Abstract
Macrophage activation syndrome (MAS) is a rare and potentially fatal disorder, thought to result from uncontrolled activation and proliferation of T cells and excessive activation of macrophages. The term MAS designates a clinicopathologic entity that occurs in different hemophagocytic syndromes (HSs). Primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is recognized to have an immunogenetic basis, but in the secondary HS (also referred to as secondary HLH), the cause is unknown. The pathogenesis of the accelerated disease phase typical of MAS remains incompletely understood. This report describes the immunohistochemical findings on liver tissues from 5 children, each of whom presented with MAS in the context of a different type of HS. The data provide direct evidence for the involvement of activated CD8+ lymphocytes through the production of interferon-γ and of macrophages through hemophagocytosis and production of interleukin 6 and tumor necrosis factor-α, and underscore the view that MAS in different HSs share a common effector pathway. (Blood. 2005;105:1648-1651)
Introduction
Macrophage activation syndrome (MAS) is a rare but often fatal condition, which characteristically presents acutely with nonremitting high fever, lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, pancytopenia, liver dysfunction, hypertriglyceridemia, and hyperferritinemia. Coagulopathy and central nervous system dysfunction often ensue, and less frequently, the lungs, kidneys, and cardiac tissues are involved. The diagnosis is usually suspected on clinical and biochemical grounds and is supported by the finding of well-differentiated macrophages phagocytosing hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow.1-3 The course of MAS is often dramatic, and fatality rates of 15% to 60%, despite prompt aggressive treatment, have been reported.1-3
MAS is a descriptive term to designate the clinicopathologic entity that can occur in a varied group of diseases, which are now classified among the histiocytic disorders as the hemophagocytic syndromes (HSs).4,5 Primary or familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (primary HLH or FHL) is regarded as the prototype of HS and has a genetic basis, resulting in the inability of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) or natural killer (NK) cells (or both) to efficiently kill target cells.6 Mutations in the perforin gene are found in 20% to 40% of patients with primary HLH.7 Secondary HS (also referred to as secondary HLH) designates MAS that complicates infections, malignancies, or inflammatory diseases such as juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA).2,3 Evidence is emerging indicating that in patients with systemiconset JIA, preexisting impaired NK cell function may predispose to MAS.6
The sequence of events leading to MAS remains incompletely understood, but it is thought to be essentially the same in different types of HS.3,6,8 Hypotheses on the pathogenesis of MAS are mainly derived from observations in primary HLH. In the acute phase, a lymphohistiocytic infiltrate is typically found, most commonly in the spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow.9 Furthermore, levels of circulating T-cell cytokines and monokines were found to be increased.10 These observations have led to the view that the inability of NK cells and CTLs to efficiently terminate an immune response, triggered, for example, by an infectious agent, leads to sustained activation of lymphocytes and macrophages. The result is widespread hemophagocytosis and overproduction of cytokines such as interferon γ (IFN-γ), tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), interleukin 1 (IL-1), and IL-6. Although this hypothesis is widely agreed on, it is largely based on indirect observations of excessive immune activation. We report on immunohistochemical findings on liver tissues of 5 children with MAS and provide direct evidence of massive infiltration by IFN-γ-producing CTLs and by macrophages, showing active hemophagocytosis and production of TNF-α and IL-6.
Study design
Five children presented with typical manifestations of MAS (Table 1). The diagnosis of MAS was established using the diagnostic guidelines developed and recently revised by the Histiocyte Society (Table 1).1,5 In patients B, C, and D, bone marrow aspirates failed to reveal infiltration by mononuclear phagocytes or hemophagocytosis. To substantiate the diagnosis, liver histopathology was investigated on biopsies (patients B-E) or on a postmortem sample (patient A). In patient E, liver biopsy was taken to examine the dysfunctional liver graft. Biopsy procedures were performed with cover of platelet transfusions and fresh-frozen plasma. This study was performed with the approval from the University Hospital Gasthuisberg Institutional Review Board. Tissues were obtained from patients after informed consent was provided according to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Characteristics of each of 5 patients with MAS*
. | A . | B . | C . | D . | E . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex/age | F/4 y | M/4 y | M/14 d | M/1 y | M/2 mo |
| Underlying disorder | Systemic JIA† | Leishmaniasis‡ | Probable primary HLH§ | Short bowel syndrome, chronic parenteral nutrition, EBV infection∥ | Neonatal adenoviral necrotizing hepatitis, HSV 1 hepatitis in transplant liver§ |
| Clinical findings | |||||
| Nonremitting high fever | + | + | + | + | + |
| Hepatosplenomegaly | + | + | + | + | + |
| Coagulopathy | + | − | + | + | + |
| Lymphadenopathy | − | + | − | − | − |
| Multiple organ failure | + | − | − | − | − |
| CNS dysfunction | + | − | − | + | + |
| Biochemistry | |||||
| Hemoglobin, g/L | 84 | 71 | 104 | 75 | 88 |
| Platelets, × 109/L | 46 | 91 | 16 | 20 | 36 |
| White cells (neutrophils), × 109/L | 4.9 (ND) | 2.1 (0.6) | 3.4 (1.3) | 3 (1.1) | 4.4 (2.7) |
| ESR, mm/h | 45 | 64 | ND | 39 | 39 |
| Ferritin, μg/L (15-300)¶ | ND | 645 | 11 619 | 59 240 | 7979 |
| AST/ALT, U/L (<38/40)¶ | 1721/315 | 50/25 | 1130/875 | 802/292 | 2468/2105 |
| Triglycerides, μM/L (<2034)¶ | ND | 2904 | 1141 | 3616 | 622 |
| Fibrinogen, μM/L (5.3-10.6)¶ | ND | 7.41 | 1.0 | 3.82 | 10.0 |
| Sodium, mM/L (135-145)¶ | 127 | 134 | 129 | 130 | 132 |
| Treatment | Resuscitation for overwhelming shock and DIC | High-dose CSTs, CsA, IVIG, amphotericin | High-dose CSTs, CsA, ATG | High-dose CSTs, CsA, OKT3 | CSTs, tacrolimus, azathioprine,# high-dose CSTs, acyclovir, basiliximab |
| Outcome | Rapidly fatal | Remission | Remission of MAS but fatal infection during work-up for allogeneic BMT | Remission | Ongoing MAS and fatal CMV pneumonia |
. | A . | B . | C . | D . | E . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex/age | F/4 y | M/4 y | M/14 d | M/1 y | M/2 mo |
| Underlying disorder | Systemic JIA† | Leishmaniasis‡ | Probable primary HLH§ | Short bowel syndrome, chronic parenteral nutrition, EBV infection∥ | Neonatal adenoviral necrotizing hepatitis, HSV 1 hepatitis in transplant liver§ |
| Clinical findings | |||||
| Nonremitting high fever | + | + | + | + | + |
| Hepatosplenomegaly | + | + | + | + | + |
| Coagulopathy | + | − | + | + | + |
| Lymphadenopathy | − | + | − | − | − |
| Multiple organ failure | + | − | − | − | − |
| CNS dysfunction | + | − | − | + | + |
| Biochemistry | |||||
| Hemoglobin, g/L | 84 | 71 | 104 | 75 | 88 |
| Platelets, × 109/L | 46 | 91 | 16 | 20 | 36 |
| White cells (neutrophils), × 109/L | 4.9 (ND) | 2.1 (0.6) | 3.4 (1.3) | 3 (1.1) | 4.4 (2.7) |
| ESR, mm/h | 45 | 64 | ND | 39 | 39 |
| Ferritin, μg/L (15-300)¶ | ND | 645 | 11 619 | 59 240 | 7979 |
| AST/ALT, U/L (<38/40)¶ | 1721/315 | 50/25 | 1130/875 | 802/292 | 2468/2105 |
| Triglycerides, μM/L (<2034)¶ | ND | 2904 | 1141 | 3616 | 622 |
| Fibrinogen, μM/L (5.3-10.6)¶ | ND | 7.41 | 1.0 | 3.82 | 10.0 |
| Sodium, mM/L (135-145)¶ | 127 | 134 | 129 | 130 | 132 |
| Treatment | Resuscitation for overwhelming shock and DIC | High-dose CSTs, CsA, IVIG, amphotericin | High-dose CSTs, CsA, ATG | High-dose CSTs, CsA, OKT3 | CSTs, tacrolimus, azathioprine,# high-dose CSTs, acyclovir, basiliximab |
| Outcome | Rapidly fatal | Remission | Remission of MAS but fatal infection during work-up for allogeneic BMT | Remission | Ongoing MAS and fatal CMV pneumonia |
EBV indicates Epstein-Barr virus; HSV 1, herpes simplex virus 1; CNS, central nervous system; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; AST/ALT, aspartate aminotransferase/alanine aminotransferase; +, finding was present; −, finding was absent; ND, not determined; DIC disseminated intravascular coagulation; CSTs, corticosteroid; CsA, cyclosporin A; IVIG, intravenous immunoglobulin; ATG, antithymocyte globulin; OKT3, anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody; BMT, bone marrow transplantation; CMV, cytomegalovirus.
Diagnostic guidelines developed by the Histiocyte Society. The diagnosis of HLH can be established either if a molecular diagnosis consistent with HLH is established, or, if 5 of the 8 diagnostic criteria for HLH are fulfilled: (1) fever; (2) splenomegaly; (3) cytopenias affecting 2 or more of 3 lineages in the peripheral blood (hemoglobin < 90 g/L, platelets < 100 × 109/L, neutrophils < 1.0 × 109/L); (4) hypertriglyceridemia (fasting ≥ 265 mg/dL) and/or hypofibrinogenemia (≤ 1.5 g/L); (5) hemophagocytosis in bone marrow, spleen, or lymph nodes; (6) low or absent NK cell activity; (7) ferritin ≥ 500 μg/L, (8) soluble CD25 ≥ 2400 U/mL. Of note, cerebromeningeal symptoms, hyponatremia, and disturbed liver function are consistent with the diagnosis.
The association with early phase systemic-onset JIA and the presence of severe coagulopathy was considered as supportive evidence for the diagnosis.3,11 The fulminant and fatal course precluded functional NK/CTL testing.
Diagnosed at relapse of MAS.
Family history negative. Fulminant disease course precluded NK/CTL functional testing and genetic investigations.
Family history and mutational analysis of perforin gene negative. Prolonged cytopenia and protracted treatment with cyclosporine precludes NK/CTL functional testing.
Reference ranges for normal values of biochemical parameters are indicated in parentheses.
Immunosuppressive treatment in the context of the recent liver transplantation would have interfered with functional NK/CTL testing.
Liver biopsy specimens were partially embedded in paraffin and partially snap frozen in isopentane, cooled in liquid nitrogen. Hematoxylineosin (HE) stain and immunohistochemical stainings were performed as described.12 Primary antibodies used were mouse monoclonal anti-CD4, anti-CD8, anti-HLA-DR, anti-TNF-α (Becton Dickinson Biosciences, Erembodegem, Belgium), and anti-CD68 antibodies (Dako, Glostrup, Denmark); rabbit polyclonal anti-IL-6 antibody (Genzyme, Zaventem, Belgium); mouse monoclonal anti-IFN-γ antibody (D9D10),13 kindly provided by I. Ronse, Rega Institute, Leuven, Belgium). Specimens were counterstained with Mayer hemalum.
Results and discussion
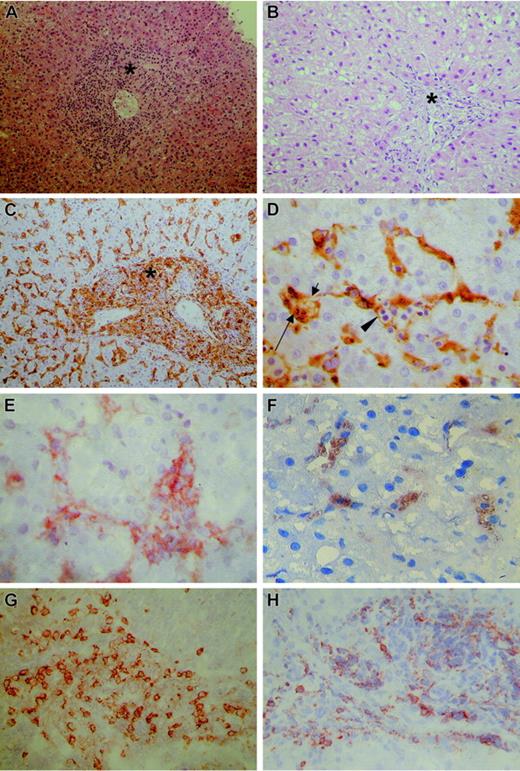
In patients A, B, C, and E, liver biopsy specimens were taken in the early stage of MAS. Histologic and immunohistochemical findings were similar in all 5 patients; Figure 1A and Figure 1C-H show representative images. HE staining revealed massive infiltration of portal tracts and sinusoids by mononuclear cells (Figure 1A). Immunohistochemical stainings showed numerous CD68+ macrophages (Figure 1C) and CD8+ lymphocytes (Figure 1G), expressing HLA-DR (not shown). Only few cells stained positive on CD4 staining (not shown). Lymphocytes expressed IFN-γ (Figure 1H) and macrophages expressed TNF-α (Figure 1E) and IL-6 (Figure 1F). Hemophagocytosis was recognizable on HE staining and was unequivocally detected in the cytoplasm of CD68+ macrophages (Figure 1D).
Routine and immunohistochemical stainings of liver biopsies. (A) Hematoxylin-eosin stain shows massive infiltration of portal tract (asterisk) and sinusoids by mononuclear cells. (B) Hematoxylin-eosin stain of specimen from patient D reveals a blank appearance of the portal tract. The numerous macrophages cannot be recognized. (C) CD68 stain shows numerous macrophages as large, irregularly shaped CD68+ cells, localized both in the portal tract (asterisk) and sinusoids. (D) Detail of CD68 stain shown in panel C shows active phagocytosis by CD68+ macrophages of lymphocytes (arrowhead), erythrocytes (short arrow), and polynuclear cells (long arrow). (E) TNF-α stain shows TNF-α production by macrophages, identified as large irregularly shaped cells in portal tracts and sinusoids. (F) IL-6 stain shows IL-6 production by macrophages, identified as large irregularly shaped cells in portal tracts and sinusoids. (G) CD8 stain shows numerous CD8+ lymphocytes as small, round CD8+ cells, with a small rim of cytoplasm. (H) IFN-γ stain shows IFN-γ production by lymphocytes, identified as small, round cells with a small rim of cytoplasm. The microscope was a Leitz Laborlux 5 (Wetzlar, Germany); objective lenses × 2.5, × 10, × 40, and × 100. The digital camera was a Nikon Coolpix 950, and image processing was done with Adobe Photoshop CS.
Routine and immunohistochemical stainings of liver biopsies. (A) Hematoxylin-eosin stain shows massive infiltration of portal tract (asterisk) and sinusoids by mononuclear cells. (B) Hematoxylin-eosin stain of specimen from patient D reveals a blank appearance of the portal tract. The numerous macrophages cannot be recognized. (C) CD68 stain shows numerous macrophages as large, irregularly shaped CD68+ cells, localized both in the portal tract (asterisk) and sinusoids. (D) Detail of CD68 stain shown in panel C shows active phagocytosis by CD68+ macrophages of lymphocytes (arrowhead), erythrocytes (short arrow), and polynuclear cells (long arrow). (E) TNF-α stain shows TNF-α production by macrophages, identified as large irregularly shaped cells in portal tracts and sinusoids. (F) IL-6 stain shows IL-6 production by macrophages, identified as large irregularly shaped cells in portal tracts and sinusoids. (G) CD8 stain shows numerous CD8+ lymphocytes as small, round CD8+ cells, with a small rim of cytoplasm. (H) IFN-γ stain shows IFN-γ production by lymphocytes, identified as small, round cells with a small rim of cytoplasm. The microscope was a Leitz Laborlux 5 (Wetzlar, Germany); objective lenses × 2.5, × 10, × 40, and × 100. The digital camera was a Nikon Coolpix 950, and image processing was done with Adobe Photoshop CS.
Patient D had experienced several febrile episodes before liver biopsy was performed. Although HE stain failed to reveal a massive mononuclear infiltrate (Figure 1B), the CD68 stain revealed the presence of numerous macrophages, showing active hemophagocytosis and expression of TNF-α and IL-6 (Figure 1C-F).
Previous studies have addressed the phenotype of the infiltrating cells in MAS and showed histiocytes to be of the monocyte/macrophage lineage, and the lymphocytic infiltrate to be composed mainly of T cells.14,15 Henter et al studied 9 children with primary HLH and found elevated serum levels of IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-6, and soluble CD8.10 Others also reported on the occurrence of high levels of IL-1, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and soluble IL-2 receptor (IL-2R) in serum/plasma of patients with various HSs.16-18 Akashi et al found that CD2+ circulating lymphocytes from patients with primary HLH spontaneously secreted IFN-γ in vitro, and monocytes TNF-α and IL-6.18 Our report directly substantiates the presumed immunopathogenesis of MAS by documenting in situ expression of IFN-γ by activated CD8+ lymphocytes, and of IL-6 and TNF-α by hemophagocytosing macrophages, on liver tissues of patients with MAS. Our findings are in agreement with the recent report by Jordan et al, who used perforin-deficient mice to show that CD8+ lymphocytes and IFN-γ play a pivotal role in lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-induced HLH.19
Although all patients suffered from a different type of HS, their liver biopsy specimens showed a strikingly similar pattern of infiltrating cell types and cytokine expression. This is consistent with the view, now shared by rheumatologists and hematologists, that MAS has a unique pathogenesis, irrespective of cause or eliciting factors.3,4,8 In patient D, liver biopsy was performed in a later, persistently active, stage of MAS; the cellular infiltrate consisted predominantly of hemophagocytosing macrophages, whereas lymphocytes were present in smaller numbers. Of interest, it was only after the addition of anti-CD3 to the treatment that MAS remitted. Likewise, treatment with basiliximab resulted in transient improvement in patient E. These observations underscore the primary role of activated T cells in the pathogenesis of MAS.
Reportedly, the pathologic picture of liver tissue from patients with HS is consistent with chronic persistent hepatitis.20 Ost et al found a chronic hepatitis-like picture in postmortem specimens from 22 of 27 primary HLH patients.21 Favara et al reviewed the liver histopathology of 32 children with various HS.22 Portal infiltrates were seen, with numerous T lymphocytes and few histiocytes. Massive infiltration by activated macrophages, as seen in our series, was not reported on, but Kupffer cells appeared enlarged and showed, in about half the specimens, hemophagocytosis. In our experience, macrophage-specific stainings were not only necessary to demonstrate the presence of macrophages/Kupffer cells, they also facilitated the detection of hemophagocytosis.
The frequent occurrence of coagulopathy in acute MAS poses a considerable risk to performing biopsies of target organs other than the bone marrow, and the authors restrain from proposing liver biopsy as a routine diagnostic investigation for MAS. However, in this particular group of patients, the necessity of obtaining conclusive evidence of MAS and of excluding other pathology, justified the risk of performing a liver biopsy.
In conclusion, this study on 5 patients with different types of HS is the first to deliver direct evidence on the involvement of activated, IFN-γ-producing CD8+ lymphocytes, and of TNF-α- and IL-6-producing macrophages, in the pathogenesis of MAS. Our findings support the prevailing hypothesis on the immunopathogenesis of this syndrome and underscore the view that MAS in different types of HS share a common inflammatory effector pathway.
Prepublished online as Blood First Edition Paper, October 5, 2004; DOI 10.1182/blood-2004-08-2997.
A.D.B. and P.M. are postdoctoral research fellows of the FWO, Belgium.
An Inside Blood analysis of this article appears in the front of this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
We thank our colleague pediatricians for referring these patients and for the excellent medical care they have provided during the treatment of these children: Rita Van Damme-Lombaerts, Ilse Hoffman, Hugo Devlieger, Gunnar Naulaers, Kristina Casteels, and Jean Herman from the University Hospital Gasthuisberg, Leuven, Belgium, and Hilde Dotremont from the Franciscusziekenhuis, Roosendaal, The Netherlands. We thank Ilse Hoffman for her expertise in performing the liver biopsies. Finally, we thank Alfons Billiau, from the Laboratory of Immunobiology, Rega Institute for Medical Research, Leuven, Belgium, for critical revision of this manuscript.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal