BACKGROUND:
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) is increasingly used to treat a wide range of non-malignant disorders. However, the optimal strategy to be employed for GvHD prevention remains a matter of debate. In particular, the use of ATLG for the prevention of immune-mediated complications in patients transplanted from a matched-related donor (MRD) is still controversial. In the matched unrelated donor (MUD) setting, there is retrospective evidence that Rituximab used as prophylaxis of EBV viremia may protect from acute GvHD (aGvHD) development, but the clinical benefit of pre-transplant Rituximab has never been assessed in prospective randomized studies.
METHODS:
We conducted a multicentre, randomized, open-label, trial (NCT01810926) in 5 Italian centres enrolling patients with non-malignant haematological and inherited metabolic disorders transplanted from either a MRD or a MUD, selected using high-resolution typing for HLA-class I/II loci and stringent criteria of HLA-compatibility (>9/10). All patients received the same myeloablative regimen consisting of Treosulfan, Thiotepa and Fludarabine. Enrolled patients were randomized (1:1) to receive either standard or intensified GvHD prophylaxis. Cyclosporine-A plus short-term methotrexate was the standard GvHD prophylaxis in MRD HSCT recipients. In the experimental arm, patients were additionally given ATLG (Grafalon®, Neovii, 5 mg/kg/day on day -4,-3, and -2). In patients transplanted from a MUD, standard GvHD prophylaxis consisted of Cyclosporine-A plus short-term methotrexate and ATLG (10 mg/kg on day -4,-3 and-2). In the experimental arm, patients were additionally given Rituximab 200 mg/sq on day -1 (Mabthera®, Roche). In MRD group randomization was stratified by disease (hemoglobinopathies vs. other conditions) and in the MUD group by center.
For patients given MRD HSCT, the primary end-point was the probability of survival (SUR) free from: a) primary and secondary GF, b) grade II-IV aGvHD, c) chronic GvHD (cGvHD), d) death, whichever occurred first. For patients transplanted from a MUD, the primary end-point was the SUR probability free from: a) grade II-IV aGvHD, b) EBV viremia (>1,000 copies of viral DNA/ml whole blood), whichever occurred first. Secondary endpoint was overall SUR (OS). Statistical analyses were conducted according to intention-to-treat.
FINDINGS:
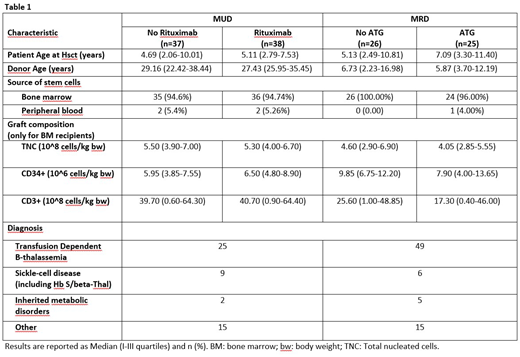
Between August 2011 and February 2018, 126 patients were enrolled. Patient and disease characteristics by randomized treatment are shown in Table 1. Median age at HSCT was 6.1 years in the MRD group (range 0.8-38) and 4.9 years in the MUD group (range 0.9-20.7). Median follow-up was 3.6 years.
Among the 51 MRD-HSCT recipients, 25 were randomly assigned to the ATLG group and 26 to the NO-ATLG group. No death and no cases of grade II-IV aGvHD were observed in either of the two randomization arms. Two GF occurred in each of the two arms, while 1 and 2 cases of cGvHD occurred in the ATLG and NO-ATLG groups, respectively. Consequently, no statistically significant difference in the probability of SUR without events was observed (p=0.75) and the 3-years estimates (±SE) were 86.9%±7.1% vs. 83.8%±7.5%, respectively.
In the MUD setting, 38 patients were allocated in the Rituximab group and 37 in the NO-Rituximab group. Although no statistically significant difference in OS (p=0.21) was observed between the two arms (3-years estimates: 94.1%±4.1% for Rituximab, 85.7%±5.9% for No-Rituximab), patients receiving Rituximab had a better probability of SUR without events (73.0%±7.3% vs 26.5%±7.3%, respectively; p=0.0002), entirely due to a lower incidence of EBV viremia. One case of fatal post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder was observed in the No-Rituximab arm. Eight patients developed grade II-IV aGvHD in each of the two arms. No patient has persistent dependence on ivIG replacement therapy.
CONCLUSIONS
Our data indicate that, in patients with non-malignant disorders given a MRD HSCT, the addition of ATLG does not confer any advantage in the prevention of both acute and chronic GvHD, as well as of GF.
In MUD-HSCT recipients, the administration of a fixed dose of pre-transplant Rituximab as part of the conditioning regimen does not affect the risk of aGvHD and transplant-related mortality, while it significantly reduces the incidence of episodes of EBV-viremia, without impairing B-cell recovery.
Algeri:Bluebird bio: Consultancy, Honoraria; Miltenyi: Honoraria; Atara Biotherapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria. Merli:Novartis: Honoraria; Sobi: Consultancy; Amgen: Honoraria; Bellicum: Consultancy. Locatelli:Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; bluebird bio: Consultancy; Miltenyi: Honoraria; Bellicum: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.