Allogeneic stem cell transplantation (SCT) is a potentially curative treatment for MDS. Besides the innate heterogeneity of MDS, intensity of the conditioning regimen (myeloablative (MAC) versus reduced intensity/non-myeloablative (RIC)), specific agents used in conditioning, donor and source of stem cells and GVHD prevention regimens further influence outcomes. We sought to determine how conditioning regimens influenced MDS subgroup cohort outcomes.
We retrospectively analyzed outcomes of 107 MDS patients (63 male and 44 females) with median age 61.8 (17-73 years) who underwent allogeneic SCT at our institution between 2008 and 2017. For the purposes of this report, patients were grouped according to WHO classification into non-RAEB (RCMD, RA, RARS RCUD or 5q deletion, n=49) and RAEB (RAEB1 and RAEB2, n=58) categories. Median time from MDS diagnosis to transplantation was 139 days (20-3175). No patients were in complete remission (CR) at time of SCT. Allogeneic donor types were matched related, matched unrelated, haplo-identical and cord blood in 30, 65, 10 and 2 patients, respectively. Stem cell source was peripheral blood (91 patients) and bone marrow in 14. Forty patients (median age 52.2 (17-61) years) underwent MAC and 67 (median age 63.7 (23-73) years) RIC. Twelve patients died within 100 days of transplantation, 3 due to disease progression, 5 to acute GVHD, and 4 to other transplant-related causes.
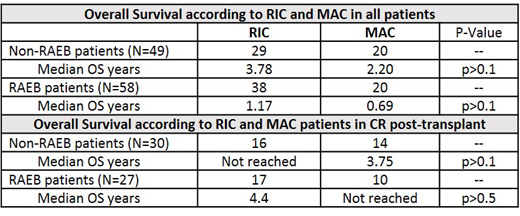
Median overall survival (OS) for all 107 patients was 1.3 years with 54%, 47% and 40% alive at 1, 2 and at 5 years. OS was slightly higher in patients undergoing RIC with OS of 57%, 48% and 40% (median 1.532 years) versus 50%, 40% and 38% with MAC (median 0.92 years) at the same time points (p>0.1). Median OS of the 49 patients with non-RAEB and 58 patients with RAEB MDS was 3.01 years versus 0.92 years (p>0.1). GVHD was the most frequent cause of death (46%), followed by relapse/progression (28%), infection (14%) and other (12%). Of 29 patients undergoing RIC with non-RAEB MDS, median OS was 3.78 years while for 38 RAEB patients it was 1.17 years (p>0.1). See table for OS according to conditioning regimen and WHO classification. For MAC, in 20 non-RAEB patients median OS was 2.2 years while the median OS was 0.69 years for 20 RAEB patients (p>0.1).
CR after SCT was achieved in 57 patients (53%), 33 receiving RIC (CR 49.2%) and 24 receiving MAC (CR 60%). Seven patients subsequently relapsed, 4 RIC and 3 MAC. Of the non-RAEB patients achieving CR, median OS in the 16 patients treated with 111 RIC was not reached and in 14 patients receiving MAC, median OS was 3.75 years (p>0.1). For the 27 RAEB patients achieving CR, median OS was 4.4 years in 17 patients treated with RIC versus not reached in 10 patients treated with MAC.
Overall, death in non-RAEB patients occurred in 26/49 (53%) compared to 38/58 (66%) RAEB patients and in 40/67 (59%) patients undergoing RIC versus 25/40 (63%) MAC patients (p>0.5). The hematopoietic transplant comorbidity index did not predict OS outcomes in these MDS patients (p>0.1) and the cytogenetic score according to the IPSS-R "very good -very poor" groups indicated no differences in OS in the non-RAEB patients but in RAEB patients significant differences according to the cytogenetic score was evident (P<0.01).
Conclusions: In this retrospective analysis of MDS patients undergoing allogeneic SCT, achieving CR led to improved survival. In non-RAEB MDS patients achieving CR, OS was similar irrespective of conditioning intensity (RIC or MAC). Furthermore, outcomes did not differ in RAEB patients who achieved CR according to intensity of conditioning regimen. However, those receiving MAC had not reached median OS at 5 years. The outcomes in this analysis indicate that improvement in the incidence of deaths due to GVHD would likely have the greatest impact in improving survival in MDS patients undergoing allogeneic transplantation.
Abhyankar:Therakos: Other: Consulting, Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Speakers Bureau. Lin:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Yacoub:Incyte: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Ganguly:Kite Pharma: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board; Seattle Genetics: Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board; Daiichi Sankyo: Research Funding. McGuirk:Pluristem Ltd: Research Funding; Gamida Cell: Research Funding; Kite Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Bellicum Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Astellas: Research Funding; Fresenius Biotech: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Juno Therapeutics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; ArticulateScience LLC: Other: Assistance with manuscript preparation.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.