Abstract
Abstract 667
Targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy efficiently induces rapid hematologic and cytogenetic responses in most CML patients. In vitro studies have suggested that CML stem cells are resistant to TKIs and therefore the treatment may need to be life-long. However, the in vivo effects of TKIs on the leukemic stem cell pool in a patient population have not been prospectively assessed. In addition, the biological impact and prognostic value of leukemic stem cell burden at diagnosis is unknown.
To analyze the proportions of Ph+ cells in the stem cell compartment in newly diagnosed CP CML patients at diagnosis, and correlate the initial leukemic stem cell burden to biological variables and hematological toxicity during first 3 months of TKI therapy.
42 newly diagnosed CP CML patients within the Nordic countries were randomized to receive either dasatinib 100 mg (n=21) or imatinib 400 mg (n=21) once daily. Stem cell assays were performed at diagnosis and at 1, 3, and 6 months from start of TKI therapy. After pre-selection of CD34+ cells from large volume bone marrow (BM) aspirates with paramagnetic beads, the CD34+ cells were fractionated into CD38 positive and negative pools using a sorting flow cytometer. The proportion of Ph+ cells in the stem cell fractions was assayed by counting 1000 cells with interphase FISH for BCR-ABL1.
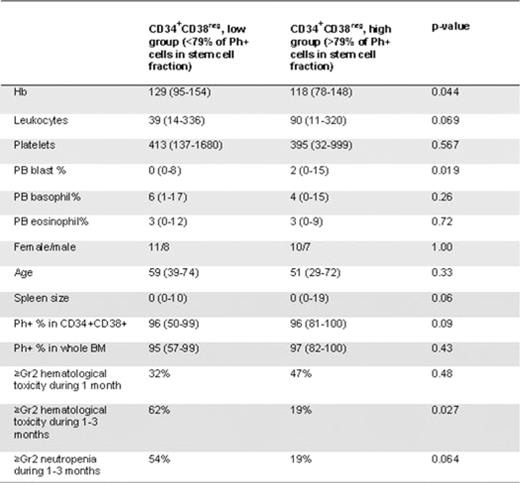
Measurement of Ph+ stem cells was feasible in most patients at diagnosis and results from 36 evaluable patients will be presented. The median volume of BM aspirate was 28, 37, 40 and 36 ml at diagnosis, 1, 3, and 6 months after therapy start, respectively. The median yield of BM mononuclear cells was 1000, 110, 93 and 79 ×106, respectively. The median proportion of Ph+ cells was significantly lower in the more primitive CD34+CD38neg fraction when compared to the CD34+CD38+ fraction or to unfractionated BM (79%, range 0.6–100%; 96%, 50–100%; and 96%, 57–100%, respectively, p=0.0001). The proportion of Ph+ cells in the CD34+CD38neg fraction at diagnosis correlated with high leukocyte count (r=0.59, p<0.001), enlarged spleen size (r=0.46, p=0.005), low hemoglobin concentration (r=-0.46, p=0.006) and high blast percentage in peripheral blood (r=0.62, p<0.001). No correlation was found to age, gender, platelets, eosinophils or basophils. The proportion of Ph+ cells in the CD34+CD38+ fraction correlated only to the leukocyte count (r=0.33, p=0.049). Patients with high Sokal risk had a significantly higher proportion of Ph+ CD34+CD38neg stem cells at diagnosis as compared to low and intermediate risk patients (94% vs. 75%, respectively, p=0.036). Patients who had a higher leukemic stem cell burden (more than the median value of 79% of Ph+ CD34+CD38neg cells, Table 1) at diagnosis experienced more grade ≥2 hematological toxicity (neutropenia in particular) during first 3 months of TKI therapy as compared to patients with a lower (<79%) stem cell burden (62% vs. 19%, respectively, p=0.027).
The proportion of Ph+ stem cells at the time of diagnosis varied from 1 to 100% between individual CML patients. It was correlated with hemoglobin concentration, leukocyte count, blast percentage and spleen size at diagnosis and with hematological toxicity during early course of treatment, mirroring paucity of healthy hematopoietic stem cell reservoir. The size of the leukemic stem cell pool at diagnosis may be a powerful prognostic marker and a major biological determinant for the high Sokal risk group. The effect of TKI therapy on the malignant stem cell pool size and correlation to therapy responses will be evaluated when all patients have reached the primary study endpoint of 6 months.
Mustjoki:BMS, Novartis: Honoraria. Richter:BMS, Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria. Simonsson:BMS, Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Porkka:BMS, Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Hjorth-Hansen:BMS, Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal