Introduction: Idelalisib (IDELA) is the first-in-class PI3Kδ inhibitor and is approved as a monotherapy for relapsed or refractory (R/R) follicular lymphoma and in combination with rituximab for R/R chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). We previously evaluated IDELA treatment interruption as a mechanism to mitigate treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) and found that limited interruption with clinically appropriate re-challenging resulted in superior clinical outcomes. These findings did not comprehensively address the potential confound of interruptions inherently being associated with longer duration of therapy (DoT). Furthermore, the compound effect of IDELA dose reduction together with treatment interruption on IDELA efficacy was not assessed.
Objectives: 1) To evaluate whether the benefit of IDELA interruption is retained in patients on therapy >180 days, a duration previously found to be associated with longer overall survival among patients who discontinued IDELA due to an AE; and 2) To compare clinical outcomes of patients who reduced IDELA dosing in addition to interrupting IDELA with those of patients who interrupted IDELA without additional dose reduction.
Methods: Using data from Gilead-sponsored trials of patients with R/R indolent non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (iNHL) treated with IDELA monotherapy (N=125, Gopal et al., N. Engl. J. Med., 2014) or with R/R CLL treated with IDELA + anti-CD20 (N=110, Furman et al., N. Engl. J. Med., 2014; and N=173, Jones et al., Lancet Haematol., 2017), DoT, progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS) were compared between patients on IDELA therapy >180 days with vs. without interruption and between patients who experienced Interruption and Dose Reduction (IDR) vs. patients who experienced Interruption but NoDose Reduction (INoDR) at any point during IDELA treatment. Interruption was defined as missing at least one IDELA treatment day due to an AE and dose reduction could have occurred before or after the first interruption. PFS and OS were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and were compared using a log-rank test.
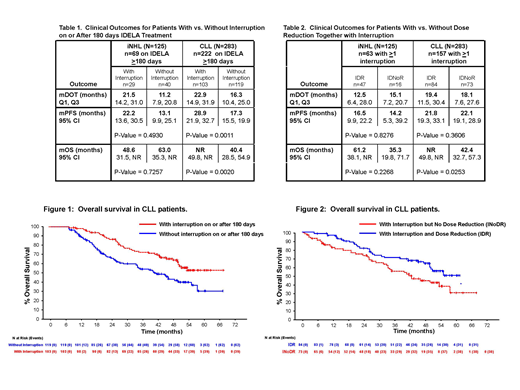
Results: Sixty-nine of 125 patients with R/R iNHL (55.2%) and 222 of 283 patients with R/R CLL (78.4%) remained on IDELA therapy >180 days with 29 (42.0%) and 103 (46.4%) of them, respectively, experiencing interruption on or after day 180 (Table 1). The proportions of patients with interruption before day 180 were similar within each of these populations. Among patients on therapy >180 days, those with treatment interruption on or after 180 days had a longer median (m) DOT than patients without interruption (Table 1). Both PFS and OS were longer in CLL patients who interrupted compared to those who did not interrupt (mPFS=28.9 mos. vs. 17.3 mos. and mOS=not reached [NR] vs. 40.4 mos. for with interruption vs. without interruption, respectively, Table 1 and Figure 1). In patients with iNHL, no difference was observed in PFS or OS between patients who interrupted vs. those who did not (Table 1).
Of patients who experienced at least one AE-induced interruption at any point during IDELA therapy (n=63 iNHL and n=157 CLL), 47 iNHL patients (74.6%) and 84 CLL patients (53.5%) also had dose reduction. Two iNHL patients (1.6%) and 5 CLL patients (1.8%) had IDELA dose reduction but no interruption. Both iNHL and CLL patients with IDR experienced a similar PFS compared to patients with INoDR (mPFS=16.5 mos. vs. 14.2 mos. for iNHL and 21.8 mos. vs. 22.1 mos. for CLL with IDR vs. INoDR, respectively, Table 2). However, OS was longer in both iNHL and CLL patients with IDR compared to INoDR (mOS=61.2 mos. vs. 35.3 mos. for iNHL and NR vs. 42.4 mos. for CLL, respectively, Table 2; CLL patients shown in Figure 2).
Discussion: IDELA treatment interruption is not associated with rapid clinical deterioration, as observed with some B-cell receptor signaling pathway inhibitors. No clear relationship between IDELA DoT and frequency of interruption was observed. When normalized for DoT >180 days, IDELA treatment interruption retained its clinical benefit in the CLL population. When utilized together with IDELA interruption, dose reduction did not lead to inferior clinical outcomes but instead extended OS in both iNHL and CLL populations. Adherence to treatment interruption and dose reduction guidance as outlined in the IDELA USPI may optimize IDELA tolerability and efficacy for patients with iNHL and CLL.
Ma:Janssen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; Juno: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Xeme: Research Funding; Beigene: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Kite: Consultancy; Acerta: Research Funding; Bioverativ: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy. Chan:Gilead Sciences, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Gu:Gilead Sciences, Inc.: Employment. Xing:Gilead Sciences, Inc.: Employment. Rajakumaraswamy:Gilead Sciences, Inc.: Employment. Ruzicka:Gilead Sciences, Inc.: Employment. Wagner-Johnston:Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; ADC Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Jannsen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bayer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.