Abstract
Progressively transformed germinal centers (PTGCs) are histologic structures mainly composed of small resting B cells and intermingled proliferating centroblast-like cells. The B-cell differentiation processes within PTGCs and their relation to classical germinal centers (GC) and to lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin disease (LPHD), with which PTGCs are often associated, are largely unknown. To address these issues, single small resting (Ki67−) and proliferating (Ki67+) centroblast-like cells were isolated from 7 PTGCs of 5 lymph nodes, and rearranged immunoglobulin genes were amplified and sequenced. Most small resting B cells were clonally unrelated, and most carried unmutated immunoglobulin gene rearrangements resembling mantle zone B cells. Small resting B cells with mutated immunoglobulin gene rearrangements may represent centrocytes, memory B cells, or both. Among the centroblast-like Ki67+ cells, expanded B-cell clones were observed in 6 of 7 PTGCs analyzed. Clonally related V region genes showed extensive intraclonal diversity, and the mutation pattern indicated stringent selection of the cells for the expression of functional antigen receptors. Thus, somatic hypermutation, clonal expansion, and selection occur also in the disorganized PTGC microenvironment, as in classical GCs. In lymph nodes affected by PTGCs, no clonal expansion across the borders of individual PTGCs was observed, distinguishing PTGCs from LPHD.
Introduction
Progressively transformed germinal centers (PTGCs) are follicular structures observed in approximately 4% of patients with unspecific lymphadenitis.1 In affected lymph nodes, usually several PTGCs are found between the smaller regular follicles. Although relapses are frequent (in approximately 20% of patients), PTGCs are considered nonmalignant lesions.2-4
PTGCs are primarily composed of small, tightly packed CD20+B cells positive for immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgD, resembling the mantle zone B cells of secondary follicles. Intermingled are large single or clustered cells that resemble centroblasts. However, the clear compartmentalization of secondary follicles into mantle zone and germinal center (GC) is missing. T cells are scattered throughout the PTGCs as single cells or occasionally as small groups of cells, and regular or broken-up meshworks of follicular dendritic cells are also observed.1,5,6 Because of their cellular composition and organization, a derivation of PTGCs from regular GCs has been hypothesized.3 4
A relation between PTGCs and lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin disease (LPHD) is suggested by their similar morphologic and immunohistochemical appearance. The most important difference between PTGCs and LPHD is the presence of lymphocytic and histiocytic cells—representing the tumor B-cell population—only in LPHD.3,4,7 Moreover, LPHD usually differs from PTGCs by less well-circumscribed nodules and a broken-up pattern and greater numbers of T cells, which may form aggregates and rings around the lymphocytic and histiocytic cells.6 Further indication for a relation between PTGCs and LPHD is the occurrence of PTGCs in approximately 15% of patients with LPHD before, during, or after LPHD.1 PTGCs were observed only in 2% of patients with nodular sclerosis or mixed cellularity HD.1
To study the relation between PTGCs and normal GCs on the one hand and LPHD on the other, we micromanipulated Ki67+ and Ki67− cells from single PTGCs of 3 patients and Ki67+ cells from 2 PTGCs of each of 2 more patients. Ki67 was used to identify proliferating cells; resting cells are Ki67−. Rearranged immunoglobulin genes from the single cells were amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and sequenced. These sequences were analyzed for clonal relatedness and for presence and pattern of somatic mutation.
Patients, materials, and methods
Tissues and clinical data
All lymph node biopsies were taken for diagnostic purposes. Clinical data of the 5 patients are summarized in Table1.
Immunohistochemistry and micromanipulation
Immunostaining with Ki67- and CD3-specific antibodies (both from DAKO, Hamburg, Germany) was carried out with the avidin-biotin complex technique using Fast Red (DAKO) as chromogen. For Ki67/CD38 double-stainings, antirabbit (for Ki67) and antimouse (for CD38) secondary antibodies directly conjugated to horseradish peroxidase and alkaline phosphatase (DAKO), respectively, were used with DAB and Fast Red as chromogens. Micromanipulation and transfer of single cells or groups of cells from 5 μm frozen tissue sections stained for Ki67 and CD3 were performed with a hydraulic micromanipulator, as previously described.8
Single-cell polymerase chain reaction and sequence analysis
After proteinase K digestion (Boehringer, Mannheim, Germany), seminested PCR for IgH, Igκ, and Igλ gene rearrangements was performed for each single cell or group of cells, as previously described.9-11 PCR products were gel-purified and directly sequenced. Sequences were analyzed with the EMBL IMGT database (http://www.uni-koeln.de/dnaplot/). Unmutated Vκrearrangements were regarded as uninformative for mutation analysis.12 13
Results
Histology and immunohistology
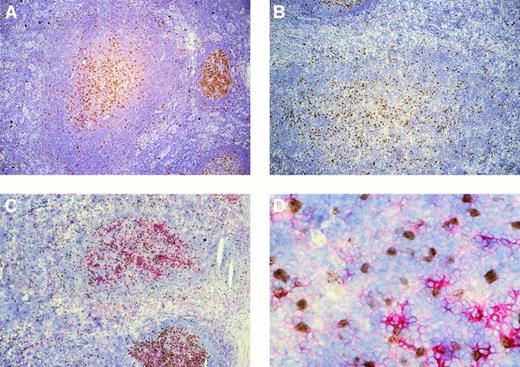
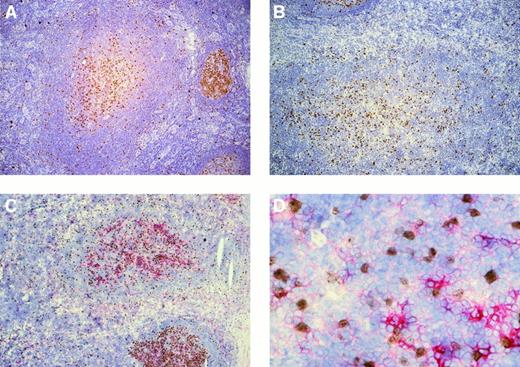
In all 5 patients whose lymph nodes showed follicular hyperplasia, several PTGCs were observed among normal follicles. Single Ki67+ cells were scattered throughout the PTGCs, whereas more or less connected clusters of Ki67+ cells were concentrated in the centers of the PTGCs (Figure1). The Ki67+ cells were a minor fraction of all PTGC cells (approximately 10%). Double staining of 3 patients with Ki67 and the GC B-cell marker CD38 revealed that varying numbers of the Ki67+ cells (approximately 50% to 80%) were also positive for CD38 (Figure 1). Most Ki67−cells were also CD38− and only a small fraction were CD38+; the staining intensities were comparable to those observed for CD38+/Ki67+ cells. In addition, varying numbers of Ki67− cells within the PTGCs were strongly positive for CD38, likely representing plasma cells.
Immunostaining of progressively transformed germinal centers for Ki67 and Ki67/CD38.
(A,B) PTGCs of patients 3 and 5 stained for Ki67 using peroxidase to detect binding. (C) Ki67 and CD38 double staining of a PTGC of patient 5. Ki67 was visualized using peroxidase and DAB as substrate (brown) and CD38 with alkaline phosphatase and Fast Red. (D) High-power magnification of panel C (40 ×).
Immunostaining of progressively transformed germinal centers for Ki67 and Ki67/CD38.
(A,B) PTGCs of patients 3 and 5 stained for Ki67 using peroxidase to detect binding. (C) Ki67 and CD38 double staining of a PTGC of patient 5. Ki67 was visualized using peroxidase and DAB as substrate (brown) and CD38 with alkaline phosphatase and Fast Red. (D) High-power magnification of panel C (40 ×).
Micromanipulation and single-cell analysis
To compare the B-cell populations of PTGCs to those of classical GCs, Ki67+ cells—resembling the Ki67+centroblasts of classical GCs—and small resting Ki67−cells—resembling centrocytes and mantle zone cells of classical GCs—were micromanipulated from 3 PTGCs.
In normal GCs, expanding clones are restricted to the individual GCs,14,15 whereas in LPHD the clonal lymphocytic and histiocytic cells were found in all nodules of the patients analyzed.10,16 17 Consequently, to study the relation between LPHD and PTGCs, we analyzed, from each of 2 lymph nodes, Ki67+ cells from 2 individual PTGCs for clonal expansion across the borders of individual PTGCs.
Ki67+ cells were always micromanipulated as single cells, whereas the small Ki67− cells were micromanipulated and transferred to PCR tubes as groups of 2 to 4 cells to reduce PCR work. PCR efficiencies for small cells are usually low, and a fraction of the small cells may be T cells. As negative controls, aliquots of the buffer covering the Ki67-stained sections and CD3+ T cells micromanipulated from adjacent sections were used (Table2). After proteinase K digestion, seminested PCR for IgH, Igκ, and Igλ gene rearrangements were performed, and the PCR products were sequenced.
Analysis of small resting cells
Groups of 2 to 4 small Ki67− cells distributed throughout the PTGCs were analyzed from patients 1 to 3 (Table 2). In all 3 patients, unmutated rearrangements were amplified from most (57%-81%) cell groups. For mutated VH rearrangements, the average mutation frequency was 1.7% (n = 6; range, 0.3%-5.7%).
No clonally related rearrangements from patient 1 were identified among 43 rearrangements amplified from 21 PCR-positive samples. In patients 2 and 3, 56 and 50 rearrangements were amplified from 23 and 24 PCR-positive samples, respectively. From each patient, identical rearrangements were amplified from 2 groups of cells. Clonally related rearrangements were unmutated in each (Table3). In addition, in patient 2 the same unmutated Vλ rearrangement obtained from a Ki67− sample was amplified from a Ki67+ cell.
Analysis of Ki67+ cells
Single Ki67+ cells were analyzed from 7 PTGCs in patients 1 to 3 from one PTGC per patient and in patients 4 and 5 from 2 PTGCs per lymph node. The fraction of cells with mutated rearrangements was approximately 50% (range, 32%-69%) in 6 PTGCs (Table 2). In the seventh PTGC, 93% of the cells carried mutated rearrangements. The average mutation frequency for mutated VH rearrangements was 5.1% (range, 0.3%-11.9%; n = 66). Because of the pronounced intraclonal diversity, the mutation frequencies of clonally related rearrangements were counted separately (see below).
With the exception of patient 1, clonally related cells were identified in all PTGCs (Table 2). Among the unmutated Ki67+ cells in each of 2 PTGCs, only a single clone consisting of 2 cells was identified. Among the mutated Ki67+ cells, the numbers of clones and the degrees of clonal expansion were variable. In 3 PTGCs, single clones encompassing 50% to 70% of the mutated Ki67+ cells were identified. In 2 PTGCs, 2 clones per PTGC encompassing 15% to 63% of the mutated Ki67+ cells per clone were identified. In one PTGC, 3 clones encompassing 15% to 54% of the mutated Ki67+ cells were identified. In all 6 PTGCs with identified clones, at least half the mutated Ki67+cells were assigned to expanded B-cell clones.
Among 9 of the 10 clones with mutated rearrangements, intraclonal diversity was observed (Table 3). Usually all mutated, clonally related rearrangements of a given clone were diverse, indicating extensive ongoing, somatic hypermutation. The ratio of replacement to silent mutations in the framework regions of potentially functional, clonally related rearrangements of 1.1 (125 replacement versus 110 silent mutations; shared mutations in clonally related rearrangements were counted only once) indicates selection of the respective cells for expression of a functional antigen receptor.13 18
Analysis of Ki67+ cells from 2 PTGCs of one patient
From patients 4 and 5, Ki67+ cells were micromanipulated from 2 different PTGCs each, separated by several regular GCs in patient 4 and lying adjacent to each other in patient 5. No clonally related sequences were obtained from the 2 different PTGCs of one patient, though each PTGC was populated by clonally related cells. In PTGC1 of patient 5, a single clonal expansion encompassed 70% of the Ki67+ cells (Tables 2, 3).
Discussion
B-cell differentiation in PTGCs
PTGCs are largely composed of small resting B cells. In our analysis, most of the small Ki67− cells carried unmutated immunoglobulin gene rearrangements (57%, 74%, and 81% for patients 1-3). In addition, most small resting cells were negative for the GC marker CD38. Thus, most of the B cells constituting a PTGC are naive B cells, which are largely clonally unrelated. A single clone consisting of 2 cells was identified in each of only 2 PTGCs among these cells.
A considerable fraction of the resting B cells carried mutated immunoglobulin gene rearrangements. Some of these may represent centrocytes, which are CD38+/Ki67−. However, because most of the Ki67− cells were also CD38−, they are likely memory B cells, which are clonally unrelated in the 3 PTGCs analyzed.
Proliferating (ie, Ki67+) cells constitute approximately 10% of the cells in a PTGC. In the 7 PTGCs analyzed, usually approximately half of the proliferating cells carried unmutated rearrangements (range, 31%-68%; the exception was PTGC1 of patient 5, with only 7% unmutated cells). Except for 2 small clones, no clonal expansions were observed among these unmutated cells. Because approximately 20% to 50% of the Ki67+ cells lack expression of the GC B-cell marker CD38, we assume that a fraction of the Ki67+ cells with unmutated V-region genes represents proliferating pre-GC (ie, naive B) cells. Thus, the large pool of IgM+ IgD+ resting naive B cells in the PTGC may not only be formed by the immigration of naive B cells but partly also by the proliferation of these cells within the structure. However, because most of the Ki67+ cells are also CD38+, a considerable fraction of the isolated Ki67+ cells with unmutated V-region genes is likely CD38+. These cells resemble GC founder cells, which already have a GC B-cell phenotype (Ki67+/CD38+) but have not yet acquired somatic mutations.19
Among the proliferating cells with mutated immunoglobulin gene rearrangements, except for those in patient 1, in all PTGCs expanded B-cell clones (1-3 per PTGC) were identified, which usually accounted for half of these cells. Within clones, considerable intraclonal diversity was observed, indicating extensive ongoing somatic mutation in the course of clonal expansion. All these features are typical for centroblasts of classical GCs,20,21 in line with the CD38+ immunophenotype of a major fraction of the proliferating cells. The ongoing mutation and selection for expression of a functional antigen receptor among the proliferating cells in PTGCs indicates that both somatic hypermutation and selection can occur in the presence of T cells and follicular dendritic cells without the regular organization found in GCs of secondary follicles. Somatic hypermutation without the properly organized microenvironment of GCs has also been described for knock-out mice with impaired GC development22,23 and for GC-like structures in extranodal sites of patients with autoimmune disease.24 25
The PTGC analyzed from patient 1 differed from all other PTGCs because clonally related cells were found neither among the Ki67+cells nor among the Ki67− cells. Fractions of mutated cells among the Ki67+ and Ki67− cells and mutation frequencies were, however, not obviously different from those observed in the other PTGCs. Perhaps this PTGC is composed of a large number of small clones that could not be identified as members of expanded clones because of the restricted number of cells analyzed.
Comparison of PTGCs and classical GCs
PTGCs are supposed to be enlarged GCs with increased numbers of small, Ki67− mantle zone cells and decreased numbers of larger Ki67+, centroblast-like GC cells.1,26 27 Indeed, we found some hallmarks of centroblasts—namely, clonal expansion with ongoing mutation and selection of the antigen receptors—among the Ki67+ cells of PTGCs, confirming at the molecular level that similar B-cell differentiation processes occur in PTGCs and classical GCs. In addition, most small resting cells, which are predominantly CD38−, carried unmutated immunoglobulin gene rearrangements like the IgM+IgD+ mantle zone cells of classical GCs (Figure 2).
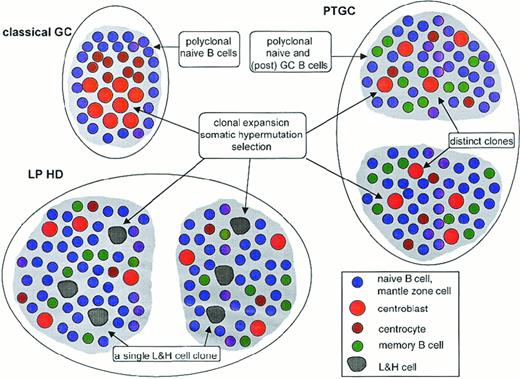
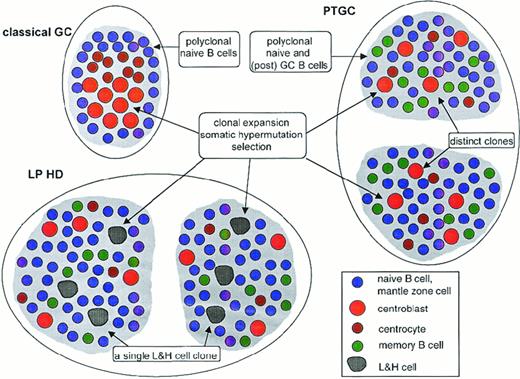
Schematic comparison of classical GC, PTGC, and LPHD.
Shown are a classical GC, 2 PTGCs, and 2 follicular structures in an LPHD lymph node. Depicted are the main B-cell types in these structures, namely naive B cells (ie, mantle zone cells in the classical GC), centroblasts, centrocytes, memory B cells, and lymphocytic and histiocytic cells of LPHD. T-helper cells and follicular dendritic cells, which are present in each of the 3 structures, are not shown. Ongoing somatic hypermutation in the lymphocytic and histiocytic cells has been observed in approximately half the patients. The composition of the population of small resting B cells in the LPHD is hypothetical.
Schematic comparison of classical GC, PTGC, and LPHD.
Shown are a classical GC, 2 PTGCs, and 2 follicular structures in an LPHD lymph node. Depicted are the main B-cell types in these structures, namely naive B cells (ie, mantle zone cells in the classical GC), centroblasts, centrocytes, memory B cells, and lymphocytic and histiocytic cells of LPHD. T-helper cells and follicular dendritic cells, which are present in each of the 3 structures, are not shown. Ongoing somatic hypermutation in the lymphocytic and histiocytic cells has been observed in approximately half the patients. The composition of the population of small resting B cells in the LPHD is hypothetical.
In classical GCs, CD38+ centrocytes carrying mutated immunoglobulin gene rearrangements are found among the Ki67− cells in the light zone of the GCs. Among the Ki67− cells analyzed from 3 PTGCs, we also found a considerable fraction of cells with mutated rearrangements among the resting cells. However, most of these cells seem to be CD38−, and thus, only a fraction may represent centrocytes, whereas most may be memory B cells, which are only rarely found in classical GCs.
Although in classical GCs clonal relatedness between the Ki67+ centroblasts and the Ki67− centrocytes has been observed,28 we found no clonal relatedness between Ki67+ and Ki67− cells with mutated rearrangements in 3 PTGCs analyzed. This is probably because most Ki67− B cells represent naive mantle zone B cells and a major fraction of Ki67− B cells with mutated V-region genes are memory B cells, hampering the identification of perhaps rare, but nevertheless existing, resting B cells belonging to clones defined by mutated Ki67+ cells.
A striking difference between PTGCs and classical GCs is the much higher frequency of Ki67+ cells with unmutated V genes in the former. Because 50% to 80% of the Ki67+ cells coexpress the CD38 GC B-cell marker in 3 patients analyzed, it is likely that besides proliferating pre-GC B cells, a fraction of the Ki67+ cells with unmutated V genes represents centroblasts. Such GC cells with unmutated V genes, which likely represent GC founder cells, have been characterized from human tonsils, where they probably account for less than 5% of the GC B cells.29 In 3 human lymph node GCs studied by micromanipulation and single-cell immunoglobulin gene PCR, only occasional unmutated GC B cells were observed.28 30 One may speculate that the apparently increased frequency of GC founder cells is related to the disorganized structure of a PTGC, preventing some GC cells from receiving the appropriate signals to initiate somatic hypermutation and to undergo massive clonal expansion.
It may be surprising that despite the disorganized structure of PTGCs when they are compared to classical GCs, the Ki67+ B cells that expand to large clones and show extensive intraclonal V gene diversity appear to be stringently and efficiently selected for B-cell receptor expression. The latter is apparent from the R/S value for mutations in the framework regions, 1.1 (range, 0.8 to 1.6), which is significantly lower than the typical value for GC B cells, 1.8.31 Indeed, the R/S value of 1.1 is in a range typical for post-GC memory B and plasma cells,13 perhaps indicating that the PTGC microenvironment supports survival of only the “very best” B cells in terms of affinity maturation. Alternatively, at the time of tissue sampling, PTGCs may often represent “old” structures that reached a degree of maturity at which members of expanded GC B-cell clones went through many rounds of selection, so that mutants with mutation patterns typical for memory B cells are enriched.
Taken together, we identified at the molecular level B-cell differentiation processes typical for classical GCs in the disorganized environment of PTGCs. However, it remains unclear whether PTGCs are the descendants of regularly organized classical GCs or develop without this initial state as a distinct type of unusual immune reaction.
Relation of PTGCs to LPHD
PTGCs have consistently been associated with LPHD.1,2,26,27,32-34 In LPHD, a single clone of lymphocytic and histiocytic cells, characterized as the descendant of a centroblast, is found in the different nodules of the lymphoma.10,16,17 Although the detection of single clones of Ki67+ cells encompassing 50% to 70% of the mutated Ki67+ cells in 3 PTGCs may be suggestive of aberrant clonal expansions, such expansions are not unusual for classical GCs.14,28,30 35
To address the question whether PTGCs might represent preneoplastic lesions, we analyzed in each of 2 patients the Ki67+ cells from 2 different PTGCs. Analysis of GCs from mouse models indicated that individual GCs are genetically isolated.14 15 Thus, clonal expansion across the borders of individual PTGCs would be indicative of a preneoplastic lesion. In both patients analyzed, no clonally related sequences from the different PTGCs were obtained, though clones were identified in the individual PTGCs; in PTGC1 of patient 5, a single expanded clone encompassed 70% of the mutated Ki67+ cells. Hence, at the molecular level we found no hints that PTGCs might be directly related to LPHD in the sense of a premalignant lesion with clonal expansions crossing the borders of separated follicular structures (Figure 2). Based on these results, it seems in principle possible (though technically demanding) to discriminate LPHD and PTGCs by molecular analysis of the proliferating cells.
In conclusion, single-cell analysis of Ki67+ and Ki67− cells from PTGCs revealed similar B-cell differentiation processes found in classical GCs, whereas no hints for clonal expansions beyond the limits of individual PTGCs were found.
Acknowledgments
We thank Christiane Gerhardt and Tanja Schaffer for excellent technical assistance.
Supported by the Deutsche Krebshilfe and the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 502). R.K. is supported by the Heisenberg program of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
References
Author notes
Andreas Bräuninger, Department of Pathology, University of Frankfurt, Theodor Stern Kai 7, 60590 Frankfurt, Germany; e-mail: braeuninger@em.uni-frankfurt.de.