Background: Multiple novel therapies have been approved for the treatment of RRMM in recent years, resulting in improvements in progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). However, clinical trials in MM often enroll only a small proportion of older patients, particularly patients ≥75 years (Kanapuru 2017). Evaluating the impact of novel therapies, especially triplet therapies, in older adults with RRMM from individual clinical trials is challenging due to the small sample size. Furthermore, significant heterogeneity exists among the older adult population with regards to tolerability of anti-myeloma therapy. In newly diagnosed transplant-ineligible patients with MM, evidence from pooled analysis indicates that patients >80 years may be at increased risk for adverse clinical outcomes (Palumbo 2015).
We evaluated the prognostic impact of age on survival outcomes in patients with RRMM receiving novel therapies.
Methods: Data from 10 clinical trials submitted for approval between 2011-2015 were pooled for this analysis. Participants were grouped according to four age strata: <65, 65-74, 75-80, and >80 years. PFS and OS were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method (K-M). Within each age stratum, we conducted a subgroup analysis comparing doublet versus triplet regimens. Cox's proportional hazards regression model was used to estimate hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs), adjusting for gender, race, ISS stage, ECOG status, regimen (only for primary age analysis) and prior transplant.
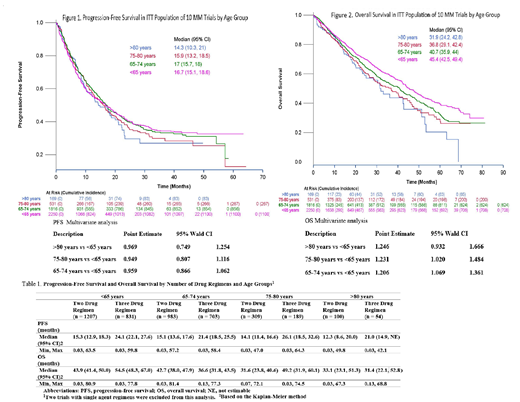
Results: In total, 4766 patients were included in the analysis. Forty-seven percent were <65 years, 39% were 65-74 years, 11% were 75-80 years and only 4% were >80 years of age. The percentage of patients with baseline ISS stage III and ECOG 2 was higher in the 75-80 years (31.0% and 11.0%) and >80 years group (32.0%, 19.0%) compared to 65-74 years (24.0%, 8.0%) and <65 years group (22.0%, 6.0%) respectively. K-M plots for PFS and OS and adjusted HR by age is shown below. Estimated median PFS and OS results by regimen type is displayed in Table 1.
Adjusted PFS HR (95% CI) for triplet versus doublet regimens was 0.69 (0.60, 0.79), 0.71 (0.61, 0.83), 0.61 (0.46, 0.81), and 0.62 (0.36, 1.05) for <65, 65-74, 75-80 and >80 years respectively. The HR (95% CI) for OS was 0.70 (0.59, 0.83), 0.86 (0.72, 1.02), 0.55 (0.40, 0.77) and 0.98 (0.56, 1.73).
Conclusions: Improvement in PFS with novel therapies, including triplet regimens, appears to extend to older adults including patients >80 years of age. No trend in treatment effect for PFS was observed across the age groups. Overall survival was lower in adults ≥65 years of age compared to patients <65 years although results were not significant for patients >80 years of age. Triplet regimens appear to improve survival over doublet regimens; however, a consistent trend across age groups was not observed. The OS results from this analysis must be interpreted with caution due to immature OS data at the time of submission, differential follow-up for individual trials, and small sample size, particularly in patients >80 years of age. Enrolling a representative population of older adults in MM clinical trials is needed to allow for an accurate assessment of outcomes in this population. Furthermore, considering biologic age rather than chronologic age to identify older patients who can benefit from these therapies would serve to further advance treatment in patients with MM.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.