Abstract
Acute myeloid leukemia expressing mutated NPM1 gene and cytoplasmic nucleophosmin (NPMc+ AML) [
Falini B et al, NEJM 2005;352:254–266
] is a new entity of WHO classification that shows distinctive biological and clinical features, including a unique molecular signature characterized by downregulation of CD34 and upregulation of most HOX genes [Falini B et al, Blood 2007;109:874–885
]. Involvement of HOX genes in the maintenance of the stem-cell phenotype strongly suggest that AML with mutated NPM1 originates from a multipotent hematopoietic progenitor (HSC). This view is also supported by immunohistological findings showing that AML with mutated NPM1 frequently displays multilineage involvement [Pasqualucci L et al, Blood 2006;108:4146–4155
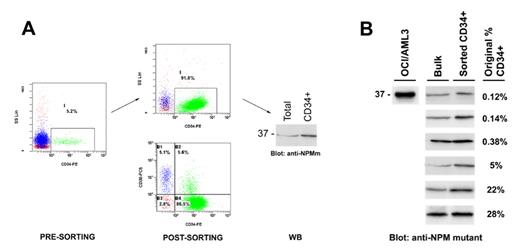
]. On the other hand, the frequent negativity of NPMc+ AML for the HSC-associated antigen CD34 raises the question of whether the mutation event occurs in a CD34-negative HSC (these cells have been identified in mice) or whether a minimal pool of CD34-positive NPM1-mutated leukemic cells does exist. Currently, the hierarchical level of stem cell involvement in NPMc+ AML is unknown. To address this issue, we purified CD34+ cells from NPMc+ AML patients and detected NPM1 mutant protein in the sorted population by Western blot with anti-NPM mutant specific antibodies [Martelli MP et al, Leukemia 2008] (Figure 1A). We investigated 6 NPMc+ AML patients presenting at diagnosis with 0.12%, 0.14%, 0.38%, 5%, 22%, and 28% of CD34+ cells in the peripheral blood. In all cases, CD34+ fractions (purity >90%) harboured NPM1 mutant protein, indicating they belong to the leukemic clone (Figure 1B). The percentage of most undifferentiated CD34+/CD38− cells in the CD34+ fractions ranged from 5 to 97%. Notably, in at least one case, all CD34+ NPM1-mutated leukemic cells were CD38−negative. Moreover in all cases, CD34+ NPM1-mutated leukemic cells appeared to express CD123 (IL-3 receptor), considered a marker of the leukemic stem cell and target of potential therapy. Double staining of bone marrow biopsies with anti-CD34 and anti-NPM antibodies revealed that the rare CD34+ cells expressed NPM1 aberrantly in the cytoplasm. Inoculation of CD34+ NPM1-mutated AML cells into sublethally irradiated NOD/SCID mice resulted into leukemia engrafment in various body sites, especially bone marrow, spleen, lung and liver. Preliminary results showed that CD34+ leukemic cells reacquired the same leukemic phenotype as the original patient’s, including CD34-negativity of the leukemic bulk in spite of any lack of differentiation. This finding suggests that NPM1 mutant protein may be involved in downregulation of CD34 antigen, while keeping a gene expression profile typical of the hematopoietic stem cell. These findings suggest the CD34+ fraction contains the SCID-leukemia initiating cells (SL-IC) and point to CD34+/CD38− HSC as the cell of origin of AML with mutated NPM1.Disclosures: Falini:Xenomics: Patents & Royalties.
Author notes
Corresponding author
2008, The American Society of Hematology
2008

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal