Abstract
Abstract 420
Primary Mediastinal Large B cell lymphoma (PMBL) is a distinct subtype of diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) that is more common in women and presents at a similar age as classical Hodgkin lymphoma (HL); and in fact gene expression profiling suggests it is more similar to HL (Blood 102: 3871–3879, 2003) than DLBCL. Patients (pts) typically present with bulky mediastinal disease and combined modality therapy (CMT) has been the mainstay of treatment; however given the risk of secondary breast cancer and coronary artery disease associated with the 36–40Gy radiation therapy to the mediastinum, programs that use chemotherapy alone are desirable provided that the favorable progression-free (PFS) and overall survival (OS) rates can be maintained.
We evaluated our dose-dense R-CHOP/ICE consolidation chemotherapy program (MSKCC protocol 01–142, J Clin Oncology 28:1896-1903, 2010) for pts with PMBL. The initial 28 pts were treated on study and the subsequent 26 were treated as per protocol. No radiation therapy was permitted. All pts underwent CT and FDG-PET imaging as well as bone marrow evaluation. Therapy was administered every 2 weeks. Induction chemotherapy: four cycles of accelerated R-CHOP (rituximab 375 mg/m2; cyclophosphamide 1000 mg/m2; doxorubicin 50 mg/m2 vincristine 1.4 mg/m2 (uncapped) IVP; and prednisone 100 mg/day orally for 5 days); growth factor support was required. Consolidation chemotherapy: three cycles of ICE+/−Rituximab (J Clin Oncology 12: 3776–3785, 1999).
Fifty-four pts receive treatment. Median age was 34 (range 19–59); 30 were female (56%). An elevated LDH, Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS) <80 and stage IV disease was seen in 87%, 24% and 52% respectively. Extranodal disease (ENS) was present in 74% of pts; 21 (39%) pts had lung involvement. Bulky disease defined as a mediastinal mass of at least 10 cm. was present in 36 pts (67%) of which 16 (30%) had clinical evidence of superior vena cava obstruction at presentation; the median SUV uptake in the mediastinum on the FDG-PET scan was 19. No patient had bone marrow or CNS involvement at diagnosis. Positive Immunohistochemistry markers were as follows: CD10 (6.7%), BCL6 (72.7%), BCL2 (51.2%) and MUM1 (50%). The median Ki-67 [MIB-1] expression was 60%, of which 26.7 % was ≥80%.
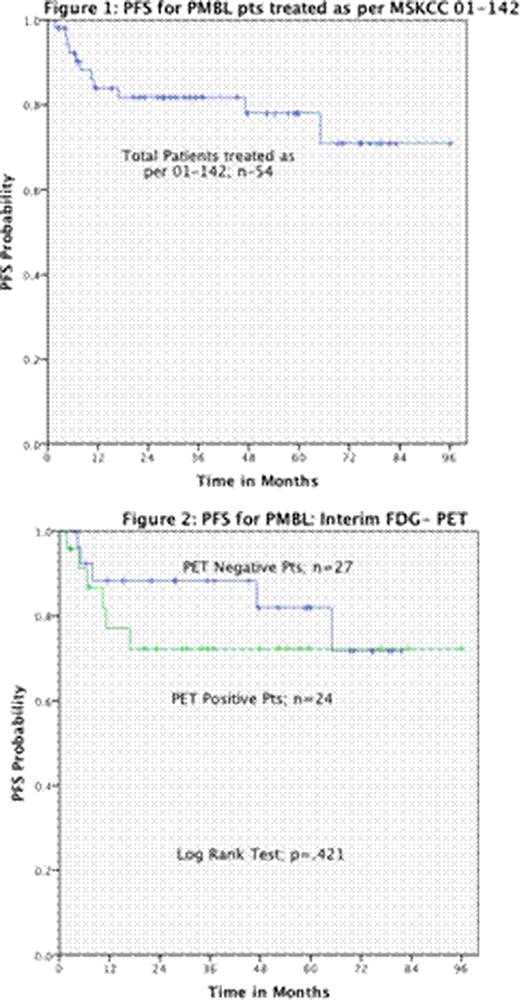
At a median followup for surviving pts of 3 years, the Kaplan-Meier estimates of the proportion of patients alive and progression-free are 88% and 78% respectively. Eleven pts failed therapy. Five are now progression-free after a salvage autotransplant that included radiation therapy to the mediastinum. Six pts have died; one from transplant-related mortality, one from secondary AML and 4 from PMBL, two of which had CNS disease at relapse despite intrathecal prophylaxis. None of the standard clinical or immunohistochemical risk factors predicted for PFS including: KPS (p=.79), LDH (p=.92), Stage (p=.25), ENS (p=.36), IPI (p=.18) or bulky disease (p=.42), Ki-67 [MIB-1] expression ≥80 (.34). An interim FDG-PET scan was performed on 51/54 pts; 24 (47%) of these scans were abnormal; however, this did not predict for PFS (p=.42). We also evaluated the change in SUV between the initial and interim scan with a positive cutoff of >66% (J Nucl Med 48:1626-1632, 2007) as being favorable; this also did not predict outcome (p=.21).
This is the largest reported series of pts with PMBL treated with a uniform chemotherapy-only strategy. The MSKCC dose-dense R-CHOP/ICE program is highly effective in these pts, it avoids radiotherapy, and importantly 50% of pts who fail can be salvaged with a radiation-based transplant. Based upon these results an interim FDG-PET scan is not warranted in pts with PMBL.
GSK: Consultancy; CTI:.

This icon denotes an abstract that is clinically relevant.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal