Background
Although the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (Btz) shows excellent efficacy in multiple myeloma (MM), some patients exhibit sub-optimal or no response to this agent. In addition, Btz-induced toxicity, such as peripheral neuropathy (PN) and skin disorders, limits its use in some patients. A comprehensive analysis of metabolites (metabolomics) in biofluids can be a potential novel strategy to predict the efficacy or adverse events of Btz treatment. With respect to the metabolic pathways in MM cells, a few studies have applied metabolomics using serum/plasma samples to elucidate MM pathogenesis or the mechanisms underlying the malignant transformation of MM cells. In addition, no metabolomic profile has been examined in terms of efficacy or toxicity of the specific MM treatment.
In this study, we performed lipid metabolomics analysis using plasma samples from patients with newly diagnosed MM (NDMM) prior to the initial Btz therapy, and have attempted to identify the association between the level of specific biomarkers in plasma lipid metabolites and the efficacy or severity of Btz-related toxicity.
Materials & Methods
Fifty-four plasma samples were analyzed from transplant-ineligible patients with NDMM enrolled in a randomized phase II study comparing two less intensive regimens of melphalan, prednisolone, and Btz (MPB) (JCOG1105; UMIN000011180). Informed consent to participate in the JCOG-BioBank, Japan Biorepository project, was obtained from the patients prior to sample acquisition. Frozen plasma samples obtained prior to MPB therapy were subjected to lipid metabolomics analysis, and the levels of phospholipids, sphingolipids, neutral lipids, and fatty acids (FAs) were measured using Liquid Chromatography/Mass spectrometry. The levels of lipid metabolites were relatively quantified as the ion peak ratio of each metabolite to the internal standard. We then evaluated whether the level of each lipid metabolite associated with the depth of response to MPB therapy and the grade of Btz-induced toxicity, such as peripheral neuropathy (PN) and skin disorders. Statistical analysis was performed by a multivariate permutation test using the Welch's t-statistic for multiple comparisons of the metabolite levels between the two groups categorized based on their response to MPB therapy or the grade of toxicity, ie. responder vs non-responder to the therapy, and grade 0-1 vs grade 2 or higher in the toxicities.
Results and Discussion
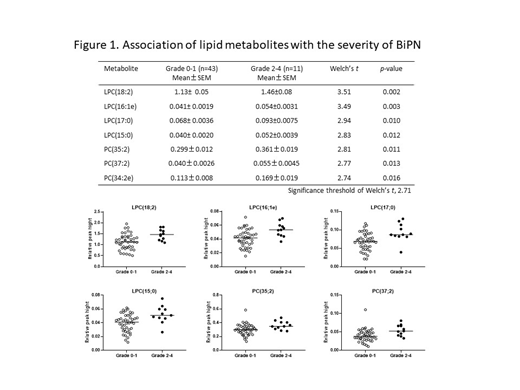
Lipid metabolomics analysis detected approximately 485 lipid metabolites in 54 plasma samples. We then evaluated the association between the level of each lipid metabolite and the grade of Btz-induced PN (BiPN) or skin disorders. As shown in Figure 1, high levels of seven phospholipids, including four lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) and three phosphatidylcholine (PC), were associated with BiPN of grade 2 or higher (n=11). LPC species were reported to facilitate neuropathic pain and nerve demyelination of the dorsal root ganglion and cuneate nucleus in the experimental model of PN. Therefore, high level of plasma LPC might worsen BiPN.
Moreover, low levels of three fatty acids-FA (18:2), FA (18:1), and FA (22:6)-were observed in patients who developed severe skin disorders of grade 2 or higher (n=10). Low level of FA (18:2), also called linoleic acid, has been reported to impair the anti-inflammatory response and repair skin barrier during the healing process. Therefore, low level of plasma FA (18:2) might associate with the aggravation of Btz-induced skin disorders.
No metabolite was significantly associated with tumor response, such as CR (n=9), in 53 samples evaluated for the best response to MPB therapy.
Conclusion
To our knowledge, this is the first plasma lipid metabolomics study to demonstrate that plasma lipid metabolite levels are associated with the severity of BiPN and skin disorders in patients with MM. These metabolites may serve as candidate biomarkers to predict Btz-induced toxicity in patients with MM before initiating Btz therapy. Our exploratory results need to be confirmed in further validation studies.
Ri:Janssen Pharmaceutical: Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda Pharmaceutical: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Research Funding; Ono Pharmaceutical: Honoraria, Research Funding; Kyowa Kirin: Research Funding; Chugai Pharmaceutical: Research Funding; Sanofi: Honoraria, Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Research Funding; MSD: Research Funding; Novartis Pharma: Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; Astellas Pharma: Research Funding; Teijin Pharma: Research Funding. Iida:Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Chugai: Research Funding; Kyowa Kirin: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; MSD: Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Research Funding; Teijin Pharma: Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Daichi Sankyo: Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria, Research Funding; Astellas: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Sanofi: Research Funding. Maruyama:Eisai: Honoraria, Research Funding. Tohkin:Towa Pharmaceutical: Research Funding. Tobinai:Kyowa Kirin: Honoraria, Research Funding; Meiji Seika: Honoraria; Zenyaku Kogyo: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda Pharmaceutical: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Verastem: Honoraria; Ono Pharmaceutical: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; HUYA Bioscience: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen Pharmaceutical: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Solasia: Honoraria; Chugai Pharmaceutical: Honoraria, Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy, Honoraria; Eisai: Honoraria, Research Funding; Yakult: Honoraria; Mundi Pharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding. Fukuhara:Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Honoraria; Zenyaku: Honoraria; Eisai: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen Pharma: Honoraria; Mochida: Honoraria; Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Honoraria; Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Honoraria, Research Funding; Mundi: Honoraria; Kyowa-Hakko Kirin: Honoraria; AbbVie: Research Funding; Celgene Corporation: Honoraria, Research Funding; Nippon Shinkyaku: Honoraria; Bayer: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Solasia Pharma: Research Funding. Miyazaki:Ono Pharmaceutical: Research Funding; Astellas Pharma: Research Funding; Eisai: Honoraria; SymBio Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; Nippon Shinyaku: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Kyowa Hakko Kirin: Honoraria, Research Funding; Chugai: Honoraria; Janssen Pharmaceutical: Honoraria. Tsujimura:Chugai Pharmaceutical: Honoraria; Eisai: Honoraria; Kyowa Kirin: Honoraria; Takeda Pharmaceutical: Honoraria. Yoshimitsu:Novartis: Speakers Bureau; Bristol-Myer-Squibb,: Speakers Bureau; Shire: Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Speakers Bureau; Chugai: Speakers Bureau; Sanofi: Speakers Bureau. Tsukasaki:Byer: Research Funding; Kyowa Kirin: Honoraria; Mundi Pharma: Honoraria; Ono Pharmaceutical: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; Eisai: Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Huya: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Chugai Pharmaceutical: Honoraria, Research Funding. Nagai:SymBio Pharmaceuticals Limited: Honoraria, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Honoraria, Research Funding; HUYA Bioscience International: Research Funding; Solasia Pharma K.K.: Research Funding; Zenyaku Kogyo: Honoraria, Research Funding; Ono Pharmaceutical: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Research Funding; Eisai: Honoraria, Research Funding; Kyowa Kirin: Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda Pharmaceutical: Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding; Bayer Pharma: Honoraria, Research Funding; Mundi Pharma: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen Pharmaceutical: Honoraria, Research Funding; Chugai Pharmaceutical: Honoraria, Research Funding; MSD: Honoraria; IQVIA: Research Funding; Otsuka Pharmaceutical: Research Funding; Sanofi: Honoraria; Novartis Pharma: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.