Abstract
Background: The combination of venetoclax and rituximab (R) effectively treats patients with CLL. In part due to highly potent apoptosis induction, there is a known risk of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) during the initiation of venetoclax. This risk is mitigated by prophylactic and monitoring measures, including inpatient hospitalization and serial lab monitoring. Debulking the CLL tumor burden prior to initiation of venetoclax may decrease the risk of TLS and improve the feasibility of this regimen, particularly for patients with high tumor burdens.
We designed and initiated this pilot trial to determine the feasibility of treating patients with High-Dose Methylprednisolone (HDMP) and R as a means of debulking prior to initiating venetoclax. HDMP + R is an effective short-term therapy that may have advantages over other potential conventional debulking strategies. It is more effective than single-agent antibodies. It maintains activity in cases with TP53 mutations, unlike standard chemoimmuntherapy regimens like BR. And its 4-day course may avoid the potential toxicities and expense of BTK inhibitor therapy.
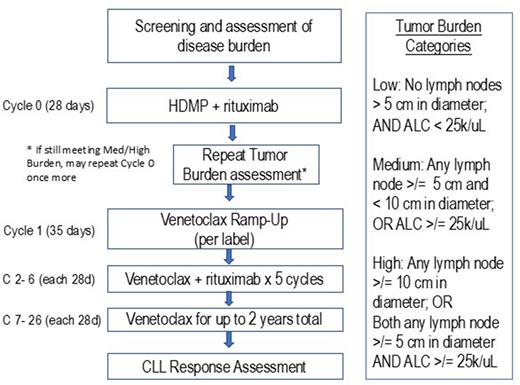
Study Design and Methods: This is a single center, open-label, pilot study to determine the feasibility of HDMP + R as a debulking approach prior to venetoclax. The primary objective is to determine the percentage of patients who have a reduction of lymphadenopathy (from greater than to less than 5 cm in largest diameter) and/or absolute lymphocyte count (from greater than to less than 25k/uL) following 1 or 2 cycles of HDMP + R.
Patients are enrolled with: CLL/SLL; requirement for therapy; and disease burden meeting criteria for medium or high-risk of TLS (based on: lymph nodes >/= 5 cm in diameter and/or absolute lymphocyte count >/= 25k/uL).
Patients receive HDMP + R for 1 cycle, followed by reassessment of Tumor Burden. If Tumor Burden classification is low after HDMP + R, patients will initiate venetoclax dose ramp-up, with standard ramp-up schedule according to venetoclax package insert. Patients who still have a disease burden that meets criteria for medium or high-risk of TLS after 1 cycle of HDMP + R are given the option to repeat a 2nd cycle of HDMP + R. Upon completion of ramp-up (venetoclax to 400 mg), all patients will continue venetoclax 400 mg (or highest tolerated dose) for up to 2 years. Patients will also continue rituximab 500 mg/m2 q 28 days through Cycle 6.
17 patients are planned to be enrolled to evaluate the primary endpoint. A success rate of 60% of patients adequately debulking (defined as having Low Tumor Burden after HDMP + R) will be considered compelling, establishing the feasibility of this approach and supporting further studies. A success rate of 30% would be not compelling for further studies. The null hypothesis that the true debulking rate is 30% will be tested against a one-side alternative, using Simon two-stage design. In the first stage, 10 patients will be accrued. If there are 2 or fewer responses (patients achieving Low Tumor Burden) in these 10 patients, the study will be stopped. Otherwise, 7 additional patients will be accrual for a total of 17. The null hypothesis will be rejected if 9 or more responses are observed in 17 patients. This design yields a type I error rate of 0.04 and power of 80% when the true response rate is 60%.
Conclusion: This clinical trial assesses the potential utility of incorporating HDMP + R with Venetoclax + R, based on a novel and clinically relevant feasibility endpoint of tumor debulking and TLS risk reduction. The study is enrolling. 3 patients have enrolled to date. (NCT04981912)
Disclosures
Choi:Abbvie, TG Therapeutics, Geron, Merck, Oncternal, Pharmacyclics: Research Funding. Heyman:Oncternal Therapeutics, INC: Research Funding; Epizyme, INC: Honoraria; Beigene: Honoraria; Aztrazeneca: Research Funding. Kipps:Genentech-Roch: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics, LLC an AbbVie Company: Consultancy, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy; Oncternal: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.