Abstract
Abstract 1442
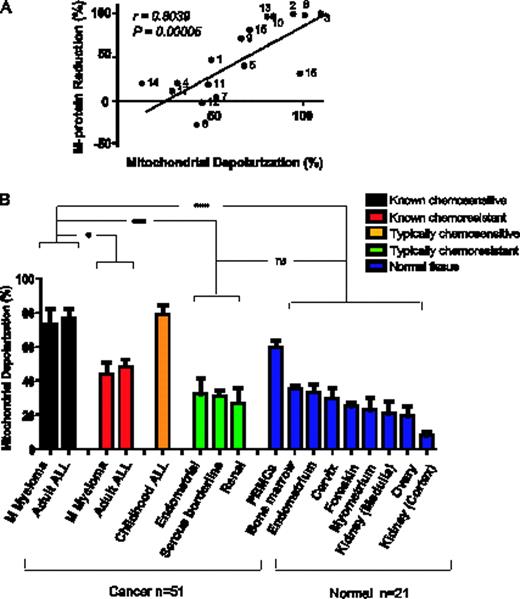
Cytotoxic chemotherapy, still a mainstay of current cancer treatment, targets ubiquitous elements such as DNA and microtubules. Despite decades of clinical use of chemotherapy, determinants of response to such treatments are poorly understood. Here, we showed that clinical response to cytotoxic agents is largely regulated by the initial proximity of tumors' mitochondria to the apoptotic threshold. Cells that are close to the apoptotic threshold we refer to as “primed” for death. Priming is assessed by a functional assay we call BH3 profiling that measures mitochondrial response to standardized death signals in the form of peptides from the pro-apoptotic BH3-only proteins. We assessed priming across a total of 51 patient samples, 25 of which had clinical follow-up. Priming correlated to % M-protein reduction, a marker of reduced disease burden in multiple myeloma following treatment (spearman r = 0.8039, P= 0.00005 Fig 1A). Patient's with highly primed mitochondria also demonstrated a better clinical response in both multiple myeloma (P= 0.001) and in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (P= 0.0119). Pediatric ALL responds better to therapy and has a much higher long term survival rate than adult ALL (80–90% vs. 40%) (Pui et. al N Engl J Med, 2006). We found that pediatric ALL samples were more primed than adult (P = 0.007). To demonstrate the relationship between priming and chemosensitivity we perturbed priming by co-culture with stroma or by pretreatment with ABT-737 and demonstrated that altering priming changed chemosensitivity predictably.
Mitochondrial priming regulates clinical response to chemotherapy in multiple myeloma and acute lyphoblastic leukemia (A) Loss of δΨm caused by the BMF peptide in myeloma patient samples correlates to %M-protein reduction. (B) Comparison of priming among all primary human cancers and normal tissues. The cancers with clinical follow up were classified as known chemosensitive or known chemoresistant. Cancers classified as typically chemoresistant (Serous borderline n=3, Endometrial n=3 and Renal n=3) or typically chemosensitive (childhood ALL n=17) lacked individual response data. Data shown are mean ± s.d. across all specimens tested. ANOVA was used to demonstrate statistical significance between the different categories with a Tukey's multiple comparison post test. ns - p value > 0.05 and *** p-value <0.001.
Mitochondrial priming regulates clinical response to chemotherapy in multiple myeloma and acute lyphoblastic leukemia (A) Loss of δΨm caused by the BMF peptide in myeloma patient samples correlates to %M-protein reduction. (B) Comparison of priming among all primary human cancers and normal tissues. The cancers with clinical follow up were classified as known chemosensitive or known chemoresistant. Cancers classified as typically chemoresistant (Serous borderline n=3, Endometrial n=3 and Renal n=3) or typically chemosensitive (childhood ALL n=17) lacked individual response data. Data shown are mean ± s.d. across all specimens tested. ANOVA was used to demonstrate statistical significance between the different categories with a Tukey's multiple comparison post test. ns - p value > 0.05 and *** p-value <0.001.
Richardson:Millennium:; Celgene:; Johnson & Johnson:; Novartis:; Bristol Myers Squibb:. Anderson:Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Millennium: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Onyx: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Merck: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Acetylon: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Mitsiades:Millennium: Consultancy, Honoraria. Sallan:Enzon Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria. Letai:Eutropics Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal