Abstract
Abstract LBA-2
5q- myelodysplastic syndrome is a rare, acquired macrocytic anemia with a female predominance. The bone marrow is characterized by a paucity of erythroid precursors with relatively normal leukocyte and platelet counts and no excess blasts. The mean age at diagnosis is approximately 70 years. The phenotype of 5q deletion has been shown to result from haploinsufficiency of the RPS14 gene. Historically red blood cell transfusions have been the primary treatment; however lenalidomide has recently been effective in ameliorating the anemia with a response rate of 67%. DBA is a rare heritable red cell aplasia which usually presents in infancy. It too is characterized by a bone marrow deficient in erythroid precursors. Mutations or deletions in eleven ribosomal protein (RP) genes, resulting in protein haploinsufficiency, have been reported in 50–60% of patients. To date RPS14 mutations have not been identified in DBA patients. Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH) has been used to identify large deletions in patients with DBA, but a more sensitive approach was hypothesized to identify additional deletions.
To address the question of whether chromosomal deletions could be the underlying defect in patients with DBA who did not have mutations in the known RP genes, Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) genotyping array hybridization was utilized.
Seventy-five patient samples from the DBA Registry (DBAR) underwent resequencing of 80 RP genes. Approximately 40% of the patients had no identifiable mutation. High resolution SNP array genotyping analysis was done on 23 probands who did not have a mutation detected by resequencing.
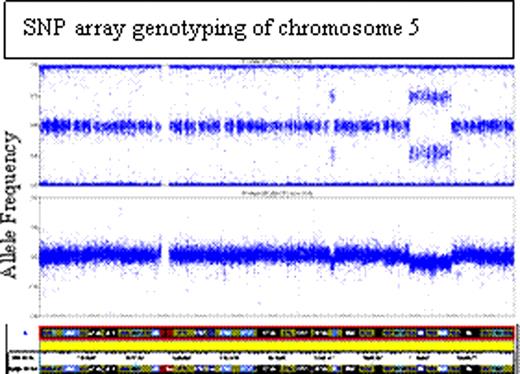
An acquired internal deletion on chromosome 5q involving RPS14 was identified in one of 23 patients with presumed DBA. The patient presented with anemia at 5 10/12 years of age. The hemoglobin was 8.4 g/dl, MCV 108.2 fL, and reticulocyte count 0.4%. The erythrocyte adenosine deaminase (eADA) activity, elevated in 85% of DBA patients, was normal. The bone marrow showed decreased cellularity and megaloblastoid changes in the erythroid series. There were adequate numbers of megakaryocytes with no hypolobulation. Cytogenetics performed at diagnosis in 1991 appeared normal. The patient had no significant family history or congenital anomalies. A diagnosis of non-classical DBA was made. The patient failed a trial of corticosteroids and had remained transfusion-dependent for 19 years. No RP gene mutation was identified by sequencing. SNP array genotyping analysis identified mosaicism in two discrete regions covering ∼17.7 Mb on 5q-, with an estimated 63.7% monosomy and 36.3% disomy in this region. The major region extends from 141.1M to 157.2M (hg18), including all of the 5q- syndrome commonly deleted region (CDR) at 5q33, though it excludes the 5q31 CDR, miR146a, as well as Cdc25C and PPP2Acα, factors for which haploinsufficient expression has previously been suggested to be important in response to lenalidomide. SNP array genotyping from purified populations indicated that lymphocytes were >95% normal, while the myeloid cells were >95% 5q-. CD34+ cells showed a marked decrease in both myeloid and erythroid colony formation. Patient fibroblasts were normal and neither of the parents have 5q abnormalities by SNP analysis. Although the deletion was not identified in 1991, the 46,XX,der(5)del(5)(q15q22)del(5)(q32q33) deletion was detected on high resolution karyotyping in a post-SNP array genotyping marrow sample. Haploinsufficiency of RPS14 was confirmed by quantitative RT-PCR. After a trial of lenalidomide, complicated by Grade 4 neutropenia and Grade 3 thrombocytopenia, the patient has a reticulocyte count of 7.4% (from a previous baseline of <0.2%) and has achieved a hemoglobin of 11.1 gm/dl without transfusion support.
Patients with non-classical DBA, who also have no congenital anomalies and normal eADA activity, may have somatically acquired 5q deletions with RPS14 haploinsufficiency. The DBAR is presently performing SNP array genotyping on other DBA patients who fit these criteria. These data suggest that haploinsufficiency of Cdc25C and PPP2Acα are not required for an erythroid response to lenolidamide. Reclassification of non-classical DBA patients as 5q- MDS offers them a potential treatment option with lenalidomide.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal