Abstract
Abstract 750
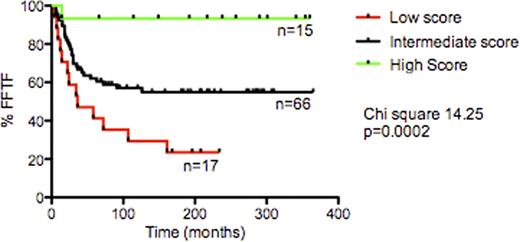
The non-malignant immune infiltrate comprises the bulk of pathologic tissue in classical Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL). This microenvironment has the potential to induce both malignant cell suppression and support. Increased macrophage infiltration assessed by CD68 expression has been shown to confer adverse prognostic significance (Steidl et al. N Engl J Med, 2010; 362:875-85) while increased FOXP3 expressing T cells are beneficial in this disease (Tzankov et al. Haematologica, 2008; 93: 193–200). However no histological score routinely leads to modification of treatment. Assessing outcomes by the parameters of overall survival (OS), disease specific survival (DSS) and freedom from first line treatment failure (FFTF) at 5 years in a cohort of patients treated at St Bartholomew's Hospital (Barts), London we developed a prognostic score based upon expression of both FOXP3 and CD68 in the CHL microenvironment which defined poor and good risk groups in both early (Stages I and IIA) and advanced stage disease, including a 'poor risk' early stage group with 25% FFTF and a ‘good risk' advanced stage group with 90% FFTF. Immunohistochemical analysis was performed on tissue microarrays (TMAs) from previously untreated patients' diagnostic lymph node biopsies in whom clinical outcome was available. From all 1056 adult patients with HL diagnosed at Barts between 1972 and 2005, high quality formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue was available for 122 (12%), with characteristics representative of the whole group. Median age of the 122 patients was 30 (range 18–80) years, 35% female, 71% advanced stage with median follow up 16.5 (range 2–40) years. Triplicate cores were made from areas of high cellularity, containing malignant cells and avoiding fibrotic, acellular portions, arrayed onto glass slides and stained immunohistochemically for FOXP3 or CD68. Absolute and proportional numbers of FOXP3+ nuclei and CD68+ cell bodies were counted across all intact cores using an automated image analysis system (Ariol), confirmed by expert histopathologists, and means calculated and corrected to a single high powered field (hpf). Recursive partitioning was used to generate optimal cutoff values discriminating prognostic groups and comparisons performed by the chi-square test. Using cutoffs of <5%, 5–15% and >15% to define low, intermediate and high CD68 density, 3 prognostic groups were defined, the favourable group having the lowest CD68+ density. OS for low, intermediate and high groups were 89%, 80% and 65% respectively (p=0.02), with FFTF 82%, 64% and 29% (p=0.001). Prognostic significance was maintained in subgroups presenting with advanced stage (FFTF 73%, 63% and 33%, p=0.03), as well as early stage disease (FFTF 92%, 70% and 20%, p=0.01). Using cutoffs of <12.5, 12.5–50 and >50 nuclei/hpf to define low, intermediate and high FOXP3+ cell density, 3 prognostic groups were defined, the favourable group having the highest FOXP3+ density. OS for low, intermediate and high groups were 68%, 80% and 94% respectively (p=0.006), with FFTF 50%, 62%, and 84% (p=0.002). Prognostic significance was maintained for both advanced (FFTF: 48%, 60% and 72%, p=0.04) and early stage disease (FFTF: 57%, 67% and 100%, p=0.04). A combined ‘FOXP3/CD68 score' derived from the patient's prognostic group for both markers, for which suitable cores were available on 98 patients, further improved the predictive value of each individually (See Figure). In this model, favourable, intermediate and unfavourable groups had 5 year FFTF of 93%, 62% and 47% (p=0.0002), DSS 93%, 82% and 63% (p=0.03) and OS 93%, 82% and 59% (p=0.002). The score retained prognostic significance for 5 year FFTF and OS in the subgroup of patients presenting with advanced (FFTF: 90%, 59% and 46%, p=0.008; OS: 90%, 80% and 54%, p=0.004) as well as early stage disease (FFTF: 100%, 71% and 25%, p=0.005; OS: 100%, 82% and 75%, trend only, p=ns). We conclude that FOXP3 and CD68 are important independent factors, which in combination have considerable predictive power and will now be validated prospectively.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This icon denotes an abstract that is clinically relevant.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal