Abstract
Abstract 4478
The optimal therapy after transformation of follicular lymphoma into diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is unknown. Most of retrospective registry data and phase II studies suggest a potential benefit of high-dose therapy and autologous transplantation (HDT-ASCT) for patients with transformed lymphoma (TL). Addition of rituximab to CHOP chemotherapy could improve survival in TL. However, the effect of prior rituximab-based therapy upon the efficacy of subsequent autologous stell cell transplantation (ASCT) in TL is still unknown.
We have identified the patients with follicular lymphoma who developed confirmed histological transformation to DLBCL treated with HDT-ASCT included in the Grupo Español de Linfomas/Trasplante Autólogo de Médula Osea (GEL-TAMO) Spanish registry between October 1994 and March 2011. Patients were divided into two groups, according to whether rituximab-based regimens were given (n = 28, ‘R+’ group) or not (n = 22, ‘R-’ group) at the time of transformation. Kaplan-Meier survival curves were estimated, and differences in survival curves between groups were assessed using the log-rank test.
Fifty patients (23 women) with a histological diagnosis of TL who underwent HDT-ASCT were included. Median age at transplantation was 55 years (range 32–70). Patients had received a median of 2 (range 1–5) chemotherapy regimens prior to ASCT. Median time from diagnosis of follicular lymphoma to transformation was 49 months (range 8–135). Age-adjusted International Prognostic Index (IPI) was 2 or 3 in 11 patients (22%).
Disease status prior to ASCT was first complete remission in 4 patients (8%), second CR in 56% and active diseasein 14%: sensitive disease in 11 (22%) and refractory disease in 3 (6%) patients. Conditioning regimen consisted of BEAM in 92% of patients, BEAC in 4%, and cyclophosphamide /TBI in 4%. With a median follow-up of 61 months, estimated overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) at 5 years after ASCT were 56.5% and 51.3%, respectively. No patients died of transplant-related mortality. Thirteen patients experienced relapse or progression after HD-ASCT; nine of these patients have died because of disease progression. By multivariate analysis three variables significantly influenced both OS and PFS: number of regimens prior to ASCT, disease status at transplant and achievement of response after HD-ASCT. Age-adjusted IPI at transformation had significant influence only on OS.
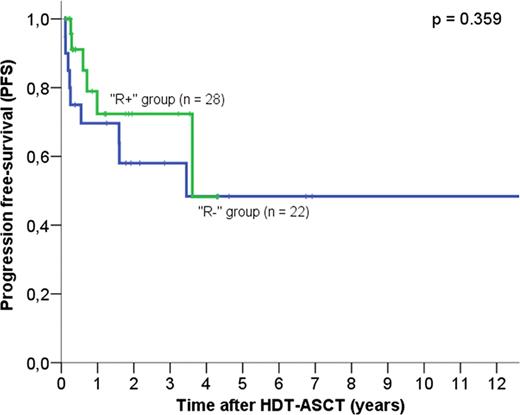
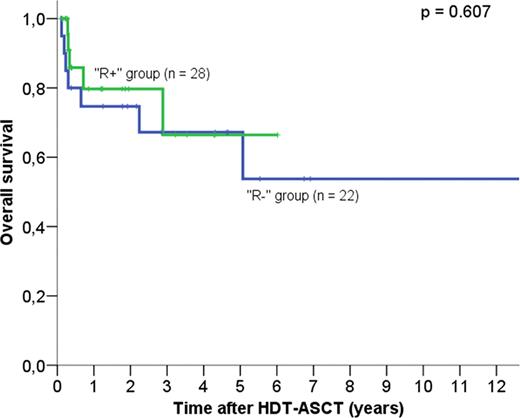
Patients who did not receive rituximab-based regimens had similar characteristics to patients who received rituximab at transformation. Patients in the R+ group had similar 5-year PFS (48.2% vs 48.4%, P = 0.359) and 5-year overall survival (OS) (66.4% vs 67.2%, P = 0.607) compared to patients in the R- group (Figures 1 and 2). Eight out of 28 “R+” patients had not received rituximab prior to transformation; these patients had better PFS (69% vs 38%, p = 0.912) and OS at 5 years (74.1% vs 54.5%) compared to the 20 patients who were treated with rituximab prior to transformation, but the difference did not reach statistical significance (p >0.1). Patients treated with rituximab-based regimens at any time prior HDT-ASCT had similar OS (70% versus 63.8% at 5 years, P = 0.697) and PFS (50% versus 44% at 5 years, P = 0.445) than patients who received chemotherapy alone before ASCT.
Our results show that HDT-ASCT remains a valuable therapeutic choice for patients with histological confirmed TL since it allows a long-term disease control in a significant proportion of patients. The addition of rituximab to conventional chemotherapy after transformation does not appear to improve the outcomes of subsequent ASCT, although larger prospective studies are required.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal