Background: Achieving sustained DMR (variably described as ≥ MR4 or ≥ MR4.5) is an emerging treatment goal for patients with CML. DMR is associated with excellent long-term clinical outcomes and a higher likelihood of successful treatment-free remission (TFR) upon discontinuation of tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy. Biological predictors of patients likely to achieve DMR are unknown. Here, we present an exploratory analysis of gene expression signatures in order to predict DMR to TKI therapy, as well as understand the biological underpinnings that allow a DMR, based on patients treated with imatinib or nilotinib in the ENESTnd study (NCT00471497).
Methods: ENESTnd is a phase 3, randomized, open-label study comparing nilotinib 300 mg twice daily (BID), nilotinib 400 mg BID and imatinib 400 mg once daily (QD) in patients with newly-diagnosed CML. To maximize the likelihood of defining predictive and biologically relevant gene signatures, samples from a group of poor responders (BCR-ABL1IS > 10% by 3 months of therapy) and good responders (BCR-ABL1IS < 0.01% by 12 months of therapy) were selected across all treatment arms. Whole blood samples collected prior to study treatment initiation were available from 112 such patients from the total 846 patients enrolled in ENESTnd, and were subjected to RNA sequencing. DMR was assessed using quantitative polymerase chain reaction transcript ratios standardized to the international scale (IS) and was defined as BCR-ABLIS ≤ 0.01% (MR4) or ≤ 0.0032% (MR4.5). For statistical analysis, responders were defined as patients having achieved DMR by 5 years, whereas non-responders were in the trial for ≥ 5 years without achieving DMR. Five years was selected to ensure that patients on both imatinib and nilotinib arms had adequate time to reach MR4.5. The association of clinical variables with responder status (good or poor) was assessed via a multivariate logistic regression model.
Results: We correlated clinical variables (eg, Sokal risk score, TKI, age, sex) with responder status for 112 ENESTnd study patients who received 400 mg imatinib QD (n = 47), 300 mg nilotinib BID (n = 33), or 400 mg nilotinib BID (n = 32). Of the 112 patient samples, 70 were included in the analysis using MR4.5 as an endpoint, with 47 patients characterized as responders (imatinib: 16; nilotinib: 31), and 23 as non-responders (imatinib: 13; nilotinib: 10). Of the 112 samples, 42 were excluded from analysis because the patients discontinued the trial before 5 years and did not achieve MR4.5 (imatinib: 18; nilotinib: 24). Younger age (< 35 years) was associated with good response (p < 0.02) in a multivariate analysis.
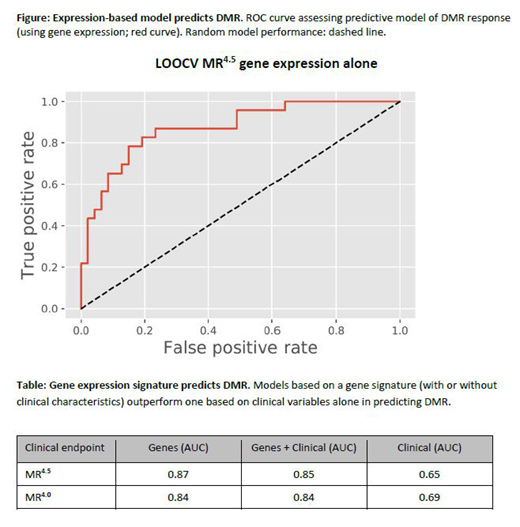
We developed a predictive model of responder status by applying penalized regression to clinical variables and gene expression (13569 genes) in independent (clinical or gene expression) and combined gene and clinical models. The best performing model used patients with MR4.5 vs poor responders, with an area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC) of 0.87 (Figure; Table). Including clinical variables did not result in markedly different performance (AUC = 0.85). Significantly, both models outperformed a model that included clinical variables only (AUC = 0.65). Relaxing the definition of good responders to include patients with MR4 yielded similar results (Table).
Detailed biomarker/pathway analysis to explore the biological pathways that separate good and poor response are underway.
Conclusions: We present a gene expression model that distinguishes patients who achieved a DMR from those with a poor response to treatment at 5 years. The approach for sample selection optimized the chances of finding a biological and clinical signal and may be applicable to all CML patients initiating TKI therapy. This work could yield new therapeutic targets that could potentially turn a patient biologically determined to be a poor responder into a good responder who might even achieve a TFR.
Radich:Novartis: Other: RNA Sequencing; TwinStrand Biosciences: Research Funding. Larson:Novartis: Honoraria, Other: Contracts for clinical trials; Celgene: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy. Kantarjian:Ariad: Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria; Astex: Research Funding; Immunogen: Research Funding; Actinium: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Daiichi-Sankyo: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Cyclacel: Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Agios: Honoraria, Research Funding; Jazz Pharma: Research Funding. Deininger:Blueprint: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Ascentage Pharma: Consultancy, Honoraria; TRM: Consultancy; Sangoma: Consultancy; Fusion Pharma: Consultancy; Adelphi: Consultancy; Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Humana: Honoraria; Incyte: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Sangamo: Consultancy. Pinilla Ibarz:Novartis: Consultancy; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Teva: Consultancy; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy; Bayer: Speakers Bureau; Sanofi: Speakers Bureau. DeAngelo:Abbvie: Research Funding; Takeda Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Jazz Pharmaceuticals Inc: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy; GlycoMimetics: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Blueprint: Consultancy, Research Funding; Shire: Consultancy. Branford:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Qiagen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Cepheid: Consultancy, Honoraria. Sadek:Novartis: Employment. Chaturvedi:Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Employment. Sondhi:Novartis: Employment, Other: Stock; Sanofi: Other: Stock. Mishra:Novartis: Employment. Purkayastha:Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Employment. Shrestha:Novartis: Employment. Obourn:Novartis: Employment. Druker:Cepheid: Consultancy, Honoraria; Burroughs Wellcome Fund: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GRAIL: Equity Ownership, Other: former member of Scientific Advisory Board; CureOne: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Beat AML LLC: Other: Service on joint steering committee; Vivid Biosciences: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Stock options; The RUNX1 Research Program: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Patient True Talk: Consultancy; Pfizer: Other: PI or co-investigator on clinical trial(s) funded via contract with OHSU., Research Funding; Aptose Biosciences: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; ALLCRON: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Research Funding; Aileron Therapeutics: #2573, Constructs and cell lines harboring various mutations in TNK2 and PTPN11, licensing fees , Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; OHSU (licensing fees): Patents & Royalties: #2573, Constructs and cell lines harboring various mutations in TNK2 and PTPN11, licensing fees ; Celgene: Consultancy; Merck & Co: Patents & Royalties: Dana-Farber Cancer Institute license #2063, Monoclonal antiphosphotyrosine antibody 4G10, exclusive commercial license to Merck & Co; Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (antibody royalty): Patents & Royalties: #2524, antibody royalty; Beta Cat: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Stock options; Blueprint Medicines: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Other: PI or co-investigator on clinical trial(s) funded via contract with OHSU., Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Other: former member of Scientific Advisory Board; ICON: Other: Scientific Founder of Molecular MD, which was acquired by ICON in Feb. 2019; Monojul: Other: former consultant; Novartis: Other: PI or co-investigator on clinical trial(s) funded via contract with OHSU., Patents & Royalties: Patent 6958335, Treatment of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors, exclusively licensed to Novartis, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.