Abstract
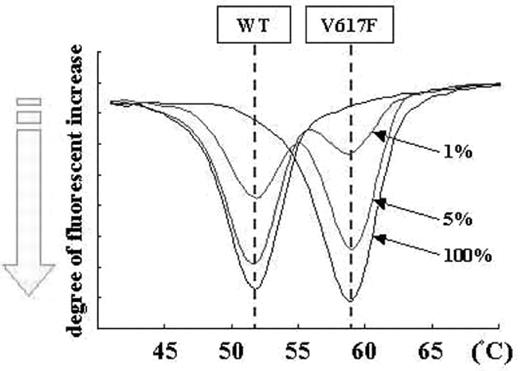
The JAK2 V617F substitution mutation (JAK2V617F) is one of the genetic hallmarks of chronic myeloproliferative diseases (CMPDs), such as polycythemia vera (PV), essential thrombocythemia (ET), or chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis (CIMF). Accurate and rapid detection of this mutation is essential for diagnosing and treating CMPDs today. We have developed a novel, rapid, sensitive and fully-automated single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) detection system, termed ARKRAY SNP Detection System (ASDS), and used it to detect JAK2V617F in patients with CMPDs. With ASDS, diagnosis requires only 100ml of whole blood (or DNA), and the system automatically performs DNA extraction and PCR. The detection of both wild type and mutant jak2 alleles from PCR amplicons was measured by the increase in fluorescence produced by the dissociation of a JAK2V617F-specific guanine-quenching probe, and was completed within 75 minutes. In dilution assays of HEL cells (a JAK2V617F-positive leukemia cell line) using MYL cells (a chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)-derived cell line with wild type JAK2), the system reliably quantified the mutation in a cell population containing as few as 1.0% mutant cells (Figure). We tested 44 samples from CMPDs patients using ASDS and direct sequencing (DS) (13 PV, 23 ET, 3 CIMF, 1 chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMMoL), 1 chronic neutrophilic leukemia (CNL), 3 unclassifiable CMPD (uCMPD)), which included samples from 3 post-allogenic bone marrow transplantation (BMT) patients with CIMF or uCMPD. Using ASDS, we detected JAK2V617F in 12/13 PV, 13/23 ET, 0/1 CIMF without BMT, 1/1 CMMoL, 0/1 CNL and 1/3 uCMPD. Overall, these results were comparable to previous results using relatively sensitive detection strategies, such as allele-specific PCR (AS-PCR). One of the 3 post-BMT CIMF samples was positive for JAK2V617F, which indicated that there were residual disease clones after BMT. ASDS detected JAK2V617F in one PV and eight ET patients, while DS failed to detect the mutation in these same samples, which clearly indicated that ASDS has a higher sensitivity than DS. JAK2V617F was absent in all samples from secondary erythrocytemia and healthy volunteers. Collectively, these results demonstrate that ASDS is a powerful and convenient tool for detecting JAK2V617F. With its associated high sensitivity, convenience and rapidity, this system will enable “Point-of-care” testing in clinical laboratories and “Patient-oriented” therapy for CMPDs. ASDS could also be applied to the detection of other point mutations relevant to cancer treatment, such as mutations in the BCR-ABL kinase domain that are associated with CML.
Author notes
Disclosure: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal