Background
Age and fitness typically enter into decisions regarding "intensity" of initial induction therapy for newly-diagnosed AML or its prognostic equivalent myelodysplastic syndrome with 10-20% blasts (hrMDS); patients with either are eligible for most of our institution's AML studies. However, "fitness" is a non-specific term. Here we examined the relation between specific covariates and intensity of initial induction. The primary goal was to examine the ability of multivariate models to identify objective characteristics associated with choice of intensity of induction: high + intermediate vs. low, and of high vs. intermediate + low.
Patients and Methods
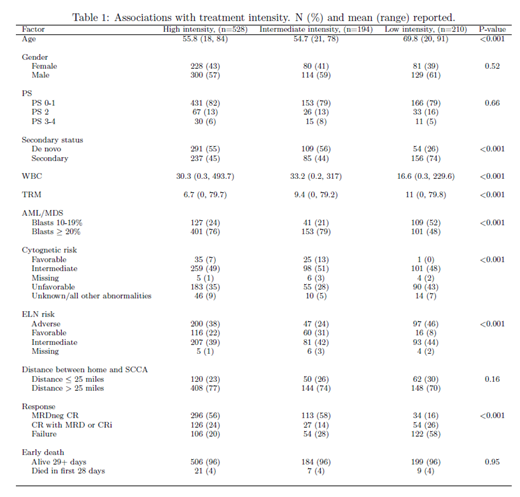
We reviewed 1,346 newly diagnosed AML/hrMDS patients seen at our center from January 2008 through May 2018. We excluded 226 patients who received palliative care only or unknown treatment outside our center and 188 patients given uncommon regimens, generally on a clinical trial. High-intensity treatment consisted of ara-C in single doses ³ 1g/m2, intermediate intensity was 7+3 +/- other drugs, and low intensity was azacitidine or decitabine +/- other drugs. Pre-treatment characteristics examined in the 932 analyzed patients (29% with 10-20% blasts) for potential inclusion in multivariate models were year of treatment, age, gender, de novo or secondary disease, performance status (PS), white blood cell count, treatment related mortality score (TRM, predicting death by day 28 after receipt of intermediate or intense induction), blast percentage, ELN 2017 risk, and distance from home to our center (Table 1). P-values < 0.01 were considered "significant" in the multivariate models with values for area under receiver operating characteristic (AUC) curves of 0.6-0.7, 0.7-0.8, and 0.8-0.9 considered, as commonly understood, to respectively denote "poor", "fair", and "good" predictive ability.
Results
57% of the 932 patients received high intensity treatment, 21% intermediate intensity, and 23% low intensity. Covariates significantly associated with receipt of high vs. intermediate/low intensity on multivariable analysis were younger age, (surprisingly) PS 3-4 (OR 1.4, 95% CI 1.1, 1.8), lower TRM score, and > 20% blasts. The model's AUC was 0.69. Older age, higher TRM score and blasts 10-20% were associated with receipt of low rather than high or intermediate intensity induction. This model's AUC was 0.85. With the marginal exception that patients with ELN 2017 adverse risk were more likely to receive high intensity induction (OR 1.1, 95%CI 1.0-1.2) neither ELN 2017 risk nor secondary vs. de novo AML were associated with decisions regarding intensity. Although rates of CR without MRD and of induction failure (neither CR nor CRi) were better following high (56%, 20% respectively) or intermediate (58%, 28%) than low intensity induction (16%, 58%), after accounting for age, PS (2 rather than 0-1), TRM score and ELN risk, overall survival was similar in high vs. low intensity [OR 0.95, 95%CI 0.8-1.2], high vs. intermediate (0.99, 95%CI 0.8-1.3) and intermediate vs. low (0.96, 95%CI 0.7-1.3) groups.
Conclusion
A multivariable model provided reasonably accurate prediction of which patients with newly-diagnosed AML or hrMDS will receive low intensity induction at our institution, but a poor prediction of which patients will receive high intensity. Other, perhaps less objective, covariates subsumed under "fitness" may play an important role, particularly in the latter decision.
Gardner:Abbvie: Speakers Bureau. Othus:Celgene: Other: Data Safety and Monitoring Committee; Glycomimetics: Other: Data Safety and Monitoring Committee. Becker:The France Foundation: Honoraria; Accordant Health Services/Caremark: Consultancy; AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Glycomimetics, Invivoscribe, JW Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Trovagene: Research Funding. Halpern:Pfizer Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Bayer Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding. Scott:Agios: Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Research Funding; Celgene Corporation: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Alexion: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Walter:Argenx BVBA: Consultancy; New Link Genetics: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Race Oncology: Consultancy; Boehringer Ingelheim: Consultancy; Boston Biomedical: Consultancy; Covagen: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Kite Pharma: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy; BiVictriX: Consultancy; BioLineRx: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy; Amphivena Therapeutics: Consultancy, Equity Ownership; Aptevo Therapeutics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Astellas: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.