Background:
The number of non T depleted haploidentical stem cell transplantations (haplo SCT) with post transplantation cyclophosphamide (PTCy) in adult patients (pts) with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is increasing (Shemtov N et al, Leukemia 2019). Although the original haplo SCT with PTCy were performed with bone marrow (BM) grafts, the use of peripheral blood stem cells (PBSC) as the stem cell source may provide some advantages in engraftment and anti-leukemic effect which may be of special importance in ALL.
Aim:
The goal of this study was to compare BM to PBSC as stem cell source for non-T-cell-depleted haplo SCT with PTCy in adult pts with ALL in first or second complete remission (CR).
Methods:
The study was based on the haplo SCT with PTCy in adult pts with ALL that met the study inclusion criteria and that were reported to the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) registry from 2010 to 2018. Multivariate analyses (MVA) were performed using the Cox proportional hazard model.
Results:
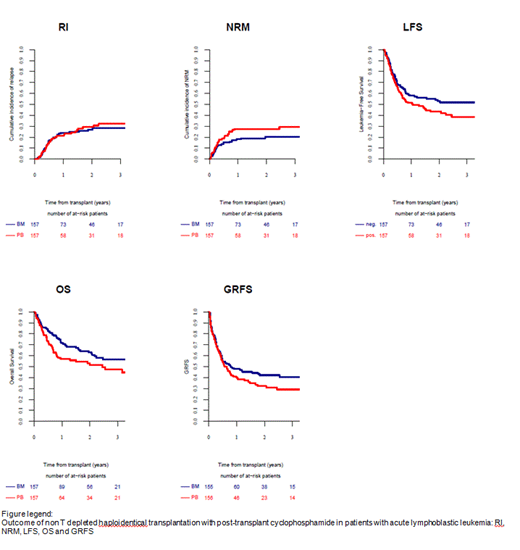
A total of 314 pts were reported, 157 of whom received BM and 157 received PBSC as the stem cell source. The median age at transplantation was 37 years (range, 18-68 years) and 36 years (range, 18-73 years), 66% and 62% were males, respectively. Diagnosis was Ph negative B-ALL in 39% and 41% of the pts, Ph positive in 32% and 34 % and T ALL in 29% and 25%, respectively.61% and 65% were in CR1, while 39% and 35% were in CR2. Pts and donor characteristics did not differ between the groups. More pts in the BM group received myeloablative conditioning (MAC), 87% vs 71% in the PBSC group, p<0.0001. The cumulative incidence of engraftment at d60 was higher in the PBSC group compared to BM: 98% vs 93%, respectively p=0.0005. The incidence of 100 days acute(a) and 2y chronic(c) graft vs host disease (GVHD) were not significantly different between the BM and the PBSC graft source; Grade (Gr) II-IV 26% and 36%, III-IV 14% and 14%, total chronic 31% and 36% and extensive 12% in both, respectively. GVHD was the cause of death in 18% of pts receiving PBSC graft in comparison to 13% of those that received BM grafts. In MVA there was a trend for higher incidence of aGVHD II-IV HR 1.52 (0.973-2.38), p=0.065 and cGVHD HR 1.58 (0.995-2.51), p=0.053 in pts receiving PBSC vs BM grafts, respectively. Similarly, there was a trend for higher non relapse mortality (NRM) in the PB vs BM group HR 1.66 (0.99-2.8), p=0.056. There was no difference in relapse incidence (RI) HR 1.23 (0.76-2.0), p=0.416.While, leukemia free survival (LFS), overall survival (OS) and GVHD rel free survival (GRFS) were significantly better in pts receiving BM in comparison to PBSC graft HR 1.43 (1.0-2.03), p=0.047, HR 1.59 (1.08-2.34), p=0.018 and HR 1.42 (1.03-1.95), p=0.03, respectively.
Conclusion: In pts with ALL in remission receiving haplo SCT with PTCy, the use of BM versus PBSC grafts resulted in better LFS, OS and GRFS.
Angelucci:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Other: Local advisory board; Roche: Other: Local advisory board; Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated, and CRISPR Therapeutics: Other: Partecipation in DMC; BlueBirdBio: Other: Local advisory board; Novartis: Honoraria, Other: Chair Steering Committee TELESTO protocol; Celgene: Honoraria, Other: Partecipation in DMC. Socie:Alexion: Consultancy. Blaise:Molmed: Consultancy, Honoraria; Sanofi: Honoraria; Pierre Fabre medicaments: Honoraria; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria. Mohty:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.