Abstract
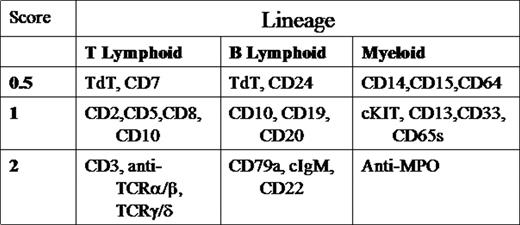
Current classification of childhood leukemia relies on morphologic, immunophenotypic, and molecular characteristics. aBL is rare and poorly understood. We retrospectively evaluated 7 patients diagnosed with aBL according to European Group for Immunological Classification of Leukemias (EGIL) criteria(2 or more lineages with a score greater than 2).
Among 269 leukemia patients diagnosed in 2001–2004, 7 (2.6%) were classified as having aBL. Clinical characteristics/course and laboratory data are listed below in Tables1&2.
CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS & COURSE
| PATIENT . | AGE . | SEX . | RACE . | INITIAL WBC . | TREATMENT . | COURSE . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12 | F | AA | 5,600 | CCG1961-> CCG2891, HDARAC, HSCT | IND. FAILURE; R1:CNS,BM R2:BM R3:CNS,BM DOD, 24M |
| 2 | 17 | F | C | 81,600 | CCG2891 | R1:CNS,BM DOD, 10M |
| 3 | 2 | M | C | 40,000 | CCG1961 | RER; CR1, 16M |
| 4 | 2 | M | H | 5,630 | CCG1991-> CCG1961, HSCT | SER; CR1, 14M |
| 5 | 6 | F | H | 38,000 | CCG1961 | RER; CR1, 12M |
| 6 | 16 | M | AA | 150,000 | CCG1961-> AAML03P1 | IND. FAILURE; R1:BM DOD, 9M |
| 7 | 11 | M | C | 77,100 | AAML03P1, HSCT | RER; CR1, 7M |
| PATIENT . | AGE . | SEX . | RACE . | INITIAL WBC . | TREATMENT . | COURSE . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12 | F | AA | 5,600 | CCG1961-> CCG2891, HDARAC, HSCT | IND. FAILURE; R1:CNS,BM R2:BM R3:CNS,BM DOD, 24M |
| 2 | 17 | F | C | 81,600 | CCG2891 | R1:CNS,BM DOD, 10M |
| 3 | 2 | M | C | 40,000 | CCG1961 | RER; CR1, 16M |
| 4 | 2 | M | H | 5,630 | CCG1991-> CCG1961, HSCT | SER; CR1, 14M |
| 5 | 6 | F | H | 38,000 | CCG1961 | RER; CR1, 12M |
| 6 | 16 | M | AA | 150,000 | CCG1961-> AAML03P1 | IND. FAILURE; R1:BM DOD, 9M |
| 7 | 11 | M | C | 77,100 | AAML03P1, HSCT | RER; CR1, 7M |
MORPHOLOGY, IMMUNOPHENOTYPE & CYTOGENETICS
| PATIENT . | FAB MORPHOLOGY . | FLOW CYTOMETRY . | EGIL SCORE(T/B/M) . | CYTOGENETICS/FISH . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| * =Peripheral Blood | ||||
| 1* | L1, M5 | CD3, CD7, pCD5, CD33,MPO | 3.5/0/3 | 6,XX,add(1)(p22);t(3;12)(p24;p13),del(6)(q21q22),del(8)(p21),-9,del(13)(q13q14), +22 |
| 2* | L1, M2 | P1: CD19, CD22, CD33, Tdt P2: CD2,CD14,CD15, CD33, MPO | 2/3.5/4 | 46,XX,der(8)t(8;?;17)(q11.2;?;q21),der(9)t(8;9)(q21.2;p12),del(15)q21), der(17)t(15;?;17)(q21;?;q11.2) |
| 3 | L2 | P1: CD33, CD34 P2: CD13, CD15, CD10, CD19, CD22 | 0/4/2.5 | 46, XY, del12p-/TEL deletion |
| 4 | L1 | CD19,CD22, CD13, CD15, CD33 | 0/3/2.5 | 46, XY |
| 5 | L1, M5 | CD19, pCD20, CD22, CD13, CD15, pCD33 | 3.5/0/3.5 | 46, XY, del(5)(q15q33), dic(7;9)(p11.2;p12),inv(9)c,t(10,11)(p13;q21) |
| 6 | L2 | cCD3, pCD5, CD7, CD13, CD15, CD33,pCD117 | 0/4/3.5 | 46, XX/Trisomy 10 |
| 7* | L1, M5 | CD2,CD3,CD7, TdT, pCD22,CD13, CD15, pMPO, CD117 | 4/1/4.5 | 46, XY |
| PATIENT . | FAB MORPHOLOGY . | FLOW CYTOMETRY . | EGIL SCORE(T/B/M) . | CYTOGENETICS/FISH . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| * =Peripheral Blood | ||||
| 1* | L1, M5 | CD3, CD7, pCD5, CD33,MPO | 3.5/0/3 | 6,XX,add(1)(p22);t(3;12)(p24;p13),del(6)(q21q22),del(8)(p21),-9,del(13)(q13q14), +22 |
| 2* | L1, M2 | P1: CD19, CD22, CD33, Tdt P2: CD2,CD14,CD15, CD33, MPO | 2/3.5/4 | 46,XX,der(8)t(8;?;17)(q11.2;?;q21),der(9)t(8;9)(q21.2;p12),del(15)q21), der(17)t(15;?;17)(q21;?;q11.2) |
| 3 | L2 | P1: CD33, CD34 P2: CD13, CD15, CD10, CD19, CD22 | 0/4/2.5 | 46, XY, del12p-/TEL deletion |
| 4 | L1 | CD19,CD22, CD13, CD15, CD33 | 0/3/2.5 | 46, XY |
| 5 | L1, M5 | CD19, pCD20, CD22, CD13, CD15, pCD33 | 3.5/0/3.5 | 46, XY, del(5)(q15q33), dic(7;9)(p11.2;p12),inv(9)c,t(10,11)(p13;q21) |
| 6 | L2 | cCD3, pCD5, CD7, CD13, CD15, CD33,pCD117 | 0/4/3.5 | 46, XX/Trisomy 10 |
| 7* | L1, M5 | CD2,CD3,CD7, TdT, pCD22,CD13, CD15, pMPO, CD117 | 4/1/4.5 | 46, XY |
5 patients had abnormal karyotypes and/or FISH studies; none had MLL rearrangements or t(9;22). Induction treatment consisted of AML-type therapy (CCG 2891 /COG AAML03P1) in 2 patients who achieved CR by day 28. Two patients received ALL-type therapy (CCG 1961) and entered CR by Day 28. Three patients required dose intensification due to induction failure: 2 switched from ALL to AML-type therapy. Post induction chemotherapy was given in 4 cases; allogeneic HSCT in 3 cases (2 in CR1; 1 in 2nd relapse). 2/4 and 2/3, respectively, remain alive in 1st CR after chemotherapy or HSCT. All 3 deaths were from relapse of aBL within 2 yrs from diagnosis & occured in adolescents with complex karyotypes. In our experience, pediatric aBL represents a high risk population, especially in adolescents. Intensive induction chemotherapy is necessary in the majority of cases to achieve CR, although it is unclear whether ALL or AML-type therapy is superior. MLL & t(9;22) may not be as common in pediatric aBL as previously described. Collaborative trials and biologic studies are clearly needed for better understanding and outcomes.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal