Abstract
Abstract 4135
Multiple myeloma (MM) is the second most common adult hematologic malignancy. High dose chemotherapy (HDC) and autologous stem cell transplantation (auto-SCT) have become the standard of care for eligible patients. Though the impact of bone marrow (BM) plasma cell (PC) percentage has been explored in the post-SCT setting, its role before SCT is not yet known
We performed a retrospective review of 1826 MM pts who underwent HDC and auto-SCT at our institution from 7/8/98 – 12/31/2010. We further identified patients who had post-induction, pre-SCT BM biopsy information available. Patients were divided into 2 groups: those with <10% PC infiltration (“PC low”) and those with ≥10% plasma cell infiltration (“PC high”). Additional data, such as demographics, time of diagnosis, response, time to progression and time of death were also collected. Progression-free (PFS) and overall (OS) survivals were estimated by the Kaplan-Meier method. Log-rank test was performed to test the difference in survival between groups.
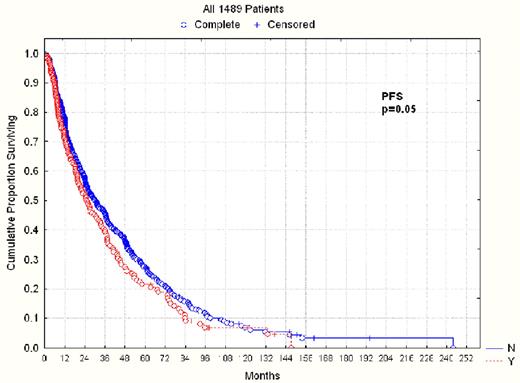
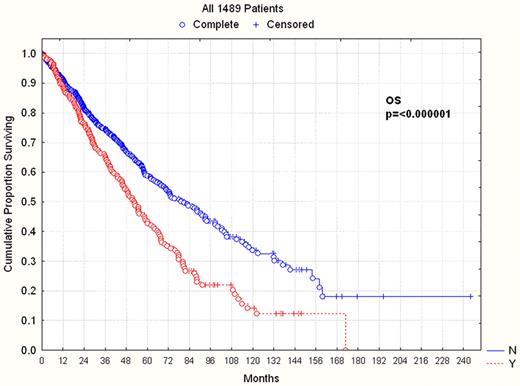
1489 pts were studied, 605 female and 884 male. Patient characteristics are detailed in Table 1. Median time from diagnosis to auto-SCT was 247 days (range 45–7895). 1299 (87%) patients underwent auto-SCT after 2000. Nearly all patients received melphalan-based conditioning. 1174 patients had <10% involvement of BM by PCs and 315 had > 10% involvement. The details of best responses before and after auto-SCT are also listed in Table 1. For patients in the PC low group, 32% had a CR, 20% had a VGPR, 31% had a PR, 13% had <PR and 3% had progressive disease after auto-SCT. For patients in the PC high group, 11% had a CR, 14% had a VGPR, 48% had a PR, 21% had <PR and 5% had progressive disease (PD) after auto-SCT. Median PFS was significantly shorter for the PC high group versus the PC low group (24.8 vs 29.5 months, p=0.05), as was median OS (52.5 vs 79.4 months respectively, p<0.001). When only those patients who had a PR to induction were examined, there was again a significant difference in both PFS (24.4 vs 33.2 months, p=0.04) and OS (58.3 vs 81.2 months, p =0.002) for those patients in the PC high versus PC low groups, respectively. Finally, when looking at those patients who underwent auto-SCT in the era of novel therapeutics (after 2000), the differences between the PC high and PC low groups were maintained for both PFS (24.4 vs 29.5 months respectively (p=0.029)) and OS (54.8 vs 88.4 months respectively, p<0.001).
Patient characteristics and responses
| . | All patients (n=1489) . | PC <10% (n=1174) . | PC ≥ 10% (n=315) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 884 (59%) | 718 (61%) | 166 (53%) |
| Female | 605 (41%) | 456 (39%) | 149 (47%) |
| Race | 988 (66%) | 784 (67%) | 204 (65%) |
| Caucasian | 230 (15%) | 181 (15%) | 49 (16%) |
| African American | 33 (2%) | 24 (2%) | 9 (3%) |
| Asian Unknown/other | 238 (16%) | 185 (16%) | 53 (17%) |
| Durie-Salmon Stage (1440 pts) | |||
| I | 218 (15%) | 179 (16%) | 39 (13%) |
| II | 597 (41%) | 486 (43%) | 111 (37%) |
| III | 626 (43%) | 472 (42%) | 154 (51%) |
| Cytogenetics (1265) | |||
| Normal | 943(75%) | 782 (79%) | 161 (58%) |
| Abnormal | 322 (25%) | 207 (21%) | 115 (42%) |
| Response prior to auto-SCT | |||
| CR | 66 (4%) | 66 (6%) | 0 (0%) |
| VGPR | 255 (17%) | 244 (21%) | 11(3%) |
| PR | 817 (55%) | 655 (56%) | 162 (51%) |
| <PR | 232 (16%) | 144 (12%) | 88 (28%) |
| PD | 93 (6%) | 45 (4%) | 48(15%) |
| unknown | 26 (2%) | 20 (2%) | 6 (2%) |
| Median time to SCT (range) | 247 days (45–7895) | 239 days (45–7895) | 259 days (74–5580) |
| SCT after 2000 | 1299 (87%) | 1037 (88%) | 262 (83%) |
| Best response after SCT | |||
| CR | 384 (26%) | 350 (32%) | 34 (11%) |
| VGPR | 298 (20%) | 253 (20%) | 45 (14%) |
| PR | 510 (34%) | 359 (31%) | 151 (48%) |
| <PR | 223 (15%) | 157 (13%) | 66 (21%) |
| PD | 45 (3%) | 30 (3%) | 15 (5%) |
| Not evaluable | 29 (2%) | 9 (1%) | 4 (1%) |
| PFS from SCT (months) | 29.5 | 24.8 | |
| P=0.05 | |||
| OS from SCT (months) | 79.4 | 52.5 | |
| P<0.001 | |||
| PR-PFS from SCT (months) | 33.2 | 24.4 | |
| P = 0.04 | |||
| PR- OS from SCT (months) | 81.2 | 58.3 | |
| P = 0.002 | |||
| Post-2000 SCT PFS from SCT (months) | 29.5 | 24.4 | |
| P = 0.029 | |||
| Post-2000 SCT OS from SCT (months) | 88.4 | 54.8 | |
| P<0.001 | |||
| . | All patients (n=1489) . | PC <10% (n=1174) . | PC ≥ 10% (n=315) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 884 (59%) | 718 (61%) | 166 (53%) |
| Female | 605 (41%) | 456 (39%) | 149 (47%) |
| Race | 988 (66%) | 784 (67%) | 204 (65%) |
| Caucasian | 230 (15%) | 181 (15%) | 49 (16%) |
| African American | 33 (2%) | 24 (2%) | 9 (3%) |
| Asian Unknown/other | 238 (16%) | 185 (16%) | 53 (17%) |
| Durie-Salmon Stage (1440 pts) | |||
| I | 218 (15%) | 179 (16%) | 39 (13%) |
| II | 597 (41%) | 486 (43%) | 111 (37%) |
| III | 626 (43%) | 472 (42%) | 154 (51%) |
| Cytogenetics (1265) | |||
| Normal | 943(75%) | 782 (79%) | 161 (58%) |
| Abnormal | 322 (25%) | 207 (21%) | 115 (42%) |
| Response prior to auto-SCT | |||
| CR | 66 (4%) | 66 (6%) | 0 (0%) |
| VGPR | 255 (17%) | 244 (21%) | 11(3%) |
| PR | 817 (55%) | 655 (56%) | 162 (51%) |
| <PR | 232 (16%) | 144 (12%) | 88 (28%) |
| PD | 93 (6%) | 45 (4%) | 48(15%) |
| unknown | 26 (2%) | 20 (2%) | 6 (2%) |
| Median time to SCT (range) | 247 days (45–7895) | 239 days (45–7895) | 259 days (74–5580) |
| SCT after 2000 | 1299 (87%) | 1037 (88%) | 262 (83%) |
| Best response after SCT | |||
| CR | 384 (26%) | 350 (32%) | 34 (11%) |
| VGPR | 298 (20%) | 253 (20%) | 45 (14%) |
| PR | 510 (34%) | 359 (31%) | 151 (48%) |
| <PR | 223 (15%) | 157 (13%) | 66 (21%) |
| PD | 45 (3%) | 30 (3%) | 15 (5%) |
| Not evaluable | 29 (2%) | 9 (1%) | 4 (1%) |
| PFS from SCT (months) | 29.5 | 24.8 | |
| P=0.05 | |||
| OS from SCT (months) | 79.4 | 52.5 | |
| P<0.001 | |||
| PR-PFS from SCT (months) | 33.2 | 24.4 | |
| P = 0.04 | |||
| PR- OS from SCT (months) | 81.2 | 58.3 | |
| P = 0.002 | |||
| Post-2000 SCT PFS from SCT (months) | 29.5 | 24.4 | |
| P = 0.029 | |||
| Post-2000 SCT OS from SCT (months) | 88.4 | 54.8 | |
| P<0.001 | |||
Extensive BM infiltration by PCs before auto-SCT is associated with a worse outcome in patients treated with HDC and auto-SCT. This finding persists when looking specifically at patients with a PR before auto-SCT. Thus, BM disease burden may further assist us in stratifying patients with a PR and may warrant further disease reduction before stem cell collection. Additionally, the differences between PC high and PC low groups are maintained in the modern era, despite the availability of several new salvage agents over the last 10 years. Further prospective study is warranted to determine the true impact of PC infiltration in the BM.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal