Abstract
Abstract 1004
Data from single institutional clinical studies have indicated that the content of CD34+ cells, T-cells, and dendritic cells in a bone marrow allograft are associated with clinical outcomes. The relationship between the cellular constituents of hematopoietic allografts and clinical outcomes was prospectively studied in BMT CTN 0201 in which patients with hematological malignancies (and their donors) were randomized to transplantation with bone marrow or G-CSF-mobilized peripheral blood stem cell (PB) allografts. A secondary objective of this study was to correlate graft characteristics with overall survival (OS).
551 patients were enrolled at 50 North American centers between January 2004 and September 2009 in a BMT CTN-sponsored randomized clinical trial supported by the NHLBI and NCI. Of the 278 subjects randomized to BM, aliquots from 173 BM allografts collected in North America were analyzed at a central laboratory for the content of CD34+ progenitors and immune cell subsets by flow cytometry, and of 151 of these BM transplants had complete clinical data and are the subject of this analysis. The subset of 151 patients were similar to the total group of patients transplanted in BMT CTN 0201, with a median age of 38, and 42% of patients with AML, 26% with ALL, 10% CML, and 21% MDS. 74% of patients had low risk disease, and 47% received 12 Gy TBI and cyclophosphamide with the remainder receiving myeloablative busulfan-based (48%) or fludarabine/melphalan conditioning (5%). GvHD prophylaxis was predominately a calcineurin inhibitor plus methotrexate (91%). 26.5% of patients received grafts from HLA mismatched donors.
Clinical outcomes, including OS, acute GVHD III–IV and chronic GVHD, were similar between the subset of patients with analysis of BM cells and the 127 BM recipients without product analysis. 46 progenitor and immune cell subsets were selected for study based upon the absence of a strong correlation with another graft subset (Pearson or Spearman correlation >0.8) and a priori interest or the number of evaluable patients. Graft characteristics were then described separately for survivors and those who died and compared using a nonparametric Mann-Whitney Wilcoxon test. P-values were not adjusted for multiple comparisons, but only covariates for which the q value is <0.2 are presented.
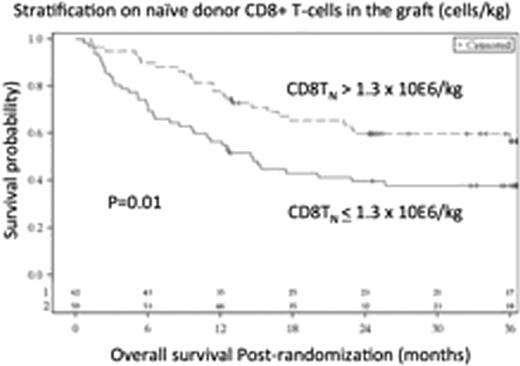
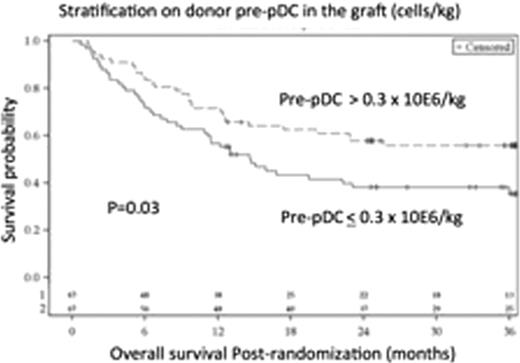
Overall survival for recipients of allogeneic BM grafts stratified by the median numbers of Left: donor naive CD8+ T-cells (> or ≤ 1.3 × 10E6/kg) or Right: donor pDC precursors (> or ≤ 0.3 × 10E6/kg) in the BM graft.
Overall survival for recipients of allogeneic BM grafts stratified by the median numbers of Left: donor naive CD8+ T-cells (> or ≤ 1.3 × 10E6/kg) or Right: donor pDC precursors (> or ≤ 0.3 × 10E6/kg) in the BM graft.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal