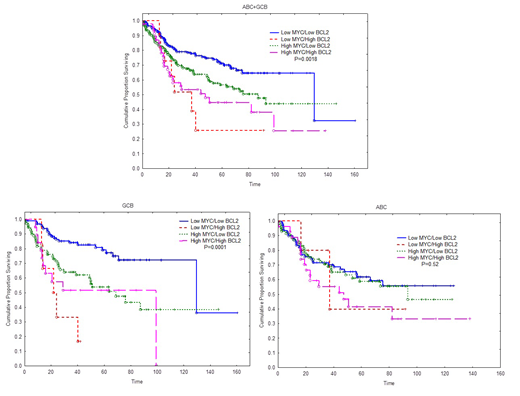
Introduction: RNA expression profiling using Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) provides important and reproducible information on expression levels of various genes. We studied the expression levels of MYC and BCL2 in patients with diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma (DLBCL) using NGS targeted RNA sequencing. We correlated levels of expression of these genes with outcome. Methods: RNA extracted from 441 FFPE samples with DLBC lymphoma and sequenced targeting 1408 genes. The RNA sequencing is based on hybrid capture and the number of reads ranged from 5 to 10 million. RNA quantification was performed using Cufflinks. The RNA levels were normalized to PAX5 mRNA levels. Of these cases, 380 were subclassified as ABC or GCB using expression profiling. The rest were classified as "undetermined", therefore were not included in further analysis. All patients were treated with R-CHOP. Results: The expression of MYC and BCL2 mRNA was slightly higher in ABC as compared with GCB (P=0.01 and P=0.02, respectively). However, in the GCB subtype, patients with MYC expression above the median showed significantly shorter survival as compared with those below the median (P=0.0007, Log-rank test). In contrast, there was no significant difference in survival using median of MYC expression as cutoff in patients classified as ABC subtype (P=0.38). Using upper 15% cut-off point for BCL2 mRNA expression, GCB patients with high BCL2 expression had significantly shorter survival (P=0.005). In contrast, there was no significant difference in survival between high and low BCL2 expression groups in the ABC subtype (P=0.1). When both MYC and BCL2 are considered, patients with high expression of both BCL2 and MYC (double-RNA expression) had significantly shorter survival as compared with patients with low expression of both MYC and BCL2 (P=0.0009) when both GCB and ABC groups are considered. Patients with high BCL2 expression also had poor survival similar to those double-RNA expression. Considering only patients with GCB, high expressor of both MYC and BCL2 had significantly worse outcome (P=0.0015) as compared with low expressors of both MYC and BCL2, but patients with high BCL2 also had significantly poor outcome as compared to low expressor of both MYC and BCL2 (P=0.0005). In contrast, there was no difference in survival for high or low MYC and BCL2 expressor in the ABC group. Conclusion: The data support the concept that in DLBCL, MYC and BCL2 mRNA expression levels are clinically relevant in GCB, but not ABC subtype. Furthermore, targeted RNA sequencing might provide a reliable and practical objective approach for the subclassification of DLBCL and determining double-RNA expression lymphoma.
Albitar:Genomic Testing Cooperative: Employment, Equity Ownership. Tam:Takeda: Consultancy; Paragon Genomics: Consultancy. Hsi:Abbvie: Research Funding; Eli Lilly: Research Funding; Cleveland Clinic&Abbvie Biotherapeutics Inc: Patents & Royalties: US8,603,477 B2; Jazz: Consultancy. Piris:Calgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Jansen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Lecture Fees; Nanostring: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kyowa Kirin: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kura: Research Funding; Millenium/Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Lecture Fees, Research Funding. Kantarjian:Immunogen: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Cyclacel: Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding; Agios: Honoraria, Research Funding; Ariad: Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Astex: Research Funding; Jazz Pharma: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Actinium: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Daiichi-Sankyo: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal