationship with a correlation (r) of 0.91 and a coefficient of determination (R2) of 0.84, which was significantly inferior (r=0.71; R2=0.5) in AdvSM patients. In 45/121 (37%) and 76/121 (63%) of AdvSM patients, the EAB/VAF ratio was ≤2 (cohort A) or >2 (cohort B). To confirm the significant disparity between EAB and VAF in individual patients, serial analyses of at least 3 samples in 12 patients revealed a stable EAB/VAF ratio during follow-up. The comparison between cohort A and cohort B revealed significant differences in terms of a higher median hemoglobin level (p=0.006), a lower percentage of patients with hemoglobin <10g/dL (p=0.02), a lower median monocyte level (p=0.01), a lower median alkaline phosphatase level (p=0.03), and a lower number of patients with a high risk molecular profile (at least one gene mutation in SRSF2, ASXL1, and/or RUNX1, S/A/R, p=0.02) in cohort A. Moreover, patients of cohort A had a significantly better overall survival (OS) (median OS 12.9 versus 3.3 years; hazard ratio 2.1; 95% confidence interval 1.2-3.5; p=0.005; Figure). We conclude that a) KIT D816V EAB and VAF are significantly different in AdvSM patients but not in ISM and b) AdvSM patients with an EAB/VAF ratio >2 present with an aggressive phenotype and adverse prognosis as compared to patients with EAB/VAF ratio ≤2. We therefore recommend to routinely determine KIT D816V EAB and VAF in AdvSM patients.
Fabarius:Novartis: Research Funding. Reiter:Blueprint: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel reimbursement; Deciphera: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel reimbursement; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel reimbursement, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.