Abstract
The therapeutic landscape for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) has evolved in recent years with the introduction of hypomethylating agents (HMA) and venetoclax in patients previously deemed unfit for curative - intent treatment. Some of these patients undergo allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant (alloHCT), yet there are scarce data regarding transplantation outcomes.
We conducted a multicenter nationwide retrospective cohort study to evaluate outcomes of patients with AML who underwent alloHCT in first CR (CR1) after frontline treatment with 5-azacitidine plus venetoclax (aza-ven group). In addition, we collected a historical control group of patients who achieved CR1 following first line intensive chemotherapy followed by alloHCT (intensive group).
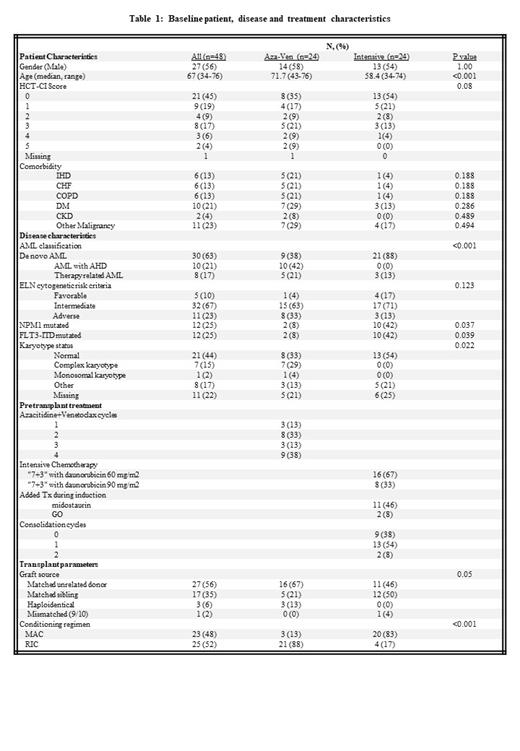
24 patients in the aza-ven group were transplanted between 2019 and 2021. Compared to the intensive group, patients in the aza-ven group were older (median age 71.7 vs. 58.4 years, p <0.001), had higher incidence of therapy related AML and AML with antecedent hematologic disorder (p <0.001) and had more often adverse cytogenetics (p=0.022). They had a higher percentage of allografts from matched unrelated donors, and reduced intensity conditioning was more commonly used (Table 1).
Median follow up was 8 (range, 0 to 25) months in the aza-ven group and 23 (range, 4 to 56) months in the intensive group. Estimated 12 months non relapse mortality was 19.1% in the aza-ven group and 11.8% in the intensive group (p=0.492). The estimated median relapse free survival (RFS) was not reached in the aza-ven group and was 19.3 months (CI 95% 1-38) in the intensive group. There was no difference between the two groups in 12 months RFS (58% and 54% in the aza-ven group and intensive group, respectively, p = 0.892). The estimated median survival of the aza-ven group was not reached and the 12 months overall survival (OS) rate was 63.2%. The estimated median survival of the intensive group was 50 months (CI 95% 5 - 96) and the 12 months OS rate was 70.8%. There was no statistical differences between the two groups regarding OS (p = 0.58).
In a subgroup Cox regression analysis of the aza-ven group, adverse ELN 2017 risk category and HCT-CI score ≥3 were predictive of decreased RFS, both in univariate analysis (UVA) and in multivariate analysis (MVA) (HR 10.56, CI 95%1.64-68.1, p=0.013 and HR 6.43, CR 95% 1.34-30.75, p=0,02, respectively). Graft source (alternative vs. matched donor) and HCT-CI score ≥3 were predictive of decreased OS in UVA (HR 19.45, CI 95% 1.66-228.13, p= 0.018 and HR 5.93, CI 95% 1.13-31.05, p=0.03], yet in MVA neither of these factors retained their predictive value.
The cumulative incidence of acute GVHD at 6 months was similar between groups: 58% in the aza-ven group vs. 62% in the intensive group (p=0.39). Likewise, there was no difference in the cumulative incidence of chronic GVHD at 12 months: 40% vs 42%, respectively (p=0.747)
In conclusion, our data suggests that alloHCT for AML patients achieving first CR with aza-ven appears feasible, with short term post-transplant outcomes comparable to those expected after traditional intensive chemotherapy. Our results were collected in the real world setting, and patients in the aza-ven group were older and had inherently worse leukemia characteristics, including more secondary AML and more adverse cytogenetic features. Future research is warranted to decipher the true spectrum of AML patients who could benefit from remission induction with this less intensive regimen prior to alloHCT.
Ram: Gilead: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria. Wolach: Janssen: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Astellas: Consultancy; Amgen: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy; Neopharm: Consultancy. Yeshurun: Astellas: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy.