Abstract
The ability of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) to regulate surface expression of the interferon-γ receptor 2 (IFN-γR2) transducing chain and activation of IFN-γ–induced signal transducer and activator of transcription-1 (STAT-1) in human T cells was analyzed. We show that, especially in the absence of serum (which contains IGF-1), IGF-1 down-regulated surface expression of the IFN-γR2 chain and inhibited both IFN-γ–dependent STAT-1 activation and apoptosis in T-cell lines ST4, Jurkat, and Molt-4. IFN-γR2 down-regulation resulted from its enhanced internalization since IGF-1 completely restored the uptake of anti–IFN-γR2 monoclonal antibody (mAb) in serum-deprived T-cell lines. When the interaction between IGF-1 and its receptor was blocked by anti–IGF-1R mAb, enhancement of IFN-γR2 surface expression, STAT-1 activation, and reinstatement of IFN-γ–induced apoptosis were observed. Enhanced expression of IFN-γR2 was also observed in phytohemagglutinin (PHA)–activated T lymphoblasts cultured in the presence of anti–IGF-1R mAb, whereas IGF-1 or anti–IGF-1R mAb did not modify the high IFN-γR2 expression in B and myeloid cell lines. Both IGF-1 and anti–IGF-1R mAb did not modify the constitutive expression of IFN-γR2 mRNA in T cells as well as the high IFN-γR1 binding chain surface expression in T, B, and myeloid cells. These data indicate that IGF-1 plays a critical role in the desensitization of IFN-γ/STAT-1 signaling in T lymphocytes by delivering a signal for IFN-γR2 internalization.
Introduction
Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) produced by T and natural killer (NK) cells is considered the principal effector cytokine of cell-mediated immunity, and many studies have indicated that it also plays an important role in controlling T-cell homeostasis and apoptosis. Activated T cells, from mice in which the genes encoding for IFN-γ or for different components of the IFN-γ signaling pathway are knocked out, exhibit increased expansion and resistance to apoptosis.1-6 Murine and human T cells activated in the presence of anti–IFN-γ or anti–IFN-γ receptor (IFN-γR) antibodies are resistant to activation-induced apoptosis.7-9
The response of T cells to IFN-γ is regulated by modulating the IFN-γR1 binding chain and IFN-γR2 signaling chain of its membrane receptor complex.10,11 IFN-γR1 is expressed on the surface of both lymphoid and nonlymphoid cells,12,13 whereas expression of IFN-γR2 is high in B and myeloid cells12 and low or absent in T cells.8,13 In T cells that differentiate along the T helper 1 (Th1) pathway, down-modulation of IFN-γR2 acts as a negative regulatory mechanism that attenuates IFN-γ/signal transducer and activator of transcription-1 (STAT-1) signaling and limits the apoptotic effect of IFN-γ.14-16
Both IFN-γ–dependent and IFN-γ–independent mechanisms have been reported to down-regulate IFN-γR2 expression in T lymphocytes. During T-helper development, the loss of IFN-γR2 that makes mouse Th1 cells resistant to IFN-γ is induced by IFN-γ itself.14 We have reported that in resting and activated human T lymphocytes, IFN-γR2 expression is prevalently cytoplasmic.9,13,17 Low surface IFN-γR2 results from fast, continuous recycling between surface and clathrin-coated vesicles.17 IFN-γR2 internalization is not affected in T cells from individuals genetically deficient for IFN-γR1,17 in established Th2 clones,9 and in T-cell lines unable to produce IFN-γ.13 However, the signals that play a major role in IFN-γ–independent down-regulation of IFN-γR2 in T cells have not yet been characterized.
Up-regulation of surface IFN-γR2 might occur following T-cell receptor (TCR) engagement8,9 or following exposure of T cells to factors that negatively regulate growth, such as galectins18 and nitric oxide.19 Serum deprivation, such as interleukin-2 (IL-2) deprivation,20 mimics the passive apoptosis induced by growth factor deprivation that T cells encounter in vivo. We have observed that serum deprivation increases surface IFN-γR2 in malignant T cells and renders them sensitive to apoptosis induced by IFN-γ.13 This suggests that serum factors or hormones may play a critical role in keeping IFN-γR2 expression low and thus limiting IFN-γ responsiveness in human T lymphocytes.
Among the factors present in serum, insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) has a profound effect on immune functions.21,22 It promotes cord blood T-cell maturation,23 proliferation, cytokine production,24 and survival,25 and inhibits their spontaneous and activation-induced apoptosis.23 Blockade of IGF-1 receptor (IGF-1R) decreases the survival of T cells activated through the TCR and CD28, and enhances their susceptibility to Fas-induced apoptosis.26
In this paper, the effect of IGF-1 or anti–IGF-1R mAb in regulating IFN-γR2 surface expression, STAT-1 activation, and apoptosis in human T lymphocytes was investigated. We show that IGF-1 delivers a signal for IFN-γR2 internalization and limits IFN-γ/STAT-1 signaling in human T cells. These results identify a new mechanism that desensitizes T lymphocytes to IFN-γ and may have implications for the regulation of apoptosis in normal and malignant T cells.
Materials and methods
Reagents
Phytohemagglutinin (PHA) was obtained from Invitrogen (Milan, Italy); rabbit anti–phospho-tyr (701)-STAT-1, anti–STAT-1 polyclonal antibodies, and horseradish peroxidase–conjugated goat anti–rabbit immunoglobulin G (IgG) were from Cell Signaling (Beverly, MA); isotype negative control mouse IgG1, fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)–conjugated rabbit anti–mouse Ig, and FITC-conjugated anti-CD3, anti-CD2, and anti-CD25 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) were from Dako (Glostrup, Denmark). The recombinant human (r-h) IGF-1 and blocking anti–IGF-1R antibody were from R&D (Minneapolis, MN); r-h insulin was from Novo Nordisk A/S (Bagsvaerd, Denmark); r-h IL-2 was from EuroCetus (Milan, Italy); mouse IgG1 antihuman IFN-γR2 mAb was from PBL Biomedical Laboratories (New Brunswick, NJ); r-h IFN-γ was kindly provided by Dr M. Brunda (Hoffman-La Roche, Nutley, NJ); and mouse IgG1 antihuman IFN-γR1 γR99 mAb was kindly provided by Dr G. Garotta (Hoffmann-La Roche, Basel, Switzerland).
Media
The culture medium was RPMI 1640 (BioWhittaker, Walkersville, MD) supplemented with penicillin, streptomycin, gentamycin, 2.5 × 10–5 M 2-mercaptoethanol (2-ME), and 10% fetal calf serum (FCS; Invitrogen) and is referred to hereafter as complete medium. All the in vitro cultures were performed at 37°C in a 5% CO2 humidified atmosphere.
PBMCs and malignant cells
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated from heparinized venous blood obtained from 5 healthy donors by Ficoll-Type 400 (Pharmacia, Uppsala, Sweden) gradient centrifugation and stimulated (1 × 106 cells/mL) with PHA (2.5 μg/mL). After 3 days, PHA-activated T lymphocytes (T lymphoblasts) were cultured in complete medium containing r-h IL-2 (20 U/mL). ST4 T cells were derived from a convoluted-type T-cell lymphoma stabilized in vitro and in nu/nu mice starting from biopsy material.27 Molt-4 (American Type Culture Collection [ATCC, Rockville, MD]; CRL1582) and Jurkat (ATCC; CRL8161) are human T cells from acute lymphoblastic leukemia. U937 (ATCC; CRL1593) is a promonocytic cell line, and Raji (ATCC; CCL86) cells are human B lymphocytes from a patient with Burkitt lymphoma.
Flow cytometry
To evaluate IFN-γR1 and IFN-γR2 expression, malignant T, B, and myeloid cells were cultured in the presence or absence of serum, with or without IGF-1 (100 ng/mL), anti–IGF-1R mAb (10 μg/mL), or insulin (3600 ng/mL). In some experiments, T lymphoblasts were cultured in the presence of IGF-1, anti–IGF-1R mAb, or insulin in complete medium, with or without IL-2 (20 U/mL). After 24 hours, cells were recovered, washed twice in cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), supplemented with 0.2% bovine serum albumin (BSA) and 0.1% sodium azide, and stained for surface protein with unconjugated anti–IFN-γR1 γR99 or anti–IFN-γR2 mAb, followed by FITC-conjugated rabbit anti–mouse Ig. All labeling steps were followed by incubation for 30 minutes at 4°C and separated by 2 washes with cold PBS supplemented with 0.2% BSA and 0.1% sodium azide. In some experiments, the expression of IFN-γR2 was evaluated in CD3+ peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs), either freshly isolated or cultured for 48 hours in complete medium alone, in complete medium containing 10 μg/mL anti–IGF-1R, or in medium without serum containing 100 ng/mL IGF-1. Cells were simultaneously stained with FITC-conjugated anti-CD3 mAb and biotin-conjugated anti–IFN-γR2, followed by phycoerythrin (PE)–conjugated streptavidin (Dako). To determine apoptosis, the Annexin-V–FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit was used (Oncogene, Boston, MA). Briefly, control cells or cells pretreated for 24 hours with IGF-1 (100 ng/mL) or anti–IGF-1R mAb (10 μg/mL) were cultured for a further 48 hours in the presence of IFN-γ (1000 U/mL), resuspended, and stained with FITC-conjugated Annexin-V and propidium iodide (PI) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Membrane expression and apoptosis were determined with a FACScan flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson, Milan, Italy). Each plot represents the results from 10 000 events.
Reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)
ST4 cells (1 × 106 cells/mL) were cultured in complete medium with or without anti–IGF-1R mAb (10 μg/mL), or in the absence of serum, with or without IGF-1 (100 ng/mL). After 24 hours, IFN-γR2 expression was evaluated by RT-PCR on the recovered cells as previously described.19 Total cellular RNA was extracted with the Trizol (Invitrogen). Specific glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (G3PDH) primer pairs were obtained from Clontech (Palo Alto, CA). PCR product (15 μL) was electrophoresed in a 2% agarose gel in Tris (tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane)/boric acid/EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) buffer. Gels were stained with ethidium bromide (Sigma Chemical, St Louis, MO) and photographed.
Endocytosis experiments
Biotin-conjugated anti–IFN-γR2 mAb was used at concentrations of 10 to 20 μg/mL. Briefly, 1 mg/mL anti–IFN-γR2 mAb was dialyzed against 0.1 M carbonate buffer (pH 8.5) and conjugated to biotin-N-hydroxysuccinimide ester (1 mg/mL; Sigma Chemical) in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) for 4 hours at room temperature and dialyzed against PBS. ST4 cells cultured for 24 hours in the presence or absence of serum were recovered and incubated with biotin-conjugated IFN-γR2 or isotype-matched mouse IgG1 control mAb for 4 hours at 37°C or at 4°C in the absence or presence of IGF-1 (100 ng/mL). Cell surface–associated mAb was removed by treating twice with acid pH (2 minutes at pH 3.0) as described.17 Then cells were fixed and permeabilized as described elsewhere17 and incubated for 30 minutes at 4°C with PE-conjugated streptavidin. In parallel endocytosis experiments, serum-deprived ST4 cells were incubated in the absence or presence of scalar doses of IGF-1 (from 1 to 100 ng/mL) with unconjugated IFN-γR2 mAb or isotype-matched mouse IgG1 control mAb as described in “Flow cytometry.” After fixation and permeabilization, cells were incubated with a rabbit F(ab′)2 FITC-conjugated anti–mouse Ig (Dako). IFN-γR2 endocytosis was measured as cell-associated specific fluorescence by flow cytometry.
Western blotting
Treated cells (5 × 106) were washed twice in cold PBS and then collected by centrifugation. Nuclear proteins (25 or 30 μg protein) were extracted as previously described13 and separated on sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis at 140 V on 8% protein mini-gels. Gels were electroblotted onto polyvinylidene fluoride membranes (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA) at 100 V for one hour, and the equality of the amount of protein analyzed was checked by nonspecific staining with Ponceau S (Sigma Chemical). The membranes were blocked with TTBS (20 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 0.5 M NaCl, and 0.05% Tween 20) and 5% nonfat dry milk for 3 hours and then incubated overnight with a 1:1000 dilution of anti–phospho-tyr (701)-STAT-1, or anti–STAT-1 rabbit polyclonal antibodies. After washing with TTBS, blots were incubated with 1:2000 horseradish peroxidase–conjugated goat anti–rabbit IgG antibody. Antibody reactions were visualized with enhanced chemiluminescence reagents according to the manufacturer's instructions (ECL plus; Amersham International, Bucks, United Kingdom). Nonphosphorylated STAT-1 was used as a control for equal protein loading. Fold increase of treated cells relative to untreated cells was quantitated after normalization with nonphosphorylated STAT-1. Density scanning was performed using the University of Texas Health Science Center (San Antonio, TX) ImageTools for Windows 2.0.
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA)
Following pretreatment with medium, IGF-1, or anti–IGF-1R mAb for 48 hours, cells (1 × 107 cells/mL) were incubated with 1000 U/mL IFN-γ at 37°C. At the appropriate time interval, 100 μL was removed and used for EMSA. Preparation of cell lysates, EMSAs, and all data analyses were performed as previously described.13 EMSAs were performed with a 22-bp sequence containing a STAT-1α binding site corresponding to the sis inducible element (SIE) from the IRF-1 gene promoter (5′-GATCG ATTTCCCCGAAATCATG-3′).13
Results
IGF-1 induces internalization of IFN-γR2 chain in human T lymphocytes
The observation that serum deprivation up-regulates IFN-γR2 on human T lymphocytes13 prompted us to evaluate whether IGF-1 (present in serum) was involved in IFN-γR2 internalization. We used 3 T-cell lines (ST4, Jurkat, and Molt-4) that do not produce IFN-γ (data not shown) and display low surface expression of IFN-γR2 when grown in the presence of serum.13 The fact that IFN-γR2 protein is prevalently accumulated in the cytoplasm of these malignant T-cell lines13 underlies an IFN-γ–independent IFN-γR2 internalization mechanism.17
Since these T-cell lines express high surface levels of IGF-1R and do not secrete IGF-1 (Schillaci et al28 and data not shown), we evaluated the effect of IGF-1 (100 ng/mL) on IFN-γR2 internalization when they were cultured in the absence of serum. Since insulin, which is also present in serum,29 activates IGF-1R, although at 10-fold higher concentration than IGF-1,30 a 36-fold higher concentration of insulin was used to assess the specificity of action of IGF-1 on IFN-γR2 expression. In addition, the effect of preventing IGF-1 from binding to its specific receptor with a blocking anti–IGF-1R mAb was evaluated on T-cell lines cultured in the presence of serum.
Flow cytometry showed that malignant T cells cultured for 24 hours in the presence of serum displayed low-level surface IFN-γR2. Only 22% to 29% of cells were IFN-γR2 positive with a mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) between 7 to 23 (Table 1). IGF-1 slightly decreased this percentage in all 3 lines, although the MFI of Molt-4 and ST4 cells was reduced more than 2-fold (Table 1). Conversely, anti–IGF-1R mAb markedly enhanced both the percentage of IFN-γR2–positive cells and the MFI in all 3 cell lines (Table 1). No differences in percent positivity or MFI were observed in the presence of insulin (Table 1).
Effect of IGF-1 on IFN-γR2 expression in human lymphoid cell lines
. | . | . | % of IFN-γR2†in the presence of . | . | . | . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line . | Lineage . | Serum* . | Medium . | IGF-1‡ . | αIGF-1R§ . | Insulin¶ . | |||
| ST4 | T | + | 26 (18) | 18 (7) | 67 (38) | 25 (19) | |||
| - | 46 (12) | 18 (8) | NE | 41 (25) | |||||
| Jurkat | T | + | 22 (7) | 13 (6) | 41 (12) | 21 (8) | |||
| - | 40 (19) | 22 (9) | NE | 45 (20) | |||||
| Molt-4 | T | + | 29 (23) | 26 (10) | 75 (48) | 32 (29) | |||
| - | 62 (34) | 21 (8) | NE | 56 (34) | |||||
| Raji | B | + | 46 (37) | 48 (53) | 49 (43) | 49 (41) | |||
| - | 44 (39) | 47 (47) | NE | 48 (40) | |||||
| U937 | Myeloid | + | 91 (105) | 93 (140) | 95 (168) | 94 (161) | |||
| - | 90 (132) | 92 (124) | NE | 91 (109) | |||||
. | . | . | % of IFN-γR2†in the presence of . | . | . | . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line . | Lineage . | Serum* . | Medium . | IGF-1‡ . | αIGF-1R§ . | Insulin¶ . | |||
| ST4 | T | + | 26 (18) | 18 (7) | 67 (38) | 25 (19) | |||
| - | 46 (12) | 18 (8) | NE | 41 (25) | |||||
| Jurkat | T | + | 22 (7) | 13 (6) | 41 (12) | 21 (8) | |||
| - | 40 (19) | 22 (9) | NE | 45 (20) | |||||
| Molt-4 | T | + | 29 (23) | 26 (10) | 75 (48) | 32 (29) | |||
| - | 62 (34) | 21 (8) | NE | 56 (34) | |||||
| Raji | B | + | 46 (37) | 48 (53) | 49 (43) | 49 (41) | |||
| - | 44 (39) | 47 (47) | NE | 48 (40) | |||||
| U937 | Myeloid | + | 91 (105) | 93 (140) | 95 (168) | 94 (161) | |||
| - | 90 (132) | 92 (124) | NE | 91 (109) | |||||
NE indicates not evaluated.
Treated cells were cultured for 24 hours in the presence (+) or absence (-) of 10% FCS.
Percentage of IFN-γR2—positive cells evaluated by flow cytometry using anti—IFN-γR2 mAb. Percentages were calculated by subtracting the positivity of nonspecific fluorescence given by isotype-matched control lg and are from 1 of 3 independently performed representative experiments. Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) is in parentheses.
100 ng/mL.
10 μg/mL.
3600 ng/mL.
When IGF-1 was depleted by serum deprivation, the percentage of IFN-γR2–positive cells was markedly enhanced in all 3 cell lines, though enhancement of the MFI was appreciable only in Jurkat and Molt-4 cells (Table 1). The enhancement of IFN-γR2 expression was not affected by the presence of insulin. In contrast, IGF-1 down-regulated IFN-γR2 expression in all 3 cell lines. In the presence of IGF-1, the percentage of IFN-γR2–positive cells and the MFI of ST4 and Molt-4 cells fell to levels lower than those found in the presence of serum (Table 1).
The effect of IGF-1, anti–IGF-1R mAb, and insulin on IFN-γR2 expression was also evaluated in B (Raji) and myeloid (U937) cells, which constitutively express high levels of both chains.13 Their high percent positivity and MFI for IFN-γR2 were not affected by the presence or lack of serum (Table 1).
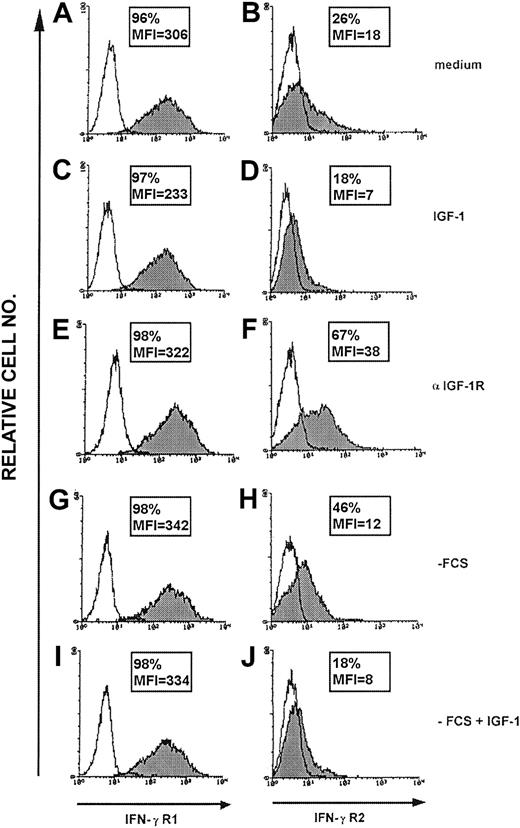
Unlike IFN-γR2, the high surface expression of IFN-γR1 on ST4 cells was not affected by IGF-1, anti–IGF-1R mAb (Figure 1), or insulin (data not shown). Similar results were observed in Jurkat, Molt-4, Raji, and U937 cells (data not shown).
IFN-γR1 and IFN-γR2 surface expression in malignant T cells. Surface expression of IFN-γR1 and IFN-γR2 in ST4 T cells evaluated by flow cytometry after 24-hour culture in the presence of complete medium (A-B), IGF-1 (100 ng/mL) (C-D) or anti–IGF-1R blocking mAb (10 μg/mL) (E-F), medium without serum (G-H) or medium without serum supplemented with IGF-1 (100 ng/mL) (I-J) using anti–IFN-γR1 γR99 (A,C,E,G,I) or anti–IFN-γR2 mAb (B,D,F,H,J). The histogram represents the expression of IFN-γR1 (left panels, gray histogram), IFN-γR2 (right panels, gray histogram), or background of mouse IgG1 negative control (white histogram) in the ST4 T-cell line in 1 representative experiment of 3 independently performed. Results in frame are expressed as percentage of positive cells calculated by subtracting the positivity of nonspecific fluorescence detected with isotype-matched control Ig from that obtained with specific fluorescence, and the mean of fluorescence intensity (MFI) is indicated.
IFN-γR1 and IFN-γR2 surface expression in malignant T cells. Surface expression of IFN-γR1 and IFN-γR2 in ST4 T cells evaluated by flow cytometry after 24-hour culture in the presence of complete medium (A-B), IGF-1 (100 ng/mL) (C-D) or anti–IGF-1R blocking mAb (10 μg/mL) (E-F), medium without serum (G-H) or medium without serum supplemented with IGF-1 (100 ng/mL) (I-J) using anti–IFN-γR1 γR99 (A,C,E,G,I) or anti–IFN-γR2 mAb (B,D,F,H,J). The histogram represents the expression of IFN-γR1 (left panels, gray histogram), IFN-γR2 (right panels, gray histogram), or background of mouse IgG1 negative control (white histogram) in the ST4 T-cell line in 1 representative experiment of 3 independently performed. Results in frame are expressed as percentage of positive cells calculated by subtracting the positivity of nonspecific fluorescence detected with isotype-matched control Ig from that obtained with specific fluorescence, and the mean of fluorescence intensity (MFI) is indicated.
Thus, it seems that IGF-1 provides a signal that mediates IFN-γR2 internalization. This signal is restricted to T cells and does not affect the expression of IFN-γR1.
IGF-1 or anti–IGF-1R mAb did not affect IFN-γR2 mRNA expression in T lymphocytes
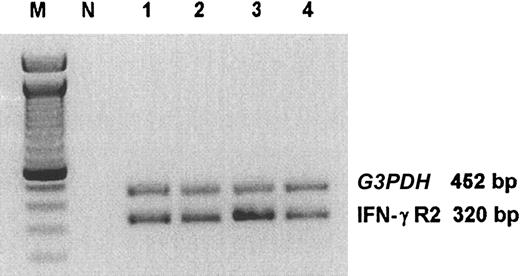
RT-PCR analysis revealed that in ST4 cells cultured in the presence of serum IFN-γR2 mRNA is constitutively expressed (Figure 2). This was not modified by 24-hour culture in the absence of serum, in the absence of serum in the presence of IGF-1, or in complete medium in the presence of anti–IGF-1R mAb (Figure 2). At this time point, cell viability of ST4 cells was increased by 6% to 7% in the presence of serum or the absence of serum in the presence of IGF-1, and reduced by 3% to 4% in the absence of serum or in complete medium in the presence of anti–IGF-1R mAb. These results indicate that modulation of IFN-γR2 surface expression by IGF-1 or anti–IGF-1R mAb did not affect T lymphocyte IFN-γR2 transcription and was not influenced by variations in cell viability due to long-term culture. Similar results were obtained with Jurkat and Molt-4 (data not shown).
RT-PCR analysis of IFN-γR2 chain in malignant T cells. ST4 cells were cultured in complete medium (lane 1), in medium without serum (lane 2), in medium without serum supplemented with 100 ng/mL IGF-1 (lane 3), or in complete medium in the presence of 10 μg/mL anti–IGF-1R blocking mAb (lane 4). After 24 hours, cells were recovered and IFN-γR2 and G3PDH (housekeeping gene) mRNA were evaluated. Lane M indicates marker; lane N, contamination control reaction containing all PCR reagents but no substrate cDNA. The size of the PCR fragments is shown on the right.
RT-PCR analysis of IFN-γR2 chain in malignant T cells. ST4 cells were cultured in complete medium (lane 1), in medium without serum (lane 2), in medium without serum supplemented with 100 ng/mL IGF-1 (lane 3), or in complete medium in the presence of 10 μg/mL anti–IGF-1R blocking mAb (lane 4). After 24 hours, cells were recovered and IFN-γR2 and G3PDH (housekeeping gene) mRNA were evaluated. Lane M indicates marker; lane N, contamination control reaction containing all PCR reagents but no substrate cDNA. The size of the PCR fragments is shown on the right.
IGF-1 induces anti–IFN-γR2 mAb uptake in human malignant T lymphocytes
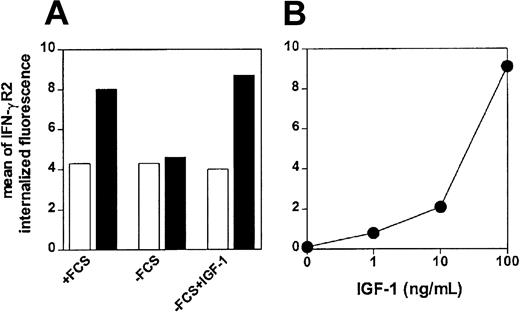
To confirm that IGF-1 induces internalization of IFN-γR2, we analyzed its effects on the accumulation of biotin-conjugated anti–IFN-γR2 mAb, at 37°C or at 4°C, in ST4 cells cultured without serum. We have previously shown that in human T lymphoblasts, internalization of IFN-γR2 induces at least a 2-fold increase of cell-associated specific fluorescence of anti–IFN-γR2 mAb uptake after 4-hour incubation at 37°C.17 In ST4 cells cultured with serum for 24 hours, an about 2-fold increase of cell-associated specific fluorescence of anti–IFN-γR2 mAb uptake was observed after 4-hour incubation at 37°C (Figure 3A). In contrast, no anti–IFN-γR2 mAb uptake was observed on ST4 cells cultured for 24 hours in the absence of serum (Figure 3A), indicating that IFN-γR2 internalization was inhibited. Similar inhibition of IFN-γR2 uptake was observed when ST4 cells were incubated for 4 hours at 37°C in potassium-free medium (data not shown), which prevents endocytosis of receptors that use clathrin for internalization.17 However, when IGF-1 was added to serum-deprived ST4 cells during the 4-hour incubation, the uptake of anti–IFN-γR2 mAb was completely restored (Figure 3A). IGF-1–induced IFN-γR2 internalization in serum-deprived ST4 cells was found to be dose dependent (Figure 3B). These data indicated that, in the absence of serum, IFN-γR2 internalization in T cells is inhibited and can be restored by IGF-1.
Flow cytometry of IFN-γR2 internalization in malignant T cells. (A) ST4 T cells cultured for 24 hours in the presence or absence of serum, or absence of serum in the presence of IGF-1 (100 ng/mL) were recovered and incubated with biotin-conjugated anti–IFN-γR2 mAb at 4°C(□)or 37°C(▪). After 4 hours, cells were permeabilized and stained with PE-conjugated streptavidin. (B) ST4 T cells, cultured for 24 hours in medium without serum in the absence or in the presence of scalar doses of IGF-1 (from 1 to 100 ng/mL), were incubated with unconjugated anti–IFN-γR2 mAb or with isotype-matched mAb at 37°C. After 4 hours, cells were permeabilized and stained with FITC-conjugated rabbit F(ab′)2 anti–mouse Ig. Mean specific internalized fluorescence was calculated by subtracting the mean internalized fluorescence obtained with specific anti–IFN-γR2 mAb from that obtained with isotype-matched mAb.
Flow cytometry of IFN-γR2 internalization in malignant T cells. (A) ST4 T cells cultured for 24 hours in the presence or absence of serum, or absence of serum in the presence of IGF-1 (100 ng/mL) were recovered and incubated with biotin-conjugated anti–IFN-γR2 mAb at 4°C(□)or 37°C(▪). After 4 hours, cells were permeabilized and stained with PE-conjugated streptavidin. (B) ST4 T cells, cultured for 24 hours in medium without serum in the absence or in the presence of scalar doses of IGF-1 (from 1 to 100 ng/mL), were incubated with unconjugated anti–IFN-γR2 mAb or with isotype-matched mAb at 37°C. After 4 hours, cells were permeabilized and stained with FITC-conjugated rabbit F(ab′)2 anti–mouse Ig. Mean specific internalized fluorescence was calculated by subtracting the mean internalized fluorescence obtained with specific anti–IFN-γR2 mAb from that obtained with isotype-matched mAb.
Anti–IGF-1R mAb enhances IFN-γR2 expression in normal human T cells
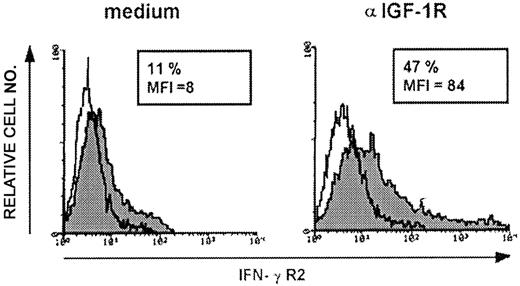
To determine whether IGF-1–induced IFN-γR2 internalization is confined to malignant T cells, the effect of anti–IGF-1R mAb on surface IFN-γR2 in normal human T lymphocytes was evaluated. In resting CD3+ PBLs, IFN-γR2 surface expression is barely detectable (Novelli et al8 and data not shown). IFN-γR2 internalization was not modified in these cells after 24- to 48-hour culture in the presence or absence of serum, nor in the presence of serum and anti–IGF-1R mAb (data not shown). This indication that IGF-1–induced IFN-γR2 internalization is restricted to cycling T cells was confirmed by stimulating PBMCs from healthy donors to proliferate with PHA. After 5 days, PHA-activated T lymphoblasts were cultured for a further 48 hours in complete medium containing IL-2, with or without anti–IGF-1R mAb. Flow cytometry showed that T lymphoblasts cultured in complete medium expressed low levels of surface IFN-γR2 (mean IFN-γR2 percent positivity, 11 ± 1; mean MFI, 7 ± 2) (Figure 4) but, in the presence of anti–IGF-1R mAb, IFN-γR2 expression was enhanced (mean IFN-γR2 percent positivity, 44 ± 4; mean MFI, 82 ± 2) (Figure 4). These data indicated that IGF-1 plays a general role in inducing IFN-γR2 internalization in cycling human T cells.
IFN-γR2 expression in PHA-activated T lymphoblasts. Surface expression of IFN-γR2 in 5-day PHA-activated T lymphoblasts evaluated by flow cytometry after 48-hour culture in the presence of complete medium or anti–IGF-1R blocking mAb (10 μg/mL) using anti–IFN-γR2 mAb. The histogram represents the expression of IFN-γR2 (gray histogram) or background of mouse IgG1 as negative control (white histogram) in PHA-activated T lymphoblasts. Shown is 1 representative experiment of 3 independently performed. Results in frame are expressed as percentage of positive cells calculated by subtracting the positivity of nonspecific fluorescence detected with isotype-matched control Ig from that obtained with specific fluorescence, and the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) is indicated.
IFN-γR2 expression in PHA-activated T lymphoblasts. Surface expression of IFN-γR2 in 5-day PHA-activated T lymphoblasts evaluated by flow cytometry after 48-hour culture in the presence of complete medium or anti–IGF-1R blocking mAb (10 μg/mL) using anti–IFN-γR2 mAb. The histogram represents the expression of IFN-γR2 (gray histogram) or background of mouse IgG1 as negative control (white histogram) in PHA-activated T lymphoblasts. Shown is 1 representative experiment of 3 independently performed. Results in frame are expressed as percentage of positive cells calculated by subtracting the positivity of nonspecific fluorescence detected with isotype-matched control Ig from that obtained with specific fluorescence, and the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) is indicated.
The same pattern of IFN-γR2 internalization in the presence or absence of anti–IGF-1R mAb was also observed in T lymphoblasts cultured in the absence of IL-2 (data not shown). Thus, although IL-2 constitutes the main growth and survival factor for T cells, it is not involved in the negative regulation of the IFN-γR2.
Effects of IGF-1 on the IFN-γ/STAT-1 pathway of human T cells
Interaction of IFN-γ with its receptor phosphorylates Janus kinase 1 (Jak-1) and Jak-2, which activate STAT-1.31,32 Since surface IFN-γR2 levels critically control the rate of IFN-γ–induced STAT-1 activation,13 the effect of IGF-1 or anti–IGF-1R mAb on the ability of IFN-γ to induce activation of STAT-1 on ST4 cells was evaluated.
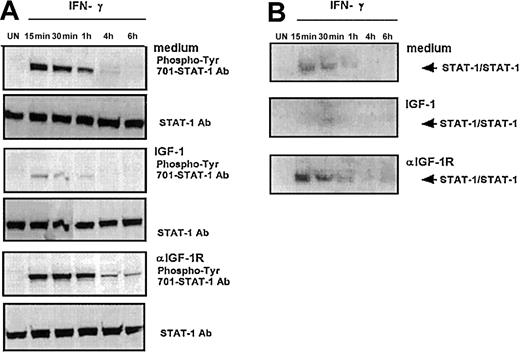
ST4 cells were cultured in complete medium in the absence or presence of IGF-1 or anti–IGF-1R blocking mAb. After 48 hours, each culture was recovered and cultured for different times in the presence of IFN-γ. Nuclear proteins were extracted at different time points and analyzed by Western blot with a specific anti–phospho-tyr (701)-STAT-1 mAb (Figure 5A) and by EMSA with a high-affinity STAT-1α binding oligonucleotide (Figure 5B).
STAT-1 activation kinetics induced by IFN-γ in malignant T cells. ST4 T cells untreated or treated for 48 hours with IGF-1 (100 ng/mL) or anti–IGF-1R blocking mAb (10 μg/mL) were cultured without (UN) or with IFN-γ (1000 U/mL) for the indicated time intervals. (A) STAT-1 activation was evaluated by Western blot analysis of nuclear cell extracts with anti–phospho-tyr (701)-STAT-1 mAb. Western blot filters were subsequently probed with an anti–STAT-1 antibody to confirm equal protein loading in each lane of the gel. (B) STAT-1 activation was evaluated by EMSA assay of nuclear extracts. Medium, IGF-1, or anti–IGF-1R mAb 48-hour–pretreated cells were incubated in the absence (UN) or in the presence of 1000 U/mL IFN-γ at the appropriate time interval. The experiments were performed independently at least 3 times.
STAT-1 activation kinetics induced by IFN-γ in malignant T cells. ST4 T cells untreated or treated for 48 hours with IGF-1 (100 ng/mL) or anti–IGF-1R blocking mAb (10 μg/mL) were cultured without (UN) or with IFN-γ (1000 U/mL) for the indicated time intervals. (A) STAT-1 activation was evaluated by Western blot analysis of nuclear cell extracts with anti–phospho-tyr (701)-STAT-1 mAb. Western blot filters were subsequently probed with an anti–STAT-1 antibody to confirm equal protein loading in each lane of the gel. (B) STAT-1 activation was evaluated by EMSA assay of nuclear extracts. Medium, IGF-1, or anti–IGF-1R mAb 48-hour–pretreated cells were incubated in the absence (UN) or in the presence of 1000 U/mL IFN-γ at the appropriate time interval. The experiments were performed independently at least 3 times.
In cells cultured in complete medium, pretreated with either IGF-1 or anti–IGF-1 mAb and not exposed to IFN-γ, no phosphorylation of STAT-1 was observed (Figure 5A). Addition of IFN-γ to cells cultured in complete medium induced phosphorylation of STAT-1, which was detectable after 15 minutes and then decreased. It was still detectable after 1 hour but not after 4 hours. In cells treated with IGF-1 prior to IFN-γ treatment, phosphorylation of STAT-1 was almost completely abrogated (Figure 5A). Compared with ST4 cells cultured in medium alone, IFN-γ–induced STAT-1 phosphorylation was approximately 3-fold lower after 15 minutes and almost disappeared after one hour (Figure 5A). In cells pretreated with anti–IGF-1R mAb, the high-level phosphorylation of STAT-1 induced by IFN-γ was much more sustained, being still detectable after 6 hours (Figure 5A).
In cells cultured in complete medium, pretreated with either IGF-1 or anti–IGF-1R mAb and not exposed to IFN-γ, no DNA binding activity of STAT-1 was observed (Figure 5B). In cells cultured in complete medium, IFN-γ treatment induced STAT-1 DNA binding activity that was detected after 15 minutes, after which it decreased and was mostly lost after 1 hour. Compared with cells cultured in complete medium, the IFN-γ–induced STAT-1 DNA binding activity of cells pretreated with IGF-1 was reduced in amplitude and delayed, as it was observed only after 30 minutes and was no longer detectable after 1 hour (Figure 5B). In contrast, compared with cells cultured in medium only, the IFN-γ–induced STAT-1 DNA binding activity of cells pretreated with anti–IGF-1R mAb was 2-fold and 3.5-fold increased after 15 and 30 minutes, respectively (Figure 5B).
Pretreatment of Raji B and U937 myeloid cells with IGF-1 did not modify the ability of IFN-γ to induce strong and sustained STAT-1 activation (data not shown).
These data indicate that, by decreasing IFN-γR2 expression, IGF-1 plays a role in extinguishing the IFN-γ/STAT-1 pathway in human T lymphocytes. By contrast, IGF-1R functional blockade strongly enhances and sustains STAT-1 activation.
Blockade of IGF-1R reinstates IFN-γ–dependent apoptosis in malignant T cells
T lymphocytes express low surface levels of IFN-γR2 and are resistant to STAT-1–dependent apoptosis induced by IFN-γ.8,13,17 Since pretreatment with IGF-1 decreased IFN-γR2 and IFN-γ–dependent STAT-1 activation in malignant T cells (Figures 1,5), we evaluated whether anti–IGF-1R mAb pretreatment reinstated their sensitivity to the apoptotic signal of IFN-γ.
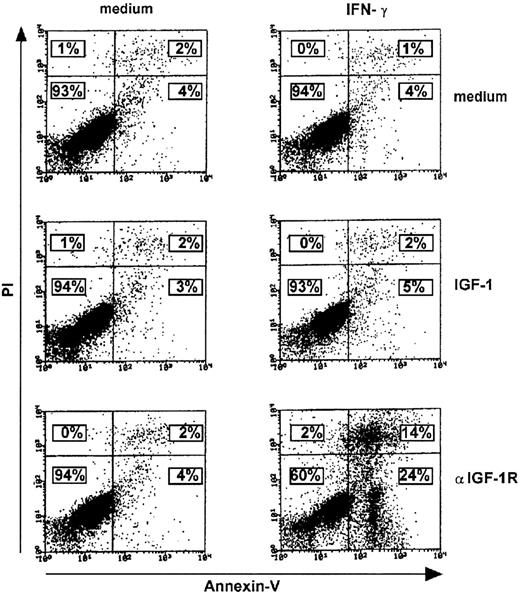
ST4 cells were cultured with or without either 100 ng/mL IGF-1 or 10 μg/mL anti–IGF-1R mAb. After 48 hours, each culture was recovered, split, and cultured for a further 24 hours in the presence or absence of 1000 U/mL IFN-γ. This was followed by staining cells simultaneously with PI and FITC-conjugated Annexin-V to evaluate apoptosis (Figure 6).
Enhanced IFN-γ–induced apoptosis in T cells cultured with anti–IGF-1R blocking mAb. Medium, IGF-1 (100 ng/mL), or anti–IGF-1R blocking mAb (10 μg/mL) 48-hour–treated ST4 T cells (0.5 × 106) were cultured for a further 24 hours in the absence or presence of IFN-γ (1000 U/mL). They were then recovered and stained with FITC-conjugated Annexin-V and PI as described in “Materials and methods.” The number of viable, early, or late apoptotic cells was determined by flow cytometric analysis. Lower left region indicates viable cells (Annexin-V–/PI–); lower right region, early apoptotic cells (Annexin-V+/PI–); upper left region, necrotic cells (Annexin-V–/PI+); and upper right region, late apoptotic cells (Annexin-V+/PI+). Percentages of positive cells are indicated. Results of 1 of 3 independently performed representative experiments are shown.
Enhanced IFN-γ–induced apoptosis in T cells cultured with anti–IGF-1R blocking mAb. Medium, IGF-1 (100 ng/mL), or anti–IGF-1R blocking mAb (10 μg/mL) 48-hour–treated ST4 T cells (0.5 × 106) were cultured for a further 24 hours in the absence or presence of IFN-γ (1000 U/mL). They were then recovered and stained with FITC-conjugated Annexin-V and PI as described in “Materials and methods.” The number of viable, early, or late apoptotic cells was determined by flow cytometric analysis. Lower left region indicates viable cells (Annexin-V–/PI–); lower right region, early apoptotic cells (Annexin-V+/PI–); upper left region, necrotic cells (Annexin-V–/PI+); and upper right region, late apoptotic cells (Annexin-V+/PI+). Percentages of positive cells are indicated. Results of 1 of 3 independently performed representative experiments are shown.
When cultured in both medium and IGF-1, ST4 displayed very low percentages of apoptotic cells, irrespective of the presence of IFN-γ (Figure 6, top and middle panels), whereas prior treatment with anti–IGF-1R mAb led to a dramatic increase in apoptosis after exposure to IFN-γ (Figure 6, lower panels).
These data indicate that IGF-1 blockade reinstates the IFN-γ–dependent apoptotic pathway in malignant T cells.
Discussion
This study shows that IGF-1 is a critical environmental factor that selectively keeps IFN-γR2 expression low and thus limits activation of the IFN-γ/STAT-1 pathway in T lymphocytes. By using 3 non–IFN-γ–producing malignant T-cell lines that express IFN-γR2 prevalently in their cytoplasm, we have demonstrated that depletion of IGF-1, by serum deprivation or by a mAb that blocks its receptor, increases surface expression of IFN-γR2. Addition of IGF-1 down-regulates surface IFN-γR2 in serum-deprived T cells. This down-regulation is the result of internalization since, in malignant T cells cultured in the absence of serum, IGF-1 induces dose-dependent enhancement of anti–IFN-γR2 mAb uptake but it does not have any effect on IFN-γR2 mRNA expression. B-, myeloid, and T-cell lines used in this study express similar IGF-1R levels and respond to IGF-1 (data not shown). However, IGF-1 regulates IFN-γR2 in T cells only. This implies that B and myeloid cells expressing high surface levels of IFNγ-R2 (Badovinac et al5 and this study) are not sensitive to the internalization signal mediated by IGF-1. Moreover, our data indicate that T-cell–specific IFN-γR2 internalization is induced by IGF-1 but not by insulin.
Our data indicate that IGF-1 induces the internalization of IFN-γR2 but not that of IFN-γR1. This provides further evidence of the independent regulation of these 2 chains in human T cells.17 In effect, T-cell surface expression is down-regulated by IFN-γ,9,11 and in IFN-γ–stimulated Jurkat T cells IFN-γR1 is endocytosed and translocated to the nucleus from plasma membrane lipid microdomains or “rafts,”33 which constitute a clathrin-independent endocytic pathway.34 In contrast, in human T cells IFN-γR2 is constitutively internalized in clathrin-coated vescicles.17 Thus, it would seem that distinct pathways of endocytosis are involved in ligand-dependent IFN-γR1 and IGF-1–dependent IFN-γR2 internalization in T cells. This hypothesis is endorsed by the observation that filipin, a cavaeolae/lipid microdomain inhibitor,33 did not affect the ability of IGF-1 to induce IFN-γR2 internalization (data not shown).
Negative regulation of IFN-γR2 by IGF-1 also occurs in normal activated T cells. We observed that in the presence of anti–IGF-1R mAb the expression of IFN-γR2 is enhanced in PHA-activated lymphoblasts but not in resting CD3+ PBLs. Thus, IGF-1 regulates internalization only in activated, cycling T cells. This is consistent with previous observations that the IGF-1R is expressed in polyclonally activated T cells35 but not in resting T cells.36 However, our data indicate that IGF-1–mediated down-regulation of IFN-γR2 expression is not influenced by IL-2 since IFN-γR2 up-regulation was observed in the presence of anti–IGF-1R mAb irrespective of the presence of IL-2. IFN-γR1 was controlled only by IL-2 withdrawal.10 In effect, both IFN-γR1 and IL-2Rβ share the same clathrin-independent pathway of endocytosis.33,35
Our data clearly show that IGF-1 desensitizes IFN-γ/STAT-1 signaling in T cells since IFN-γ–dependent STAT-1 activation was strongly inhibited by IGF-1 pretreatment. Thus, by limiting the availability of IFNγ-R2 at the T-cell surface, IGF-1 is a factor that directly prevents IFN-γ from triggering a sufficient number of heterodimeric receptors.4 The fact that IGF-1 and anti–IGF-1R mAbs appear to have a greater effect on the IFN-γ–induced activation of STAT-1 than on expression of IFN-γR2 would suggest that other IGF-1–dependent mechanisms concur in IFN-γ/STAT-1 desensitization. It is conceivable that IGF-1, by activating STAT-3,37 might suppress the STAT-1 pathway38 and enhance the ability of IFN-γ to activate STAT-3.39,40 The reciprocal influence of IFN-γ and IGF-1 signaling is further suggested by the observation that IFN-γ up-regulates the expression of IGF-1R in T lymphocytes (data not shown). Studies to dissect the role of cross-talk through the IGF-1R and IFN-γR in regulating the STAT-1/STAT-3 balance in T lymphocytes are currently in progress in our laboratory.
The ability of IFN-γ to induce apoptosis in T cells is dependent on STAT-1 activation.6,13 Our data show that blockade of IGF-1R reinstates IFN-γ–induced apoptosis of T cells. Revival of strong IFN-γ–induced apoptosis by this blockade may be of importance in regulation of IFN-γ/STAT-1–dependent apoptosis of T cells in both physiologic and pathologic scenarios. IFN-γ plays a central role in cancer immunoediting,41,42 and human tumors develop a selective insensitivity to IFN-γ signaling.43 Our data suggest that in addition to being a growth and antiapoptotic factor,44 IGF-1 acts as a negative regulator of IFN-γ signaling and thus contributes to the escape of developing tumor cells from the immunoregulatory (eg, antigen [Ag] presentation) and antiproliferative effects of IFN-γ.45 The resistance of malignant T cells to IFN-γ–induced apoptosis may be a consequence of the down-regulation of IFN-γR2.13,46 Our data suggest that by reinstating IFN-γ–induced STAT-1 activation and apoptosis, IGF-1R blockade may offer a way of overcoming the resistance of malignant T cells to IFN-γ. In vivo experiments are in progress to ascertain the effect of combined administration of anti–IGF-1R mAb and IFN-γ on the growth of malignant T cells in severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice.
During the early steps of Th1 differentiation, the IFN-γ/STAT-1 pathway is critical for the decision of naive T cells to develop along the Th1 lineage.47 Since our data show that IGF-1 is a critical factor for tuning IFN-γ induction of STAT-1 in T lymphocytes, it would be interesting to evaluate the possibility of modulating or inhibiting Th1 development by IGF-1.
Prepublished online as Blood First Edition Paper, July 3, 2003; DOI 10.1182/blood-2003-01-0100.
Supported by grants from the Istituto Superiore di Sanità (special projects on AIDS), Fondazione Piemontese Studi e Ricerche sulle Ustioni (FPSRU), Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC), Compagnia San Paolo (special project Oncology), and Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca Scientifica (MURST). P.B. was supported by a fellowship from Fondazione Italiana Ricerca sul Cancro (FIRC); S. De A. was supported by a fellowship from Fondazione Internazionale di Ricerca in Medicina Sperimentale (FIRMS).
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
We thank Drs J. Iliffe, E. Ferrero, and S. Pellegrini for critically reading the manuscript.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal