Abstract
Osteoclasts are hematopoietic cells essential for bone resorption. To study the derivation of these interesting cells, we developed a stepwise culture system where stromal cells promote embryonic stem (ES) cells to differentiate into mature osteoclasts. Three phases to this differentiation process include (1) induction of hematopoiesis, along with the generation of osteoclast precursors, (2) expansion of these precursors, and (3) terminal differentiation into mature osteoclasts in the presence of 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamine D3 . Although the transition of ES cells to the hematopoietic lineage was not blocked by an antibody to c-fms, later phases were dependent on a signaling through this transmembrane receptor as indicated by the finding that anti–c-fms treatment of cells in the second and third phases reduced the number of osteoclasts produced by 75% and more than 99%, respectively. Blockade of signaling through another tyrosine kinase–type receptor, c-kit, did not affect any stages of osteoclastogenesis, although generation of other hemopoietic lineages was reduced to less than 10% of untreated. When small numbers of ES cells were directly cultured under conditions that promote osteoclast differentiation, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase-positive multinucleated cells were observed at the edge but not inside of colonies. This suggests that some types of cell-cell interactions may inhibit development of mature osteoclasts. The culture system developed here provides an important tool for osteoclast biology.
OSTEOCLASTS ARE derived from hematopoietic stem cells and participate in bone development and remodeling.1-4 A deficiency in functional osteoclasts reduces the bone cavity and causes osteopetrosis. Mutations generating the osteopetrotic phenotype have revealed critical molecules for osteoclastogenesis.5-11 Purification and characterization of osteoclast progenitors, including hematopoietic stem cells, have been facilitated by transplantation and coculture assays with bones or stromal cells that support hematopoiesis.12,13 Cell lines that have a potential to differentiate into mature osteoclasts were also reported.14-17 Osteoclasts have been found to share characteristics with cells in the monocyte and macrophage lineages,18-20 but detailed information about the origin of these highly specialized cells is not available. Several studies suggested that osteoclasts might be generated from granulocyte-macrophage colony-forming cells.21,22 However, osteoclast formation was normal in mice whose granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) gene was disrupted.23,24 This could be interpreted to mean that GM-CSF is not critical for osteoclast development, or alternatively that signals normally provided by GM-CSF might be compensated for by other molecules. In contrast, op mice have a mutation in the gene encoding macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), lack functional M-CSF, and develop osteopetrosis caused by the absence of osteoclasts.5,6 Therefore, signaling through c-fms, the receptor for M-CSF, appears to be essential for osteoclastogenesis.4,5 25-29
Questions remain about which events are c-fms dependent and if another receptor tyrosine kinase, c-kit, is also required. We previously reported that cells that form macrophage colonies in response to M-CSF (CFU-M) are enriched in the c-kit+ subpopulation of bone marrow.30 More recently, we found that osteoclast precursors also preferentially expressed c-kit but not c-fms.31 This suggested that osteoclasts might derive from immature c-kit+ hematopoietic cells that pass through a c-fms–dependent stage at some point during their differentiation.
A stromal cell line established from an op mouse, OP9, supports the differentiation of embryonic stem (ES) cells to hematopoietic cells, including lymphocytes, but without embryoid-body formation.32 Definitive- as well as primitive-type erythrocytes develop in this situation.33 We now show that this system can be used to study the entire process of osteoclastogenesis in culture. Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP)–expressing cells are produced as well as fused multinucleated osteoclasts with the potential to resorb bone. A bone marrow–derived stromal cell line, ST2, also permitted the efficient generation of osteoclasts. As might have been predicted from whole animal studies, signaling by way of the c-fms receptor was indispensable for in vitro osteoclastogenesis. In contrast, the c-kit receptor appears not to play a functional role, even in early steps of this process.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Mice.Female 6- to 10-week-old C57BL/6 mice were purchased from Japan SLC Inc (Shizuoka, Japan). Bone marrow cells were freshly prepared from femora and used as one source of hematopoietic progenitors.
Cells.D3 ES cells34 were maintained on mouse embryonic fibroblasts in Dulbecco's modified essential medium (DMEM; Nikken Biomedical Laboratory, Kyoto, Japan) supplemented with 15% fetal calf serum (FCS; Whittaker, MD), 1× nonessential amino acids (GIBCO-BRL, Grand Island, NY), 0.1 mmol/L 2-mercaptoethanol (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd, Osaka, Japan), and a culture supernatant from CHO cells producing leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF; a gift from Genetics Institute Inc, Cambridge, MA). Bone marrow–derived stromal cell, ST2 producing M-CSF,35 and a newborn calvaria–derived stromal cell (OP9)36 were maintained in RPMI 1640 (GIBCO-BRL) containing 5% FCS (GIBCO-BRL) and in alpha-minimum essential medium (α-MEM; GIBCO-BRL) containing 20% FCS (GIBCO-BRL), respectively. All cultures were performed at 37°C with 5% CO2 in a humidified incubator.
Induction of differentiation from ES cells.Undifferentiated D3 cells (104/well) were inoculated into 6-well plates (Nunc, Roskilde, Denmark) previously seeded with OP9 and differentiated in α-MEM supplemented with 20% FCS (Hyclone, Logan, UT) without LIF (the induction culture).32 On day 5, single cell suspensions were prepared from colonies of the induction culture by 0.25% trypsin/0.5 mmol/L EDTA (GIBCO-BRL) and used for further experiments. In some experiments, 1 to 2 × 105 cells from the induction culture were passaged onto OP9 in the same condition for 5 days to expand hematopoietic cells (the expansion culture).32 Hematopoietic cells of the expansion culture were obtained only by pipetting to eliminate nonhematopoietic cells and transferred to the osteoclast culture described later. Cells thus prepared were also transferred to the OP9 monolayer at a density of 105/well in 6-well plate with the same culture medium used to assess the differentiation of hematopoietic cells.32
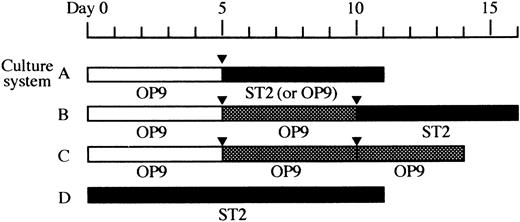
Cells obtained from the induction culture, the expansion culture, and undifferentiated ES cells were seeded in 24-well plates (Falcon Labware, Oxnard, CA) and cultured on confluent stromal cell layers in α-MEM supplemented with 10% (for ST2 monolayer) or 20% (for OP9 monolayer) calf serum (CS; Hyclone, Logan, UT), 10−7 mol/L dexamethasone (Dex; Sigma Chemical Co, St Louis, MO), and 10−8 mol/L 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1α,25-(OH)2D3 ; Biomol Research Laboratories, Inc, Plymouth Meeting, PA). This condition was designated as the osteoclast culture.37 In addition, a serial dose of human recombinant M-CSF (a gift from Dr S. Suzu, Morinaga Milk Industry Co Ltd, Tokyo, Japan) was supplied when OP9 was used. The culture medium was changed every other day. Usually 6 days later, formation of osteoclasts was evaluated by TRAP staining.38 TRAP+ cells with more than two nuclei were scored as multinucleated cells (MNCs). Combinations of these culture conditions applied for each experiment are summarized in Fig 1 as culture A, B, C, and D.
Overview of the culture systems used in this study. Time schedules of four types of cultures, culture systems A, B, C, and D, are shown schematically. The stromal cell lines used are indicated under the each column. (□), induction culture; (), expansion culture; (▪), osteoclast culture; (▾), passage.
Overview of the culture systems used in this study. Time schedules of four types of cultures, culture systems A, B, C, and D, are shown schematically. The stromal cell lines used are indicated under the each column. (□), induction culture; (), expansion culture; (▪), osteoclast culture; (▾), passage.
Assessment for hematopoiesis.The effect of blocking antibody on hematopoiesis was assessed by the culture of ES cells according to the culture system C of Fig 1. Numbers of hematopoietic clusters that contained more than eight cells were counted on day 13 of the culture. These cells were obtained the next day by pipetting, cytospun, and stained with May-Grunwald-Giemsa solution, and numbers of mature neutrophils were counted.
Pit formation assay.To analyze the potential of bone resorption, 1.5 × 103 of cells cultured in various conditions and ST2 stromal cells were simultaneously seeded onto a dentine slice (6 mm; a kind gift from Dr S. Sato, Kyowa Hakko Kogyo Co Ltd, Shizuoka, Japan) set in a 96-well plate (Falcon) and cultured in the presence of 10−7 mol/L Dex and 10−8 mol/L 1α,25-(OH)2D3 for 6 to 10 days. Cells on the dentine slice were brushed off and the slices were stained with 2% coomassie brilliant blue R250 (Fluka Chemie AG, Switzerland) in methanol (wt/vol). The number of pits were then counted with a light microscope.
Antibodies.Rat anti-mouse monoclonal antibodies against c-kit (ACK2)39 and/or c-fms (AFS98)30 were added to cultures at 10 μg/mL unless otherwise indicated.
Statistical analysis.Data were presented as means ± SD. Statistical significance was assessed by Student's t-test.
RESULTS
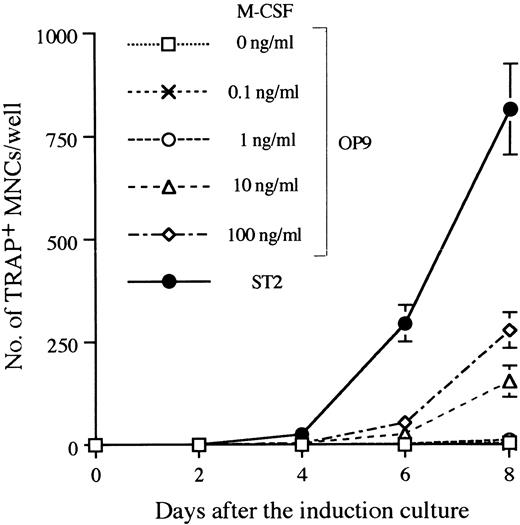
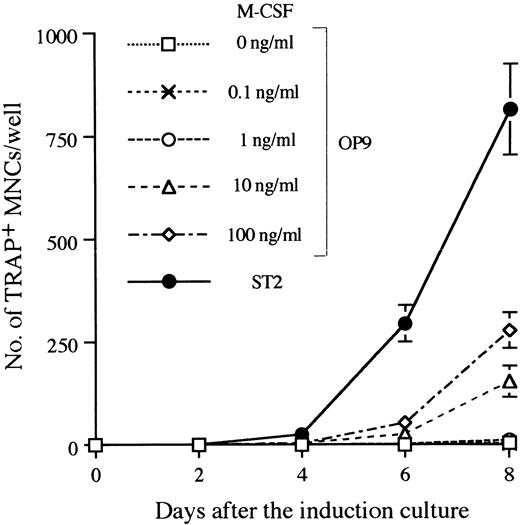
Establishment of the in vitro system that supports differentiation from ES cells to osteoclasts.There are several systems that allow ES cells to differentiate into hematopoietic cells in vitro.34,40 We used the M-CSF–deficient stromal cell line OP9, which supports hematogenesis from ES cells,32 and adapted it the study of osteoclastogenesis. D3 ES cells were first induced in a 5-day culture on OP9 to form hematopoietic lineage cells.32 We refer to this as the induction culture step. Single cell suspensions were then prepared from the induction culture by trypsinization and seeded onto freshly prepared OP9 or ST2 monolayers in the presence of Dex and 1α,25-(OH)2D3 . In addition, a serial dose of M-CSF was added to cultures with OP9. These conditions for osteoclastogenesis are designated as the osteoclast culture. Generation of osteoclasts in these cultures was revealed by TRAP staining. TRAP+ MNCs on OP9 were first detected 4 days later, and continuous generation of TRAP+ MNCs was observed up to 8 days. ST2 supported osteoclastogenesis more efficiently than OP9, even when 100 ng/mL of M-CSF was added in cultures (Fig 2). As the level of M-CSF produced by ST2 in cultures was less than 10 ng/mL (data not shown), molecule(s) other than M-CSF should account for the difference in supporting ability between OP9 and ST2. An alternative explanation is that membrane bound–type M-CSF on ST2 more effectively supports osteoclastogenesis than OP9 even in the presence of more than 10-fold more soluble-type M-CSF.
Time course of TRAP+ MNC formation in the osteoclast cultures after 5 days of induction culture. The culture system A of Fig 1 was applied with a modification during the osteoclast culture phase. Ten thousand D3 ES cells cultured on OP9 for 5 days were seeded on ST2 or OP9 and changed to the osteoclast culture condition for the indicated period, and TRAP+ MNCs were counted. A serial dose of M-CSF was added into OP9 cultures in the osteoclast culture phase. Numbers of TRAP+ MNCs are given as means ± SD of the triplicate cultures.
Time course of TRAP+ MNC formation in the osteoclast cultures after 5 days of induction culture. The culture system A of Fig 1 was applied with a modification during the osteoclast culture phase. Ten thousand D3 ES cells cultured on OP9 for 5 days were seeded on ST2 or OP9 and changed to the osteoclast culture condition for the indicated period, and TRAP+ MNCs were counted. A serial dose of M-CSF was added into OP9 cultures in the osteoclast culture phase. Numbers of TRAP+ MNCs are given as means ± SD of the triplicate cultures.
The kinetics of differentiation were similar to those observed with fresh bone marrow cells on ST2, ie, 0.3 ± 0.6 (day 2), 47.7 ± 7.1 (day 4), 616.0 ± 12.1 (day 6), and 1331.0 ± 157.4 (day 8) TRAP+ MNCs were detected when cultures were initiated by 104 marrow cells.
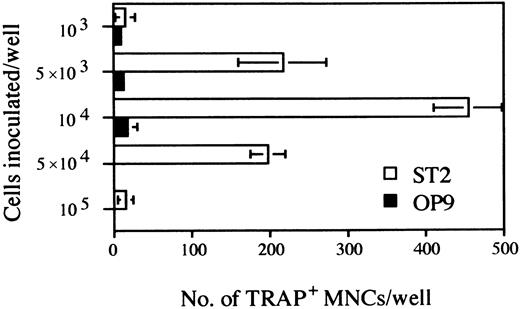
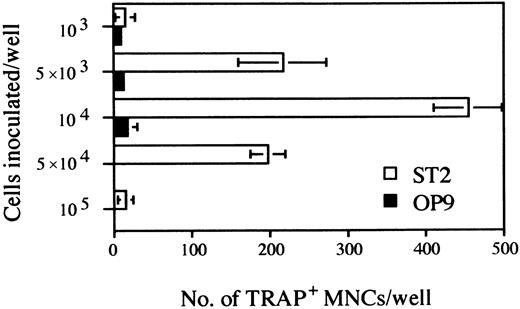
Further experimentation revealed that maximum numbers of TRAP+ cells were obtained with an initial culture period of 5 days, followed by harvesting and reseeding of 104 cells for an additional 6 days of culture under osteoclast conditions (Fig 3). Seeding higher numbers of cells in the secondary cultures resulted in a severe decline in the recovery of TRAP+ cells, suggesting that cell density and/or numbers of nonhematopoietic cells might be critical.
Determination of the optimal cell density of the inoculated D3 ES cells for osteoclastogenesis on ST2 and OP9 stromal cell lines. The duration of cultures was as outlined in culture system A of Fig 1. The indicated numbers of cells obtained at day 5 were seeded on ST2 or OP9 monolayers grown on 24-well plates. After 6 days TRAP+ MNCs were counted. Each column represents means ± SD of triplicate cultures.
Determination of the optimal cell density of the inoculated D3 ES cells for osteoclastogenesis on ST2 and OP9 stromal cell lines. The duration of cultures was as outlined in culture system A of Fig 1. The indicated numbers of cells obtained at day 5 were seeded on ST2 or OP9 monolayers grown on 24-well plates. After 6 days TRAP+ MNCs were counted. Each column represents means ± SD of triplicate cultures.
Both OP9 and ST2 stromal cells supported osteoclastogenesis when used for the osteoclast culture phase in the presence of Dex or 1α,25-(OH)2D3 , or both. In addition, 10 ng/mL of M-CSF was added to cultures with OP9. However, the glucocorticoid was only required when the OP9 stromal cells were used (Table 1). Although constitutive production of M-CSF by the ST2 stromal cell clone was apparently optimal and essential (see below), this cytokine could not be produced by stromal cells derived by mutant op mice and was an absolute requirement. Trace amounts of M-CSF might have been made by the D3 ES–derived cells because the very small number of TRAP+ mononuclear cells observed without addition of recombinant M-CSF disappeared after blocking of its receptor (data not shown). The requirements for expansion of D3 ES cells on the ST2 cells were similar to those required for the support of osteoclast precursors from bone marrow37 (T. Yamane, unpublished observations, 1996).
A further refinement of this system involved passage of cells after the initial 5-day induction culture for an additional 5 days of “expansion” culture. Cells were then obtained and transferred to osteoclast culture conditions as before. This innovation resulted in a 15- to 20-fold expansion of osteoclast precursors. Cells from this expansion step generated 1374.7 ± 313.8 TRAP+ MNCs initiated by 2 × 103 cells, although only 369.0 ± 60.0 TRAP+ MNCs were obtained from induction cultures started with 104 cells (Fig 4). Limiting dilution analysis was conducted as described previously,31 41 and this revealed that approximately one out of every six cells present at that stage had the potential to generate TRAP+ cells. Moreover, they were considerably enriched relative to the incidence of osteoclast precursors in freshly isolated bone marrow (approximately 1 out of 154).
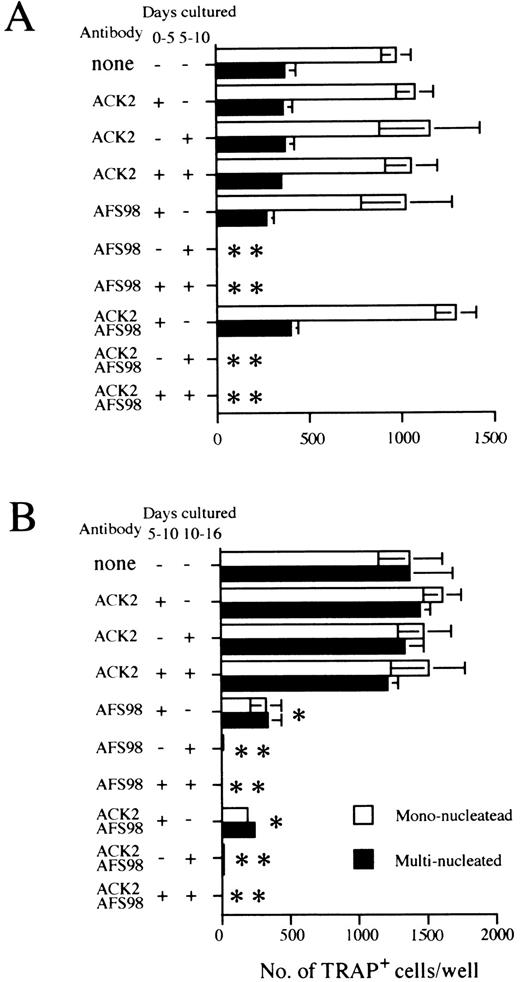
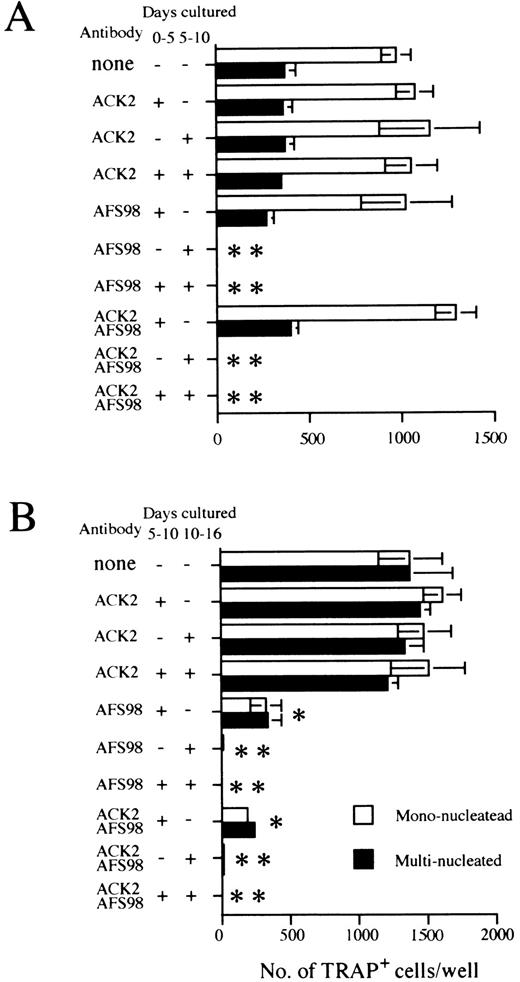
Effect of antibodies to c-kit (ACK2) or to c-fms (AFS98) on osteoclast differentiation. Experiments done according to the A schedule or B schedule of Fig 1 are summarized in (A) and (B), respectively. The period when blocking antibodies were present is indicated as + (added) or − (not added) next to the antibody used. Cultures were started by inoculating 104 cells (A) and 2 × 103 cells (B), and TRAP+ mononucleated (□) and multinucleated cells (▪) were counted on day 11 (A) or day 16 (B), respectively. Bars indicate means ± SD of triplicate cultures. * and ** show statistically assessed as P < .005 and P < .0005, respectively for both multinucleated and mononucleated cells.
Effect of antibodies to c-kit (ACK2) or to c-fms (AFS98) on osteoclast differentiation. Experiments done according to the A schedule or B schedule of Fig 1 are summarized in (A) and (B), respectively. The period when blocking antibodies were present is indicated as + (added) or − (not added) next to the antibody used. Cultures were started by inoculating 104 cells (A) and 2 × 103 cells (B), and TRAP+ mononucleated (□) and multinucleated cells (▪) were counted on day 11 (A) or day 16 (B), respectively. Bars indicate means ± SD of triplicate cultures. * and ** show statistically assessed as P < .005 and P < .0005, respectively for both multinucleated and mononucleated cells.
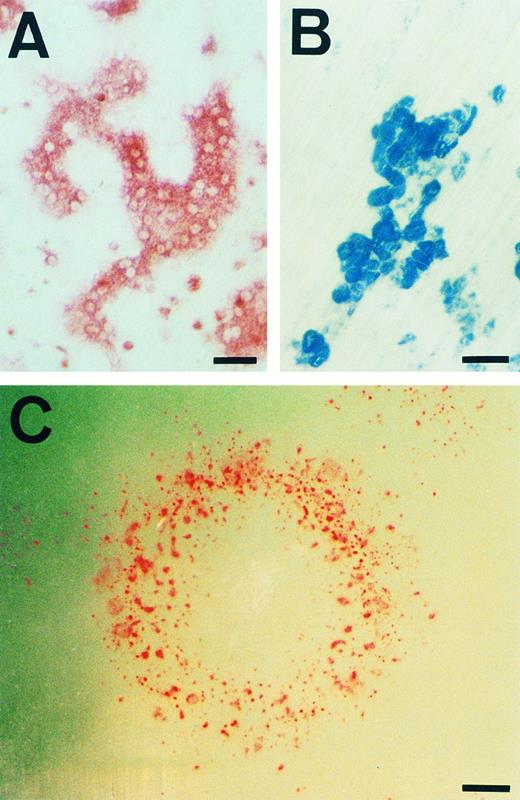
We also assessed whether the initial 5-day induction culture step was essential for osteoclastogenesis. Undifferentiated D3 cells were directly cultured on ST2 monolayers for 11 days without passage in the presence of Dex and 1α,25-(OH)2D3 (Fig 5). Osteoclasts were observed only at the periphery of growing colonies (Fig 5A and C). When cultures were initiated with higher cell densities, the resulting colonies contained few TRAP-positive cells (data not shown). Most of these colonies were fused or in close contact with each other, producing conditions that were not favorable for osteoclastogenesis. It should be noted that, other than osteoclasts, the only other hematopoietic cells to be generated on ST2 were macrophages.
Morphology and bone resorbing activity of osteoclasts. (A) TRAP staining of osteoclasts differentiated according to the culture D schedule are shown. (B) The pits formed in the dentine slice used in the experiment for first column of Table 2, indicating bone resorbing activity of osteoclasts, are shown. (C) A colony from a single ES cell generated by the culture D schedule was stained for TRAP+ cells and photographed. Note that TRAP+ cells appear in the circular edge, not inside of the colony. Scale bars: 50 μm in (A) and (B), 400 μm in (C).
Morphology and bone resorbing activity of osteoclasts. (A) TRAP staining of osteoclasts differentiated according to the culture D schedule are shown. (B) The pits formed in the dentine slice used in the experiment for first column of Table 2, indicating bone resorbing activity of osteoclasts, are shown. (C) A colony from a single ES cell generated by the culture D schedule was stained for TRAP+ cells and photographed. Note that TRAP+ cells appear in the circular edge, not inside of the colony. Scale bars: 50 μm in (A) and (B), 400 μm in (C).
Finally, the functional capability of osteoclasts generated in culture from D3 ES cells was assessed. The cells were capable of forming pits on dentine slices when transferred to osteoclast culture conditions, regardless of whether they were produced by induction culture only or by the induction step followed by expansion culture (Fig 5B and Table 2). Therefore, fully mature osteoclasts were generated from ES cells in our culture system.
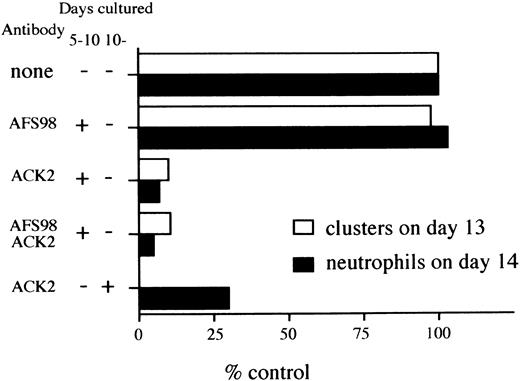
Inhibitory effect of anti–c-kit antibody (ACK2) on hematopoiesis. D3 ES cells were inoculated onto OP9 monolayers in the presence or absence of the antibody, according to culture schedule C of Fig 1. At day 10 of the culture, 105 cells were passaged and then clusters of cells composed of more than 8 cells were counted at day 13 with a light microscope. Cells were obtained from the same culture at day 14, and number of neutrophils were counted as described in Materials and Methods. The data are presented as percentages of numbers of clusters or cells from the control experiments. Numbers representing 100% are 365 (clusters counted on day 13) and 107 (neutrophils on day 14). The data presented are representative of two separate experiments.
Inhibitory effect of anti–c-kit antibody (ACK2) on hematopoiesis. D3 ES cells were inoculated onto OP9 monolayers in the presence or absence of the antibody, according to culture schedule C of Fig 1. At day 10 of the culture, 105 cells were passaged and then clusters of cells composed of more than 8 cells were counted at day 13 with a light microscope. Cells were obtained from the same culture at day 14, and number of neutrophils were counted as described in Materials and Methods. The data are presented as percentages of numbers of clusters or cells from the control experiments. Numbers representing 100% are 365 (clusters counted on day 13) and 107 (neutrophils on day 14). The data presented are representative of two separate experiments.
Signaling through c-fms but not c-kit is necessary for osteoclast development.The c-kit and c-fms receptor tyrosine kinases are both critical for normal hematopoiesis.42-47 Therefore, we exploited antagonistic antibodies directed to c-kit (ACK2) or c-fms (AFS98) to evaluate the importance of these receptors in osteoclastogenesis. Addition of either antibody during the induction culture phase had no effect on osteoclast formation (Fig 4A). However, osteoclastogenesis was completely inhibited when anti–c-fms was present during the ST2 osteoclast culture phase. In contrast, the same process was refractory to the addition of anti–c-kit (Fig 4A). Identical results were obtained when the osteoclast culture phase was initiated with monolayers of the OP9 stromal cell clone (data not shown).
As shown above, there was a substantial increase in osteoclast precursor numbers when we used an expansion culture step with OP9 stromal cells. As immature hematopoietic progenitors also expand under these culture conditions in a c-kit–dependent manner,32 33 we speculated that the antibody to this receptor might block the proliferation of osteoclast precursors. This was tested by adding either anti–c-kit or anti–c-fms antibodies to different stages of multistep cultures. Addition of anti–c-kit to the expansion phase of the culture (schedule B of Fig 1) had no influence on osteoclast precursors (Fig 4B). The addition of anti–c-fms to the osteoclast culture phase completely blocked the generation of TRAP+ MNCs, and the same antibody reduced the generation of TRAP+ MNCs to 25% of control numbers when present in the expansion phase (Fig 4B). When both antibodies were combined, a significantly greater effect was not observed compared with that obtained by the addition of anti–c-fms only (Fig 4B). These results indicate that c-fms participates in the maintenance and/or proliferation of osteoclast precursors during both the expansion and osteoclast culture phases. In contrast, osteoclastogenesis from ES cells progressed normally in the absence of signals to c-kit. This conclusion was confirmed in another situation (culture system D of Fig 1) in which the entire osteoclast differentiation process was performed in a single step on ST2 cells. In these experiments undifferentiated ES cells were plated on an ST2 monolayer at a concentration of 500 cells/well. On the 11th day in these cultures, the numbers of TRAP+ cells were counted. The continuous presence of anti–c-kit had no effect on the efficiency of osteoclastogenesis in this system, ie, 329.7 ± 174.1 cells produced without any antibody, 421.3 ± 270.4 with 10 μg/mL ACK2, 389.7 ± 125.7 with 30 μg/mL ACK2, and 1.7 ± 2.9 with 10 μg/mL AFS98.
Blockade of c-kit signaling impairs hematopoiesis in culture.It was previously reported that anti–c-kit eliminated hematopoietic progenitors from cultures of ES cells on OP9 monolayers.33 This contrasts with our finding that osteoclast precursor generation was c-kit independent. This point was further evaluated with another culture system (culture system C of Fig 1) in which cells were first held under induction and expansion culture conditions on OP9 monolayers before passage again onto fresh OP9 stromal cells. Three days later cell clusters that contained various lineages of hematopoietic cells were enumerated. The next day these cells were obtained and mature neutrophils were also scored as representative hematopoietic cells. When an antibody to c-kit was present in the expansion culture phase (from day 5 to day 10 of schedule C), the numbers of clusters and neutrophils were reduced to 10% and 7% of control values, respectively (Fig 6). In contrast, an antibody to c-fms had no effect on these parameters. Therefore, c-kit is indispensable for the development of hematopoietic lineages other than osteoclasts in culture.
DISCUSSION
We have devised and optimized a multistep culture system that supports the generation of mature osteoclasts from pluripotent embryonic stem cells. This approach was initially used so that the expansion and subsequent differentiation of osteoclast precursors could be independently manipulated. This revealed that precursors were considerably enriched even when 1α,25-(OH)2D3 was omitted from the initial phase. However, we also found that it was possible to observe osteoclastogenesis in a single step culture system when ST2 stromal cells were used. Conditions favorable for the formation of osteoclasts in culture were distinctly different from those needed to produce other hematopoietic cells, and osteoclastogenesis was unique in its lack of dependence on signaling through the c-kit receptor.
The formation of osteoclasts from ES cells could be experimentally divided into three phases: (1) induction of hematopoietic precursors including osteoclast precursors, (2) expansion of these precursors, and (3) terminal differentiation to mature osteoclasts in the presence of 1α,25-(OH)2D3 . In the first phase, osteoclastogenesis was not blocked by an antibody to c-fms. However, most of the osteoclast precursors became sensitive to anti–c-fms in the second phase and were completely abolished by antibody treatment in the third phase. Therefore, generation of early osteoclast precursors from ES cells is not markedly dependent on c-fms signaling. There is significant dependence on this receptor during the next stage, in which growth and maintenance of osteoclast precursors does not yet require 1α,25-(OH)2D3 (Fig 4B). It is possible that the induction of ES cells to the hematopoietic lineage is not completely synchronized and c-fms–independent processes initiated in the first stage may continue in the next stage. However, in our recent study bone marrow cells from the mice that had been given intravenous injections of anti–c-fms antibody contained osteoclast precursors comparable to those from untreated mice. Thus, there was no obvious influence of the in vivo administration of anti–c-fms antibody on the maintenance of osteoclast precursors in bone marrow. In other words, the second stage described here is hard to detect in vivo.31 We think that osteoclast precursors in the bone marrow must be maintained at a c-fms–independent stage so that administration of blocking c-fms antibody does not result in a decrease of the number of osteoclast progenitors. The precursors would become c-fms dependent only if they expanded efficiently as reported here. In the third phase, terminal differentiation of the osteoclast precursors into fully functional mature osteoclasts occurs, and this latter process is absolutely dependent on c-fms signaling.
Studies done with embryoid-body formation suggested that expression of the c-fms gene is first detected on day 8 to 10. These kinetics appear slow compared with our system.48-50 Presumably the microenvironmental conditions provided by stromal cells must be responsible for this difference.
Our findings show that the c-kit tyrosine kinase receptor is not required at any time during development of osteoclasts from totipotent stem cells although the c-kit gene is already expressed on undifferentiated ES cells48,49,51 or strongly induced along with hematopoiesis.50,52 This is consistent with our previous observation that in vivo administration of anti–c-kit antibody did not affect the numbers of osteoclast precursors in the bone marrow of adult mice, whereas the number of hematopoietic precursors such as CFU-GM and CFU-M were reduced.31 Although we and Hayase et al have observed that the major population of osteoclasts in bone marrow derives from c-kit–positive cells, it is clear from these culture studies that this receptor need not be ligated.31,53 It has been extensively studied and concluded that definitive hematopoiesis depends on signals delivered through the c-kit expressed on early hematopoietic precursors or hematopoietic stem cells.39 In contrast, primitive-type hematopoiesis in yolk sac and early fetal liver do not depend on c-kit.54 Taking this into the consideration, it is possible that we observed a primitive/fetal type of osteoclastogenesis, but this contrasts with the demonstration by Nakano et al that both primitive and definitive types of erythropoiesis can occur in this ES cell culture system.33 In addition, our demonstration that precursors of hematopoietic lineages other than osteoclasts were extensively depleted by a blocking antibody to c-kit (Fig 6) suggests that we observed definitive type hematopoiesis in at least in the late stage of our system.
There is no doubt that osteoclasts are descended from hematopoietic stem cells, as shown by the earlier studies performed with highly purified hematopoietic stem cells or stem cell lines.12,14,15 However, the point at which osteoclasts branch off from other lineages is ambiguous. Several studies suggested osteoclasts could be induced even from mature monocytes or macrophages.19 20 Our results described here support the alternative idea that the osteoclast lineage may diverge from other pathways at a relatively early stage of hematopoiesis.
It is noteworthy that osteoclasts were observed only at the edges of colonies that we generated with a single-step culture system (Fig 5C). Furthermore, cell density was found to be a critical variable for osteoclast formation in multistep cultures (Fig 2). We presume that close interactions between cells can deliver negative, as well as positive, signals for osteoclastogenesis. Our culture system is highly dependent on stromal cell–derived signals. Stromal cell lines established from the lungs of op/op mice did not support osteoclastogenesis, although they efficiently supported hematopoiesis (data not shown). Therefore, it will be important to identify critical molecules that are uniquely provided by stromal cells such as OP9 and ST2.
In conclusion, we have described a culture system that supports the generation of mature osteoclasts from pluripotent embryonic stem cells and have used this system to show that the production of osteoclasts does not require a signal from the c-kit receptor at any point in their differentiation. This characteristic is unique to osteoclasts among all hematopoietic cell lineages. When ES cells were directly cultured under conditions that promote osteoclast differentiation, TRAP+ MNCs were observed at the edges of the colonies obtained showing that the entire process of osteoclastogenesis could be reproduced in this culture system. Therefore, this system should provide an important tool for future studies of osteoclast biology.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We are grateful to Dr Paul W. Kincade (Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation) for critically reviewing this manuscript. Drs Shin-Ichi Nishikawa and Satomi Nishikawa (Kyoto University) are acknowledged for their encouragement and antibodies. We thank Drs Shinya Suzu (Morinaga Milk Industry Co, Ltd), Adam Weintraub (Genetics Institute, Inc), Soichiro Sato (Kyowa Hakko Kogyo Co, Ltd), and Akira Kudo (Tokyo Institute of Technology) for human recombinant M-CSF, CHO-LIF cell line, dentine slices, and valuable suggestion, respectively. We also thank Toshie Shinohara for her secretarial assistance.
Supported by grants from the Ministry of Education, Science, and Culture in Japan; from the Ministry of Science and Technology of Japan; and from the Cellular Technology Institute, Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd, Tokushima, Japan.
Address reprint requests to Shin-Ichi Hayashi, MD, PhD, Department of Immunology, School of Life Science, Faculty of Medicine, Tottori University, 86 Nishi-Machi, Yonago 683, Japan.