Abstract
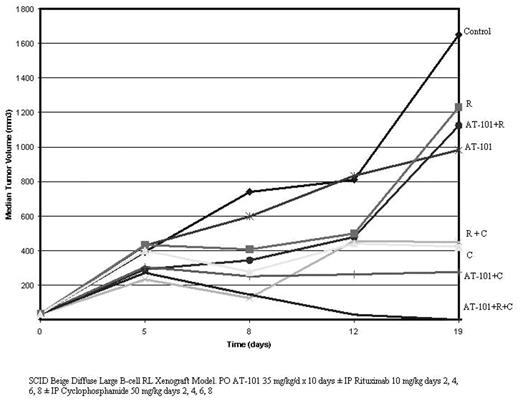
Over-expression of anti-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family, including Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL, have been observed in more that 80% of B-cell Lymphomas. AT-101 has recently been found to be a potent small molecule inhibitor of Bcl-XL and Bcl-2. We investigated the toxicity and antitumor activity of oral AT-101 in SCID beige mice following subcutaneous injection with 1 x 107 RL-DLBCL cells. In the first experiment we explored four daily (25, 50, 75, 100 mg/kg) and three weekly (200, 240, 280 mg/kg) dose levels of AT-101 in cohorts of 5 mice. The 25 mg/kg/day for 4 weeks schedule exhibited the safest profile with some tumor growth delay compared to the control. Higher daily doses of 50, 75 and 100 mg/kg/day were associated with significant weight lost (i.e. > 10% of the initial weight) after 14, 10 and 7 days respectively, with death of all animals in these dose groups by day 23, 21 and 16 respectively. The weekly schedules exhibited later onset toxicity with the 240 mg/kg cohort exhibiting the best reduction in tumor growth compared to control (p=0.063). In a second single agent experiment additional schedules were explored to try to improve the toxicity profile. These schedules included 100, 120, 140 mg/kg on days 1, 4, 8, 11 followed by 1 week; a 35 and 50 mg/kg/day for 2 weeks out of 4; a 100 mg/kg for 3 days/week for 3 weeks out of 4; and a 240 and 280 mg/kg/week for 3 weeks out of 4. Significant weight loss was noted at 5–7 days in the dose groups at 100 mg/kg daily, 120–140 and 280 mg/kg. Overall, tumor volume assessment showed a statistically significant advantage for the 35 mg/kg daily schedule compared to control (p=0.008), with this dose and schedule being the most effective and least toxic. In terms of dose intensity, it’s interesting to note that 35 mg/kg/day for two weeks delivered a total dose of 490 mg/kg. Combination experiments with cyclophosphamide (50 mg/kg) and rituximab (10 mg/mg) i.p. on days 2, 4, 6, 8 demonstrated marked improvement in favor of the triplet combination (see Fig. below). AT-101 (35 mg/kg) was administered p.o. from day 0 to day 9 These data suggest that targeting Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL with AT-101 may help chemosensitize lymphoma to conventional therapies and improve therapeutic outcomes.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal