Abstract
Lymphoma cell survival and progression are putatively dependent on a specific microanatomic localization within secondary lymphoid organs. Despite compelling data correlating homeostatic chemokine receptor expression and human lymphoma pathogenesis, genetic models that either mimic lymphoma dissemination or dissect a crosstalk of lymphoma and stromal cells are missing. Applying the genetically tractable Eμ-Myc transgenic mouse model, we show that the chemokine receptor CCR7 regulates Eμ-Myc lymphoma homing to lymph nodes and distinctive microanatomic sites of the spleen. CCR7-controlled access of lymphoma cells to the splenic T-cell zone led to a significant survival advantage compared with CCR7-deficient lymphoma cells, which were excluded from this zone. Within the niche, lymphoma cells stimulated a reciprocal cross-talk with gp38+ fibroblastic reticular cells. This reciprocal cooperation program was mediated by lymphoma B cell–presented lymphotoxin, which acted on lymphotoxin-β–receptor-bearing stromal cells followed by alteration of stromal cellular composition. Cross-talk inhibition by lymphotoxin-α deletion and using a lymphotoxin-β receptor-immunoglobulin fusion protein impaired lymphoma growth. Thus, abrogation of CCR7-governed migration and of sustained lymphotoxin signaling could provide new targets in lymphoma therapy.
Introduction
The crosstalk between lymphoid tumor cells and their microenvironment provides pivotal signals for the localization and progression of lymphoid malignancies. Thus, it has become increasingly important to define which molecular mechanisms allow the interactions between accessory cells and malignant B-cells and to identify the stromal cells that mediate such signals.1,2 In Eμ-Myc transgenic mice, a mouse model of Myc-driven aggressive human B-cell lymphoma, the precancerous state is characterized by excessive proliferation in conjunction with the onset of an apoptotic program within the bone marrow precursor and immature B-cell compartment.3,4 Although the role of genetic lesions as steps toward cell autonomy and tumor growth has been appreciated,5,6 in vivo the conditions for lymphoma cell lodging within secondary lymphoid organs (SLOs) remain to be addressed. Several in vitro studies or transfer models of human lymphoma cell lines into immunodeficient mice could demonstrate that a variety of cytokines, adhesion molecules, and growth factors were involved in the cross-talk at the stroma-lymphoma cell interface.7,8 Clinical studies have correlated the involvement of chemokine receptors with nodal homing of B-cell non-Hodgkin (NHL) and Hodgkin lymphoma.9,10 Conversely, lack of the major lymph node (LN) addressins, foremost the homeostatic chemokine receptors CXCR5 and CCR7, may predispose those tumor cells for extranodal dissemination instead.11 In vivo, the dissemination of primary central nervous system lymphoma toward brain-expressed chemokine ligand CCL21 has been shown to be controlled by CCR7 expression.12 Although this investigation considered only the role of CCR7 in extranodal dissemination, the following interactions between lymphoma cells and their microenvironment remained unresolved. Under physiologic conditions, the function of homeostatic chemokines in lymphoid organ development and organization is mutually dependent on signaling pathways activated by the tumor necrosis factor (TNF)/lymphotoxin (LT) family of cytokines.13-15 The proinflammatory and homeostatic cytokines LTα and LTβ are physiologically expressed by activated T, B, NK, and lymphoid tissue inducer cells and are the main organizers for lymphoid tissue organogenesis. Environmental cues that determine localization and survival of B-cell lymphoma might be also regulated by joint actions of the chemokine and TNF/LT-mediated signaling systems.
Here, we investigated the cooperation between homeostatic chemokine receptor-controlled dissemination and LT-promoted niche formation in a transgenic mouse model of Myc-driven lymphomagenesis. We characterized consecutive steps of CCR7-dependent nodal access and lymphoma progression within SLOs. CCR7 conferred a survival advantage for Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells, provided that they were lodging within the T-cell zone stroma. Here, tumor cells initiated a reciprocal cross-talk with gp38+ fibroblastic reticular cells (FRCs), leading to the release of homeostatic chemokines. Immunotherapeutic interference with the stromal cell meshwork using an LTβ receptor-immunoglobulin (LTβR-Ig) fusion protein impaired lymphoma growth, suggesting a sustained need for a specialized immunologic environment that supplies trophic and chemoattractant factors.
Methods
Mice
Eμ-Myc (C57BL/6) transgenic mice,16 C57BL/6 Ly5.1 (CD45.1) congenic mice, LTα−/− mice,17 and Rag2−/− mice were obtained from The Jackson Laboratory. CCR7−/− were generated as described18 and backcrossed onto a C57BL/6 background for 12 generations. CCR7−/− and LTα−/− mice were crossed with Eμ-Myc transgenic mice to generate double-transgenic mice. Animals were housed in a specific pathogen-free facility at the Max-Delbrück-Center for Molecular Medicine, Berlin. All animal studies were performed according to institutional and Berlin State guidelines (registered under LaGeSo 0371/05 and 0333/06).
Antibodies
The following primary antibodies were used for flow cytometry: FITC-labeled goat anti–mouse CD4, FITC-labeled rat anti–mouse CD62L, and CD18, phycoerythrin (PE) labeled goat anti–mouse CD3, allophycocyanin-labeled rat anti–mouse B220 (CD45R) (Caltag); FITC-labeled mouse anti–mouse CD45.1, FITC-labeled rat anti–mouse IgD, PE-labeled rat anti–mouse CD117, CCR6, CXCR4, CXCR5, IgM, and LFA-1, biotin-labeled mouse anti–mouse CD45.2, biotin-labeled rat anti–mouse preBCR, β7 integrin, rat anti–mouse CD16/CD32 (BD Biosciences); PE-labeled rat anti–mouse CCR7; PE-labeled rat anti–mouse CD210, biotin-labeled rat anti–mouse CD127, and CD49d; biotin-labeled goat anti–mouse LTβR (R&D Systems); AlexaFluor-488–labeled hamster anti–mouse gp38 (eBioscience); AlexaFluor-700–labeled mouse anti–mouse CD45.2; Pacific Blue-labeled rat anti–mouse VCAM-1 (CD106), and armenian hamster anti-mouse CD154 CD40 ligand (CD40L; BioLegend); and PE-labeled goat anti–rat IgG, allophycocyanin-, peridinin chlorophyll protein-, or PE-labeled streptavidin (BD Biosciences).
For immunohistology, the following primary antibodies were used: rat anti–mouse CD3, FITC-labeled anti–mouse MOMA-1 (Serotec); goat anti–mouse CD3e (Santa Cruz Biotechnology); AlexaFluor-488-labeled hamster anti–mouse CD11c, biotinylated, and Pacific Blue-labeled rat anti–mouse B220, biotin, AlexaFluor-488, and Pacific Blue-labeled mouse anti–mouse CD45.2, Pacific Blue–labeled rat anti–mouse CD4; biotin-labeled rat anti–mouse IgD (eBioscience); biotin-labeled hamster anti-mouse gp38 (BioLegend); rat anti–mouse ERTR7 (Acris); goat anti–mouse CCL21 (R&D Systems); rabbit anti–mouse α-smooth muscle actin, and rabbit anti–mouse Ihh (Abcam). Secondary antibodies included: donkey anti–goat IgG, AlexaFluor-568, and alkaline phosphatase-conjugated, donkey anti–goat horseradish peroxidase-conjugated, donkey anti–rabbit biotin (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories); streptavidin alkaline phosphatase (BD Biosciences); goat anti–rat IgG AlexaFluor-568- and AlexaFluor-488-conjugated, AlexaFluor-568-labeled goat anti–hamster IgG; goat anti–rabbit AlexaFluor-568, and goat anti–mouse AlexaFluor-488 (Invitrogen) were used as secondary reagents.
Generation of primary Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells for cell culture and transplantation
Eμ-Myc transgenic mice were monitored for signs of disease, which includes development of palpable lymphomas or weight loss of > 15%. LN-derived lymphoma cell suspensions were prepared from moribund mice by tissue homogenization.
Isolation and culture of FRCs
For the purification of gp38+ cells, we applied a collagenase-based purification and culturing protocol similar as described.19 Briefly, spleens and LN from naive mice were digested for 45 minutes at 37°C with collagenase D (1.0 mg/mL; Roche Diagnostics) in RPMI 1640/10% FCS. Single-cell suspensions were seeded in collagen-coated 10-cm dishes (Collagen solution type I; Sigma-Aldrich). After overnight culture, nonadherent cells were removed and fresh medium was added. Cultures were continued for 3 to 7 days and assessed for the emergence of fibroblast-shaped cells. Residual macrophages were further depleted by CD11b-coated MACS microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec). For the preparation of gp38−/CD45− stromal cell fractions, CD11b-depleted gp38+ enriched cell populations were further depleted of gp38+ cells using Biotin Binder Dynabeads (Invitrogen) in conjunction with a biotin-labeled hamster anti–mouse gp38 antibody (BioLegend). In coculture experiments, 1 × 104 FRCs were seeded in flat-bottom 96-well tissue collagen-coated culture plates. After 24 hours, 2 × 105 freshly isolated Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells were added. Cell death was assessed by annexin V +/7-amino-actinomycin D (7-AAD)+ staining (Bender Med Systems). In each individual experiment, an independent primary Eμ-Myc lymphoma cell clone was used. Cyclopamine (Sigma-Aldrich) was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide, and this solvent was used for mock controls.
Immunofluorescence staining of cultured FRCs
Stromal cells were cultured on collagen-coated cover glasses. After 24 hours, cells were fixed in 3.5% paraformaldehyde (weight/volume) or acetone. Staining was done as described.20 For surface staining, an AlexaFluor-488 coupled anti gp38+ antibody was used. Lymphoma B cells were detected with a biotinylated anti CD45.2 antibody. Detection of α-smooth muscle actin was performed on acetone-fixed samples.
Preparation of cell suspensions, flow cytometry, and cell sorting
Spleen and LN cell suspensions were obtained by gentle disruption of the organ in PBS/2% FCS followed by hypotonic lysis to deplete red blood cells. Cells were blocked with CD16/32 antibody in fluorescence-activated cell sorter buffer (PBS, 0.5% BSA, 0.05% NaN3), followed by staining with the antibodies described in “Antibodies.” Data were acquired on a FACSCantoII flow cytometer (BD Biosciences) and were further analyzed with FlowJo Version 8.8.7 software (TreeStar). Cell sorting was done on a FACSAria (BD Biosciences).
Generation of a retroviral vector and transduction of lymphoma cells
Eμ-Myc enhanced green fluorescent protein (GFP) transgenic lymphoma cells were generated by retroviral infection, essentially as described,20 enhanced GFP-stained lymphoma cells were further enriched by FACS sorting before transfer into animals.
Chemotaxis assay
Chemotaxis assays were performed in 5-μm-pore Transwell plates (Corning) for 4 hours at 37°C exactly as described.9 CCL21 and CXCL12 were used at a concentration of 100nM and 25nM, respectively (R&D Systems). Akt inhibitor (Calbiochem) was dissolved in DMSO, and the solvent was used for mock control.
Immunohistology
For frozen sections, tissues were frozen in Tissue Tek OCT compound (Sakura Finetek). Cryosections of 5-μm thickness were cut, air dried, and fixed for 10 minutes in −20°C acetone. Conventional immunohistochemistry was performed as described previously.21 For immunofluorescence, sections were blocked for 30 minutes with 10% normal mouse or goat serum, respectively, and slides were stained for 1.5 hours at room temperature with biotinylated or fluorescently labeled antibodies. For indirect staining, secondary labeled antibodies were incubated for 1 hour. Biotinylated primary antibodies were detected with streptavidin AlexaFluor-488 or -568 (Invitrogen). All slides were mounted in Mowiol solution. For terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assays, 8-μm cryosections were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde/PBS for 10 minutes. The TUNEL reaction was performed exactly as described by the manufacturer (Trevigen). Double staining of paraffin-embedded spleen sections included submersion in citrate-buffered saline (pH 6.0) in a high pressure cooker for antigen retrieval. Sections were quenched for 10 minutes with H2O2; then they were blocked sequentially with donkey serum and treatment with a biotin-avidin kit (Vector Laboratories). Primary anti-CD3 and anti-Ihh antibodies were detected sequentially with peroxidase-labeled donkey antigoat serum, or a biotinylated donkey antirabbit antibody, followed by incubation with streptavidin alkaline phosphatase. 3-Amino-9-ethylcarbazole served as a peroxidase substrate (Dako Denmark), and Fast Blue was used to develop alkaline phosphatase.
Immunofluorescence image acquisition
Fluorescently labeled tissue sections were analyzed on a Zeiss Axiophot fluorescence microscope, equipped with an Axio Cam HRc (Carl Zeiss) camera. Images were obtained with a 40× Plan-Neofluar NA 0.75 objective, or a 20× Plan-Apochromat NA 0.8 objective. Digital images were processed with Axio Vision Version 4.5 software (Carl Zeiss) and Adobe Photoshop applying the Autocontrast function. Light microscopic images were obtained with the same instrument.
Confocal microscopy images of cultured FRCs were acquired with a Zeiss LSM510Meta confocal setup on an Axiovert 200M inverted microscope equipped with a three-line laser. Digital images were collected using a 63× phase-contrast plan-apochromat oil objective NA 1.4. The image acquisition was done sequentially (multitrack) to minimize potential cross-talk between the fluorophores, and images were processed using LSM Examiner 3.2 and LSM Browser software (Carl Zeiss). Microscope settings and image processing were exactly as described.20
Confocal microscopy images of immunofluorescently stained histologies were acquired on an upright Leica TCS SPE confocal setup (Leica). Digital images were obtained using a 40× phase-contrast plan-apochromat oil objective. Serial z-stacks were obtained at 0.9-μm intervals. Images were processed using Leica LAS AF software (Leica) and Adobe Photoshop Version CS3 software.
Lymphoma cell transfer
C57BL/6 Ly5.1 (CD45.1) congenic, LTα−/−, and Rag−/− mice 7 to 12 weeks of age were injected intravenously with 1 × 104 to 2 × 105 Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells (CD45.2), as indicated. In some experiments, 1 × 104 to 2 × 105 Eμ-Myc GFP or CCR7−/− lymphoma cells were administered (as indicated). For the lymphoma cell genotypes Wt and CCR7−/−, at least 7 independent clones were tested; and for the LTα−/− genotype, 2 independent clones were used in each group with comparable results. Mice were examined 3 times per week for lymphoma growth. Onset of disease was defined as palpable tumor nodules, weight loss, and paralysis.
In vivo blockade of the LTβ-receptor pathway
A total of 100 μg of blocking LTβR-Ig (murine receptor fused to mouse monoclonal antibody IgG1, MOPC 21) or isotype control antibody (MOPC 21; all kindly provided by Jeffrey L. Browning, Biogen Idec, Cambridge, MA) were repeatedly injected intraperitoneally into C57BL/6 Ly5.1 Wt mice.
Adoptive T-cell transfer
Splenic CD4+ T cells from C57BL/6 Wt mice were purified by negative selection applying magnetic cell sorting (Miltenyi Biotec). Purity of isolated naive T cells was > 90%. Cells were adoptively transferred intravenously 4 days before Eμ-Myc lymphoma cell application. For in vivo blockade of CD40L, 200 μg of blocking antibody or isotype control antibody (armenian hamster IgG, BioLegend) was injected intraperitoneally after CD4+ T cell and Eμ-Myc lymphoma cell transfer (both day 0).
Activation-induced phosphorylation
Splenic B cells were isolated by negative selection of splenocytes applying magnetic cell sorting, followed by serum starvation for 5 hours in RPMI 1640 medium, supplemented with 0.5% BSA. Those B cells and freshly explanted Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells from enlarged LNs were resuspended at a density of 4 × 106 cells/0.5 mL in prewarmed starvation medium and stimulated for 0, 5, 10, and 20 minutes at 37°C with 500 ng/mL recombinant CCL19 or CCL21 (R&D Systems). Stimulation was terminated, and cell lysates were prepared for Western blot analysis. Cell lysates were generated in lysis buffer (20mM N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-N′-2-ethanesulfonic acid, pH 7.9, 350mM NaCl, 1% Nonidet P-40, 1mM MgCl2, 0.5mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, 0.1mM ethyleneglycoltetraacetic acid, 1mM phenylmethylsulfonylfluorid, 5 μg/mL aprotinin, 10mM NaF, 1mM Na3VO4, 2mM β-glycerolphosphate). Proteins were analyzed by Western blot and probed with anti-phospho-PKB/Akt (Ser473; Cell Signaling) antibody. Then, blots were stripped and reprobed for total Akt activity. Proteins were visualized by chemiluminescence (ECL kit; Thermo Scientific). Densitometric quantification of gel bands was performed using the TINA Version 2.0 software (Raytest).
RNA extraction and RT-PCR
Total RNA of lymphoma cells and gp38+ cells was extracted using the RNeasy Micro Kit (QIAGEN), and integrity was confirmed with an Agilent Bioanalyzer system. cDNA was synthesized with oligo(dT) primers using the SuperScript III First-Strand Synthesis System for RT-PCR kit (Invitrogen). Real-time quantitative RT-PCR was performed using the IQ5 Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad). PCR reactions contained 100 ng cDNA in a total volume of 25 μL. SYBR Green 1 reagent (Sigma-Aldrich) was used for detection of PCR products. PCR conditions included: 10 minutes, 95°C activation of Perpetual Taq polymerase (Roboklon), denaturation 10 seconds, 95°C; annealing 30 seconds (temperature according to supplemental Table 1, available on the Blood Web site; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article); elongation 30 seconds, 72°C; denaturation 1 minute, 95°C; and melt curve 10 seconds, 0.5°C, range, 55°C to 95°C (40 cycles).
Sequence specific primers (supplemental Table 1) were designed according to Primer3 Input, Version 0.4.0 software (www.frodo.wi.mit.edu). For data analysis, gene transcript expression was calculated relative to GAPDH.
For analysis of chemokine expression in whole spleen, total RNA was prepared using the Trizol reagent (Invitrogen) according to the supplied protocol. Isolation of mRNA was performed with the RNeasy purification Kit (QIAGEN). The relative CCL19 and CCL21 RNA levels of tumor challenged mice were expressed as x-fold expression of splenic chemokine RNA levels in untreated mice.
Statistical analysis
Results are expressed as arithmetic mean ± SD if not otherwise indicated. Values of P ≤ .05 were considered statistically significant, as determined by the unpaired Mann-Whitney test or the 2-tailed unpaired Student t test, where appropriate. Survival curves were calculated using the log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test.
Results
Eμ-Myc tumor cells express a distinct pattern of homing and adhesion molecules
To explore B-cell lymphoma dissemination, we used transgenic Eμ-Myc mice, which spontaneously develop lymphadenopathy.4,22-24 Hence, this model is suitable to investigate putative regulators of lymphoma cell dissemination. In this process, adhesion molecules and the homeostatic chemokine receptors CCR7, CXCR5, and CXCR4 are expected to play a leading role; in vivo their contribution remains unresolved.
In Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells, we focused on molecules that are involved in physiologic lymphoid neogenesis and maintenance. Flow cytometric analysis revealed high surface expression of CXCR4 on all Wt Eμ-Myc tumor cell clones tested, and intermediate to high expression levels of CCR7. None of the primary lymphoma clones exhibited CXCR5 surface expression (Figure 1A). CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells exhibited essentially the same expression pattern of homing receptors as shown for Wt Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells, except for CCR7 expression (Figure 1A).
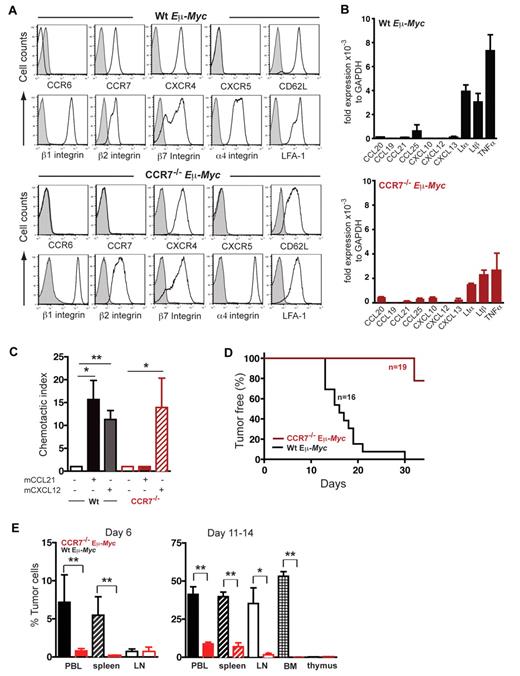
CCR7 expression is crucial for lymphoma cell homing to SLOs and lymphomagenesis. (A) Surface expression of maturation/differentiation markers, chemokine receptors, and adhesion molecules on B220+ gated tumor cells derived from LNs of lymphomatous Wt Eμ-Myc or CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc transgenic mice was assessed by flow cytometry (n = 4-7 mice per marker; isotype control; shaded curve). (B) Quantitative RT-PCR of chemokine and LT transcripts in tumor cells of Wt Eμ-Myc (n = 3 or 4) or of CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc (n = 3) transgenic mice. Transcript expression was normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. (C) Chemotaxis of tumor cells derived from Wt Eμ-Myc transgenic mice or from CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc transgenic mice toward CCL21 (100nM) and CXCL12 (25nM). Error bars represent SD for 3 or 4 independent experiments with triplicates per each group. *P ≤ .05; **P ≤ .01. (D) Tumor-free survival of mice that received 1 × 105 tumor cells derived from Wt Eμ-Myc transgenic mice or from CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc transgenic mice. Pooled data of 3 independent experiments are shown (n = 5-8 mice per group in each independent experiment. (E) Infiltration of Wt Eμ-Myc compared with CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc tumor cells into peripheral blood (PBL), spleen, and LNs of recipient congenic Wt mice on day 6, and tumor cell infiltration into PBL, spleen, LN, bone marrow (BM), and thymus of recipient congenic Wt mice on days 11 to 14 was quantitated by flow cytometry analysis after intravenously tumor cell application. Percentage of infiltrating tumor cells per organ was determined by gating on B220+/CD45.2+ double-positive cells (n = 4 mice per group on day 6; n = 5-14 mice (PBL, spleen, and LN) and n = 3-5 mice (BM, thymus) per group on days 11 to 14. *P ≤ .05; **P ≤ .01.
CCR7 expression is crucial for lymphoma cell homing to SLOs and lymphomagenesis. (A) Surface expression of maturation/differentiation markers, chemokine receptors, and adhesion molecules on B220+ gated tumor cells derived from LNs of lymphomatous Wt Eμ-Myc or CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc transgenic mice was assessed by flow cytometry (n = 4-7 mice per marker; isotype control; shaded curve). (B) Quantitative RT-PCR of chemokine and LT transcripts in tumor cells of Wt Eμ-Myc (n = 3 or 4) or of CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc (n = 3) transgenic mice. Transcript expression was normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. (C) Chemotaxis of tumor cells derived from Wt Eμ-Myc transgenic mice or from CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc transgenic mice toward CCL21 (100nM) and CXCL12 (25nM). Error bars represent SD for 3 or 4 independent experiments with triplicates per each group. *P ≤ .05; **P ≤ .01. (D) Tumor-free survival of mice that received 1 × 105 tumor cells derived from Wt Eμ-Myc transgenic mice or from CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc transgenic mice. Pooled data of 3 independent experiments are shown (n = 5-8 mice per group in each independent experiment. (E) Infiltration of Wt Eμ-Myc compared with CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc tumor cells into peripheral blood (PBL), spleen, and LNs of recipient congenic Wt mice on day 6, and tumor cell infiltration into PBL, spleen, LN, bone marrow (BM), and thymus of recipient congenic Wt mice on days 11 to 14 was quantitated by flow cytometry analysis after intravenously tumor cell application. Percentage of infiltrating tumor cells per organ was determined by gating on B220+/CD45.2+ double-positive cells (n = 4 mice per group on day 6; n = 5-14 mice (PBL, spleen, and LN) and n = 3-5 mice (BM, thymus) per group on days 11 to 14. *P ≤ .05; **P ≤ .01.
Surface staining of adhesion molecules revealed that integrins β1, β2, β7, α4, and α4β2 (LFA-1), normally expressed on mature B cells within secondary SLOs, were readily detected on all Eμ-Myc tumor cells, whereas L-selectin (CD62L) expression was variable (Figure 1A). Eμ-Myc tumor cells exhibited a pro-B or pre-B cell phenotype and displayed B220+/I-Ab+/CD127+/ CD117−/pre-BCR−/IgD−. IgM surface expression, characteristic of immature B cells, was variable among the 7 clones tested, and LTβR expression was negative (data not shown). Lack of CXCR5 and CCR6, homing receptors for mature B cells, supported our view that Eμ-Myc lymphomas were in a precursor B-cell differentiation stage.
Applying quantitative real time RT-PCR, substantial expression for LTα, LTβ, and TNF-α was obtained in both Wt Eμ-Myc and CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc cells (Figure 1B). Homeostatic chemokines were modestly or not at all expressed, thus precluding potential autocrine stimulatory signaling loops.
CCR7 regulates lymphoma cell homing in vivo
Several clinical studies correlated CCR7 expression and B-cell NHL localization within SLO; however, a genetic in vivo model that would mimic such biologic behavior is missing. To establish a genetically defined lymphoma model, we crossed CCR7−/− animals with Eμ-Myc transgenic mice. On average, Eμ-Myc transgenic mice (Wt Eμ-Myc mice) developed fatal lymphoma after 10 weeks (10 ± 4.8 weeks; n = 10), whereas CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc double-transgenic mice exhibited a delay in the development of fatal lymphoma of > 5 weeks (16.4 ± 5.6 weeks; n = 12; P = .01). Spontaneous tumors taken from such moribund Wt and CCR7-deficient Eμ-Myc mice exhibited comparable levels of apoptosis activity, as shown by annexin V +/7-AAD+ staining and caspase 3 cleavage (supplemental Figure 1A-B). Likewise, at this final disease stage, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activity as indicators of mitogenic signaling were comparable (supplemental Figure 1B).
Lymphoma cells, derived from Wt Eμ-Myc mice, showed migratory capacity in vitro in response to the chemokine ligands CCL21 and CXCL12 (Figure 1C) and no migration to CXCL13 (data not shown). CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc cells exhibited no migration toward CCL21, but the expected migration to CXCL12 (Figure 1C). Taken together, Eμ-Myc lymphoma B cells are equipped with 2 functional LN homing receptors. In conjunction with the integrins expressed, this pattern qualifies lymphoma cells for access to SLOs.
Lymphoma B cells derived from moribund Wt Eμ-Myc or CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc mice were isolated from LNs and used for transfer (intravenously) into Wt congenic recipients. This lymphoma transplant approach allowed us to compare growth kinetics of Wt and CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc cells; furthermore, in contrast to spontaneous tumors, sequence and spatial aspects of invasion and localization could be addressed. Thus, this approach was instrumental in dissecting the conditions for early growth-promoting effects.
In recipients of Wt lymphoma cells (n = 16), disease progression was highly synchronized and LNs became palpable between days 10 and 14, followed by the development of fatal disease between days 18 and 21 (Figure 1D). Strikingly, CCR7 deficiency markedly delayed lymphoma onset. In 3 independent experiments (n = 19 mice), recipients of CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells did not develop any palpable LNs up to 21 days after treatment (Figure 1D). Animals remained clinically healthy in 2 additional trials, even beyond 35 days (data not shown).
In mice that received Wt Eμ-Myc tumor cells, lymphoma cells were readily detectable in peripheral blood, spleen, LNs, and bone marrow at day 6 and at day 11 (Figure 1E). Thymus was only marginally infiltrated (< 1% tumor cells) up to 14 days after tumor challenge. At later time points (days 18-21), enlarged thymi resulting from heavy tumor load were occasionally detectable (data not shown). CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc cells were barely seen at day 6 in any of the compartments analyzed here (Figure 1E). At day 11, CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells were detectable in spleen and periphery, but at a significantly decreased number compared with control tumor cells. Strikingly, LNs, bone marrow, and thymus were almost devoid of CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells up to days 11 to 14 (Figure 1E).
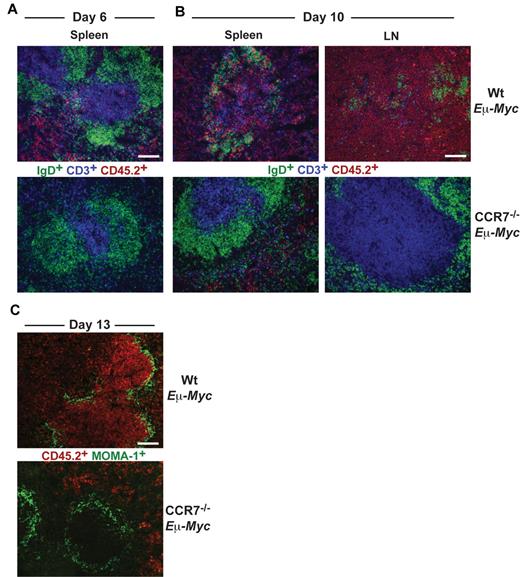
Wt Eμ-Myc tumor cells infiltrated red pulp and T-cell zone of spleen at day 6 (Figure 2A), whereas B-cell zones were largely spared. Later (day 10), Wt Eμ-Myc tumor cell infiltration of all areas within spleen and LN progressed and ultimately destroyed tissue microarchitecture (Figure 2B). In contrast, CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells first appeared within splenic red pulp at day 10 but remained clearly absent from the T-cell zone or from LNs (Figure 2B).
Differential homing preferences of Wt and CCR7-deficient lymphoma cells. Localization of tumor cells within the spleen at day 6 (A) and within LNs and spleen at day 10 (B) after tumor cell transfer. Frozen sections were immunofluorescently stained for CD45.2+ tumor cells (red), CD3+ T cells (blue), and IgD+ B cells (green). Scale bars represent 100 μm. (C) Staining for CD45.2+ tumor cells (red) and for MOMA-1+ metallophilic macrophages (green) 13 days after transfer of Wt or CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc tumor cells. Scale bars represent 100 μm.
Differential homing preferences of Wt and CCR7-deficient lymphoma cells. Localization of tumor cells within the spleen at day 6 (A) and within LNs and spleen at day 10 (B) after tumor cell transfer. Frozen sections were immunofluorescently stained for CD45.2+ tumor cells (red), CD3+ T cells (blue), and IgD+ B cells (green). Scale bars represent 100 μm. (C) Staining for CD45.2+ tumor cells (red) and for MOMA-1+ metallophilic macrophages (green) 13 days after transfer of Wt or CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc tumor cells. Scale bars represent 100 μm.
At day 13, Wt Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells heavily infiltrated the white pulp and additionally infiltrated and partially destroyed the marginal zone (MOMA-1+). In sharp contrast, CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells were completely excluded from the white pulp and also from the marginal zone (Figure 2C). Overall, these data suggested that CCR7 is a crucial homing factor for Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells into LNs, but also into spleen.
CCR7 confers access of Eμ-Myc lymphoma B cells to prosurvival signals in vivo
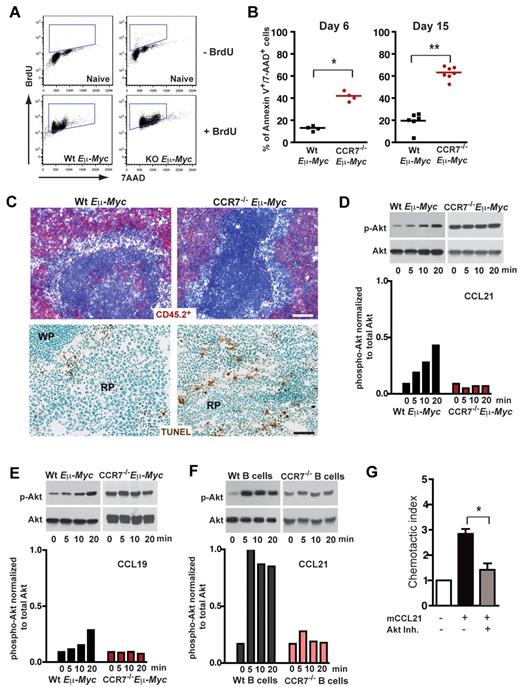
Extended survival of mice transplanted with CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells could relate to a reduced proliferation rate within SLOs. Alternatively, CCR7-deficient lymphoma cells might lack survival signals provided by a local environment, a supply that is advantageous for early onset of tumor growth. When Eμ-Myc lymphoma cell recipient mice were treated for 16 hours with 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine (BrdU), followed by anti BrdU/7-AAD staining of splenic lymphoma cells (B220+/CD45.2+), no proliferation advantage of CCR7-proficient cells could be observed (Figure 3A). The proliferative fraction (BrdU+) was 81.37% ± 4.68% for Wt and 86.38% ± 5.38% for CCR7−/− lymphomas (P = not significant). In contrast, CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells exhibited a significantly increased fraction of late apoptotic cells (annexin V+/7-AAD+), analyzed by flow cytometry either on day 6 (Wt, 13.6% ± 2.2%; CCR7−/−, 42.05% ± 4.3%; P < .05) or on day 15 (Wt, 19.63% ± 7.9%; CCR7−/−, 63.27% ± 5.7%; P < .005) after transfer (Figure 3B). Although only a minor TUNEL staining in spleen populated with Wt lymphoma cells was obtained, substantial numbers of TUNEL-positive CCR7−/− lymphoma cells within the red pulp of the spleen were seen (Figure 3C).
CCR7 mediates prosurvival signals in vivo. (A) Proliferation rate of transplanted Wt (n = 3) and CCR7-deficient lymphoma cells (n = 4) in congenic recipient mice was assessed 16 hours after intraperitoneal injection of 1 mg/animal BrdU. As a control, B cells (B220+) from untreated mice (n = 2), without lymphoma cell and BrdU application, are shown in the top panel. Viable lymphoma cells (gated on B220+/CD45.2+) were stained for BrdU and 7-AAD; gated boxes represent the fraction of BrdU+ proliferating cells (bottom panel). (B) Congenic mice were transferred with 1 × 105 Wt or CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells. Six (n = 4 mice per group) and 15 days (n = 6 or 7 mice per group) after tumor challenge, gated tumor cells (CD45.2+) were stained with annexin V and 7-AAD and analyzed by flow cytometry. Graph represents fraction of late apoptotic cells (annexin V+/7-AAD+). *P ≤ .05; **P ≤ .01. (C) Frozen spleen sections were stained for CD45.2+ (red; top panel). Tumor cell load for Wt (day 11; n = 3) and CCR7−/− lymphomas (day 28; n = 3) in splenic red pulp was comparable. Scale bars represent 100 μm. TUNEL staining (brown; bottom panel) of paraformaldehyde-fixed spleen sections (Wt, n = 4; CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc splenic tumors, n = 6). Scale bars represent 50 μm. (D-F) Akt phosphorylation on stimulation with CCL19 or CCL21. Freshly isolated LN-derived Wt or CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells were stimulated with CCL21 (D) and CCL19 (E). In addition, splenic Wt or CCR7−/− B cells were stimulated with CCL21 (F). Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting (top panels) for activation-induced Akt phosphorylation (p-Akt), and quantitation of phosphorylation relative to total Akt is shown in the bottom panels (D-F). One representative experiment of 13 (Wt Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells) and 4 (CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells) independent experiments (D). One representative experiment of 4 (Wt lymphoma cells) and 1 (CCR7−/− lymphoma cells) independent experiments (E). One representative experiment of 4 (Wt B cells) and 2 (CCR7−/− B cells) independent experiments (F). (G) Chemotaxis of tumor cells derived from Wt Eμ-Myc transgenic mice toward CCL21 (100nM) in the presence or absence of Akt inhibitor (20μM). Error bars represent SD for 4 independent experiments with triplicates per each group. *P ≤ .05.
CCR7 mediates prosurvival signals in vivo. (A) Proliferation rate of transplanted Wt (n = 3) and CCR7-deficient lymphoma cells (n = 4) in congenic recipient mice was assessed 16 hours after intraperitoneal injection of 1 mg/animal BrdU. As a control, B cells (B220+) from untreated mice (n = 2), without lymphoma cell and BrdU application, are shown in the top panel. Viable lymphoma cells (gated on B220+/CD45.2+) were stained for BrdU and 7-AAD; gated boxes represent the fraction of BrdU+ proliferating cells (bottom panel). (B) Congenic mice were transferred with 1 × 105 Wt or CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells. Six (n = 4 mice per group) and 15 days (n = 6 or 7 mice per group) after tumor challenge, gated tumor cells (CD45.2+) were stained with annexin V and 7-AAD and analyzed by flow cytometry. Graph represents fraction of late apoptotic cells (annexin V+/7-AAD+). *P ≤ .05; **P ≤ .01. (C) Frozen spleen sections were stained for CD45.2+ (red; top panel). Tumor cell load for Wt (day 11; n = 3) and CCR7−/− lymphomas (day 28; n = 3) in splenic red pulp was comparable. Scale bars represent 100 μm. TUNEL staining (brown; bottom panel) of paraformaldehyde-fixed spleen sections (Wt, n = 4; CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc splenic tumors, n = 6). Scale bars represent 50 μm. (D-F) Akt phosphorylation on stimulation with CCL19 or CCL21. Freshly isolated LN-derived Wt or CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells were stimulated with CCL21 (D) and CCL19 (E). In addition, splenic Wt or CCR7−/− B cells were stimulated with CCL21 (F). Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting (top panels) for activation-induced Akt phosphorylation (p-Akt), and quantitation of phosphorylation relative to total Akt is shown in the bottom panels (D-F). One representative experiment of 13 (Wt Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells) and 4 (CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells) independent experiments (D). One representative experiment of 4 (Wt lymphoma cells) and 1 (CCR7−/− lymphoma cells) independent experiments (E). One representative experiment of 4 (Wt B cells) and 2 (CCR7−/− B cells) independent experiments (F). (G) Chemotaxis of tumor cells derived from Wt Eμ-Myc transgenic mice toward CCL21 (100nM) in the presence or absence of Akt inhibitor (20μM). Error bars represent SD for 4 independent experiments with triplicates per each group. *P ≤ .05.
It has been appreciated that p53 is the dominant tumor suppressor in Myc-induced lymphomagenesis.5,25 In Eμ-Myc transgenic Wt mice, loss of the protective effect of p53, either through gene deletion or mutations that disable p53 phosphorylation sites for Ser/Thr kinases, including ATM, ATR, Chk1, and Chk2, leads invariably to lymphomagenesis.26 Although the mutational status of p53 in Wt Eμ-Myc lymphomas has been shown in the past,4,27,28 we could confirm low levels of p53 protein but also lack of 18-S phosphorylation in 7 of 9 CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphomas as well (supplemental Figure 2). This indicates that CCR7-deficient lymphomas exhibited similar frequencies of apoptosis defects as Wt Eμ-Myc lymphomas.
In head-and-neck cancer cells, autocrine-stimulated CCR7 mediated a survival advantage through engagement of the Akt signaling pathway.29 Furthermore, constitutive Akt signaling cooperates with Myc to accelerate B-cell lymphomagenesis.30 Here, we stimulated freshly isolated Eμ-Myc lymphoma B cells (Figure 3D-E) and splenic B cells (Figure 3F) with the CCR7 ligands CCL21 or CCL19. A time-dependent increase of Akt phosphorylation occurred after stimulation with CCL21 or CCL19, which was not the case for CCR7-deficient lymphoma or splenic B cells (Figure 3D-F).
To investigate the functional significance of Akt-pathway activation during CCR7-receptor signaling, we added CCL19 (supplemental Figure 3) or CCL21 (data not shown) to Eμ-Myc lymphoma cell cultures, in the absence and presence of Akt inhibitor. However, we failed to obtain a survival advantage in cultures supplied with the chemokines. Instead, when Akt inhibitor was included in a chemotaxis assay, CCL21 induced migration was significantly diminished (Figure 3G). Of note, Akt inhibitor-mediated proapoptotic effects were not observed in this short-term migration assay. Collectively, these data indicated that CCR7-mediated engagement of the Akt pathway controls the migratory pattern of lymphoma cells to a growth-promoting environment.
Stromal cell networks support early Eμ-Myc lymphoma lodging
In early disease stages, CCR7 mediated the access of Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells to the T-cell zone. A major T-cell zone stroma cell network is represented by gp38+ FRCs.19 In addition, signaling pathways contributing to neogenesis and lymphoid homeostasis have been partially elucidated under physiologic conditions.
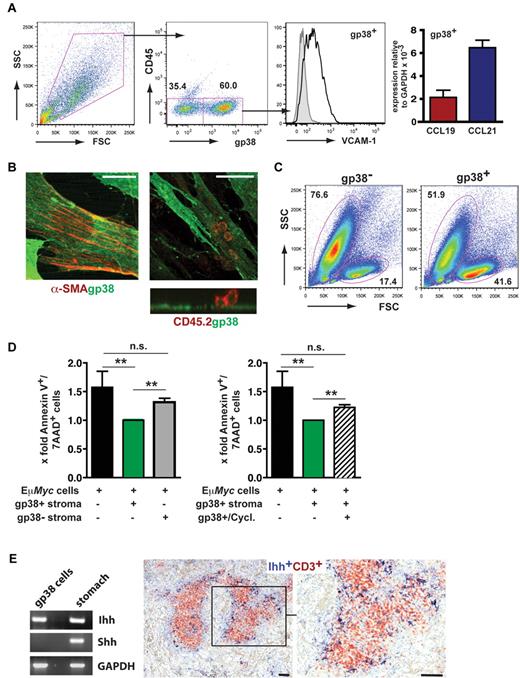
To prove whether the same structural and molecular elements supported malignant B cells in vivo, we analyzed the spatial arrangement in diseased spleen. Wt Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells lodged within the T-cell zone and intermingled with the gp38+ FRC network (Figure 4A top row). In contrast, CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells were excluded from this T-cell zone niche and restricted to the red pulp. Wt tumor cell expansion induced a dramatic reduction of CD3+ T cells (Figure 4A middle panel), whereas the gp38+ FRC network still remained intact (Figure 4A bottom panel). In this niche, CCL21 was provided by gp38+ cells, as evidenced by gp38+ CCL21+ costaining (Figure 4A bottom panel). The gp38+/CD45− stroma cell population exhibited a significant expansion in tumor-bearing mice compared with untreated animals (untreated mice, 0.40% ± 0.25%; Wt Eμ-Myc, 7.26% ± 5.35%; P < .05; Figure 4B). In contrast, relative frequencies of a CD11b+ Gr-1+ stroma cell population, also referred to as immature myeloid cells, was not altered (Figure 4C; untreated mice 1.58% ± 0.65%; Wt Eμ-Myc mice 2.16% ± 1.50%; P = not significant). We conclude that, within the gp38+ FRC network, tumor cells receive paracrine signals, among them CCL21.
Induction of stromal networks supports Eμ-Myc lymphoma growth. (A) Congenic recipient mice were transplanted with Wt and CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells, as described in Figure 2. Localization of malignant B cells in diseased spleens was visualized by immunofluorescence staining of frozen tissue sections. Wt and CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells (blue, CD45.2+), gp38+ FRC network (red), B-cell zones (green, IgD+). Wt Eμ-Myc tumor cell (blue) expansion within and adjacent to the T-cell zone (middle panel: red represents CD3+ T cells; and green, dendritic cells, CD11c+). Colocalization (in yellow) of gp38+ FRC network (red) with the chemokine CCL21 (green) (lower panel). Scale bars represent 100 μm. At higher resolution obtained by confocal microscopy imaging, CCL21 staining largely overlaps with gp38 fluorescence (merged images, yellow; bottom panel, right, representative z-stack). Scale bar represents 25 μm. Data are representative of at least 3 independent experiments, with n = 4 or 5 mice per group. (B-C) Spleen from naive (n = 5) and Wt Eμ-Myc transplanted mice (days 10-13; n = 6) were collagenase-treated, followed by antibody staining and flow cytometric analysis. Percentages of gated gp38+/CD45− and CD11b+/Gr-1+ stroma cells are shown in the plots. *P ≤ .05 for gp38+/CD45−. P = not significant for CD11b+/Gr-1+.
Induction of stromal networks supports Eμ-Myc lymphoma growth. (A) Congenic recipient mice were transplanted with Wt and CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells, as described in Figure 2. Localization of malignant B cells in diseased spleens was visualized by immunofluorescence staining of frozen tissue sections. Wt and CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells (blue, CD45.2+), gp38+ FRC network (red), B-cell zones (green, IgD+). Wt Eμ-Myc tumor cell (blue) expansion within and adjacent to the T-cell zone (middle panel: red represents CD3+ T cells; and green, dendritic cells, CD11c+). Colocalization (in yellow) of gp38+ FRC network (red) with the chemokine CCL21 (green) (lower panel). Scale bars represent 100 μm. At higher resolution obtained by confocal microscopy imaging, CCL21 staining largely overlaps with gp38 fluorescence (merged images, yellow; bottom panel, right, representative z-stack). Scale bar represents 25 μm. Data are representative of at least 3 independent experiments, with n = 4 or 5 mice per group. (B-C) Spleen from naive (n = 5) and Wt Eμ-Myc transplanted mice (days 10-13; n = 6) were collagenase-treated, followed by antibody staining and flow cytometric analysis. Percentages of gated gp38+/CD45− and CD11b+/Gr-1+ stroma cells are shown in the plots. *P ≤ .05 for gp38+/CD45−. P = not significant for CD11b+/Gr-1+.
T-cell zone FRCs confer survival signals for naive T cells by secreting interleukin-7 and the CCR7 ligand CCL19.19 To investigate whether this stromal cell population provided survival factors and chemoattractants for Eμ-Myc cells as well, we isolated LN- and spleen-derived gp38+ cells. Cultured stromal cells exhibited a gp38+/CD45−/VCAM-1+ surface marker profile and expressed mRNA for CCL19 and CCL21 (Figure 5A). Moreover, gp38+ cells grown on collagen-coated slides were stained for the myofibroblast marker α-smooth muscle actin (Figure 5B). In coculture with Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells (CD45.2+), we could visualize a tight interaction between both cell types (Figure 5B). Notably, tumor cells grown in close contact with the stromal layer usually exhibited a viable morphology, whereas tumor cells separated from gp38+ stromal cells often developed an apoptotic morphology (data not shown). We cultured freshly isolated Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells on an adherent layer of such stromal cells containing 40%-60% gp38+/CD45−/VCAM-1high FRCs. Already after 20 hours, a significantly enhanced survival of Eμ-Myc lymphoma B cells was seen (Figure 5C-D). In contrast, survival in the presence of a gp38−/CD45− stroma cell fraction was diminished (Figure 5D left panel).
FRCs support the survival of Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells in vitro. (A) Analysis of single-cell suspensions prepared from spleen and LNs by collagenase digestion (n = 4 mice), followed by in vitro culture for 3 to 7 days (n = 4 experiments). Cells were stained with anti-gp38, anti-CD45, and anti–VCAM-1. On the right, quantitative RT-PCR analysis of cell cultures that were further depleted of CD11b+ macrophages. CCL19 and CCL21 gene expression relative to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (n = 2 experiments). (B) Confocal microscopy analysis of in vitro cultured gp38+ stromal cells. Cells were stained with anti-gp38 (green) and anti-α smooth muscle actin (SMA); (red) antibodies. Anti-CD45 antibody (red) was used to detect lymphoma cells in close contact to gp38+ stromal cells (right). (Bottom) A reconstructed side view along the contact zone between gp38+ layer and tightly adherent tumor cells (n = 2 experiments). (Left) Scale bar represents 20 μm. (Middle and right) Scale bars represent 50 μm. (C) Forward scatter (FSC) and side scatter (SSC) profiles of freshly isolated Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells cocultured for 20 hours with or without stromal cells containing approximately 60% gp38+/CD45− cells. (D) Lymphoma cells were cocultured with the gp38+/CD45− fraction, or the gp38− stroma cell fraction. For inhibition of hedgehog signaling, cyclopamine (20μM) was included for 20-22 hours (right panel). Lymphoma cell apoptosis was assessed by annexin V and 7-AAD staining. Results are given as x-fold cell death relative to lymphoma cells grown in the presence of stromal cells, set arbitrarily to 1 (n = 7 independent experiments). **P ≤ .01. n.s. indicates not significant. (E) RT-PCR analysis for Ihh and Shh. RNA derived from gp38+/CD45− enriched stromal cells and stomach (left panel). The hedgehog protein Ihh is located within the T-cell zone of splenic white pulp. Formalin-fixed spleen sections from Wt animals were stained with goat anti–mouse CD3 to detect T cells (red), and a rabbit anti–mouse Ihh antibody (dark blue) to stain stromal cells. (Right) Magnification of boxed inset on the left. Scale bars represent 100 μm.
FRCs support the survival of Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells in vitro. (A) Analysis of single-cell suspensions prepared from spleen and LNs by collagenase digestion (n = 4 mice), followed by in vitro culture for 3 to 7 days (n = 4 experiments). Cells were stained with anti-gp38, anti-CD45, and anti–VCAM-1. On the right, quantitative RT-PCR analysis of cell cultures that were further depleted of CD11b+ macrophages. CCL19 and CCL21 gene expression relative to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (n = 2 experiments). (B) Confocal microscopy analysis of in vitro cultured gp38+ stromal cells. Cells were stained with anti-gp38 (green) and anti-α smooth muscle actin (SMA); (red) antibodies. Anti-CD45 antibody (red) was used to detect lymphoma cells in close contact to gp38+ stromal cells (right). (Bottom) A reconstructed side view along the contact zone between gp38+ layer and tightly adherent tumor cells (n = 2 experiments). (Left) Scale bar represents 20 μm. (Middle and right) Scale bars represent 50 μm. (C) Forward scatter (FSC) and side scatter (SSC) profiles of freshly isolated Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells cocultured for 20 hours with or without stromal cells containing approximately 60% gp38+/CD45− cells. (D) Lymphoma cells were cocultured with the gp38+/CD45− fraction, or the gp38− stroma cell fraction. For inhibition of hedgehog signaling, cyclopamine (20μM) was included for 20-22 hours (right panel). Lymphoma cell apoptosis was assessed by annexin V and 7-AAD staining. Results are given as x-fold cell death relative to lymphoma cells grown in the presence of stromal cells, set arbitrarily to 1 (n = 7 independent experiments). **P ≤ .01. n.s. indicates not significant. (E) RT-PCR analysis for Ihh and Shh. RNA derived from gp38+/CD45− enriched stromal cells and stomach (left panel). The hedgehog protein Ihh is located within the T-cell zone of splenic white pulp. Formalin-fixed spleen sections from Wt animals were stained with goat anti–mouse CD3 to detect T cells (red), and a rabbit anti–mouse Ihh antibody (dark blue) to stain stromal cells. (Right) Magnification of boxed inset on the left. Scale bars represent 100 μm.
It has been shown that hedgehog (Hh) pathway inhibition in lymphomas induced apoptosis.31 In isolated gp38+ cells, RT-PCR analysis demonstrated exclusive expression of indian hedgehog (Ihh), but not of sonic hedgehog (Shh; Figure 5E left panel). Ihh protein expression was readily confirmed by immunohistochemistry (Figure 5E right panel). The Ihh-producing cell population localized within the T-cell zone. To verify the importance of the Hh pathway for lymphoma survival in the FRC coculture system, we included the inhibitor cyclopamine, which binds to Smoothened (Smo) and arrests its inactive conformation.32 Cyclopamine treatment of Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells cultivated on gp38+ cells resulted in a significant reduction of viability already within 20-22 hours (Figure 5D right panel). Collectively, these data indicated that T-cell zone localization of Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells confers resistance to spontaneous apoptosis through the proximity to FRCs, which provide the hedgehog protein Ihh.
Maintenance or development of the stromal network requires a reciprocal stimulation between lymphocytes and stromal cells, a process where LTβR signaling is intimately involved. We made use of Rag−/− mice, which lack T- and B-cell zone stromal networks (supplemental Figure 4A-B). Rag−/− mice were reconstituted with CD4+ T lymphocytes 4 days before tumor cell injection and screened for tumor cell load within spleen (Figure 6A) and LNs (data not shown). CD4+ T cell–reconstituted recipients exhibited significantly enhanced tumor growth compared with nonreconstituted controls. Furthermore, CD4+ T-cell administration led to de novo induction of gp38+ FRC networks 13 days after tumor challenge. T cell deficient controls lacked the induction of gp38+ stromal cells (Figure 6B).
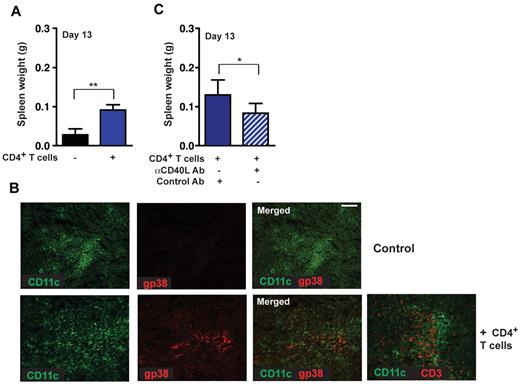
CD4+ T cell–mediated induction of gp38+ stromal cell networks enhances lymphoma growth. (A) Rag−/− mice were reconstituted with 5 × 106 naive CD4+ T cells (day −4) and challenged with 1 × 105 Wt Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells. Tumor load in the spleen was assessed 13 days after tumor challenge. Reconstituted Rag−/− mice 13 days after tumor challenge compared with nontreated controls (n = 6 or 7 mice per group). **P ≤ .01. (B) CD4+ T cell–reconstituted Rag−/− mice exhibited induction of gp38+ FRC networks (bottom panel: red represents FRCs; and green, CD11c+). Adoptively transferred T cells can also be visualized at this site (bottom panel right: red represents CD3+ T cells; n = 5 animals per group). Scale bars represent 100 μm. (C) In vivo blockage of the CD40 signaling pathway by treatment of Rag−/− mice with 3 × 200 μg anti-CD40L antibody in 5-day intervals starting on day 0, or control hamster antibody (n = 6 mice per group). *P ≤ .05. Rag−/− mice were reconstituted with 3 × 106 CD4+ T and challenged with 2 × 104 tumor cells. At day 13, tumor load in the spleen was assessed by weight.
CD4+ T cell–mediated induction of gp38+ stromal cell networks enhances lymphoma growth. (A) Rag−/− mice were reconstituted with 5 × 106 naive CD4+ T cells (day −4) and challenged with 1 × 105 Wt Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells. Tumor load in the spleen was assessed 13 days after tumor challenge. Reconstituted Rag−/− mice 13 days after tumor challenge compared with nontreated controls (n = 6 or 7 mice per group). **P ≤ .01. (B) CD4+ T cell–reconstituted Rag−/− mice exhibited induction of gp38+ FRC networks (bottom panel: red represents FRCs; and green, CD11c+). Adoptively transferred T cells can also be visualized at this site (bottom panel right: red represents CD3+ T cells; n = 5 animals per group). Scale bars represent 100 μm. (C) In vivo blockage of the CD40 signaling pathway by treatment of Rag−/− mice with 3 × 200 μg anti-CD40L antibody in 5-day intervals starting on day 0, or control hamster antibody (n = 6 mice per group). *P ≤ .05. Rag−/− mice were reconstituted with 3 × 106 CD4+ T and challenged with 2 × 104 tumor cells. At day 13, tumor load in the spleen was assessed by weight.
To analyze the role of CD4+ T cells in lymphoma progression in further detail, CD40-CD40L interactions were blocked through treatment of CD4+ T cell–reconstituted Rag−/− recipients with an anti-CD40L antibody. In these mice, we observed significantly decreased tumor growth compared with mice treated with a control antibody (Figure 6C). Thus, targeting CD40L inhibited CD4+ T cell–mediated proliferation induction in Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells.
The LTα-LTβR system controls the formation of T zone stromal cell networks, which support localization and progression of Eμ-Myc lymphomas
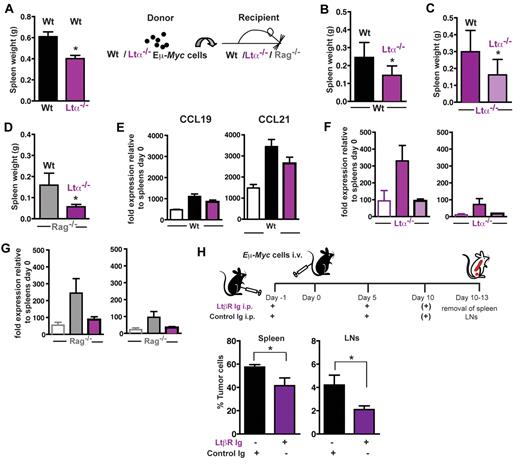
LTβR signaling is intimately linked to the expression of adhesion molecules and the homeostatic chemokines CCL19/CCL21 within the T-cell zone, thus contributing to T- and B-cell zone compartmentalization. In addition, gp38+ reticular cell networks are strongly influenced by the LTα-LTβR system. Here, tumor cells were transferred into LTα−/− animals, which exhibit a severe reduction of stromal gp38+ cells (supplemental Figure 4). At day 15 (Figure 7A), splenic tumor load in LTα−/− recipient mice was significantly decreased. Because the lymphoma cell itself is also a source for LTα production (Figure 1B), we additionally generated LTα−/− Eμ-Myc double-transgenic mice as a source for transplantable tumors. Transfer of LTα-deficient lymphoma cells into congenic Wt recipients resulted in significantly decreased splenic tumor burden (Figure 7B), which could be further reduced when LTα-deficient lymphoma cells were transferred into LTα−/− animals (Figure 7C).
LTα-LTβR signaling enhances expression of CCL19 and CCL21 and supports Eμ-Myc lymphoma progression. (A) A total of 2 × 104 Wt Eμ-Myc GFP tumor cells were intravenously transferred into LTα−/− recipients (n = 4) and Wt controls (n = 5). At day 15, splenic tumor load was compared and expressed as splenic weight. Error bars represent mean ± SD of 2 independent experiments. *P ≤ .05. (B) A total of 2 × 104 Wt (n = 6) or LTα−/− Eμ-Myc tumor cells (n = 7) were intravenously transferred into congenic Wt recipients. At days 15-18 after tumor challenge, tumor load in the spleen was assessed by flow cytometry. Error bars represent mean ± SD of 2 independent experiments. *P ≤ .05. (C) A total of 2 × 104 Wt (n = 7) or LTα−/− Eμ-Myc tumor cells (n = 6) were intravenously transferred into LTa−/− recipients. At days 14-18 after tumor challenge, tumor load in the spleen was expressed as splenic weight. Error bars represent mean ± SD of 2 independent experiments. *P ≤ .05. (D) A total of 5 × 104 Wt (n = 3) or LTα−/− Eμ-Myc tumor cells (n = 3) were intravenously transferred into Rag−/− recipients. At day 17 after tumor challenge, tumor load in the spleen was expressed as splenic weight. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. *P ≤ .05. In one of the 2 experiments performed in panels B to D, splenic CCL19 and CCL21 mRNA expression of tumor challenged Wt or KO recipients was analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR (E-G). Open bars represent basal splenic CCL19 and CCL21 level of Wt (E), LTα−/− (F), and Rag−/− (G) mice. The relative CCL19 and CCL21 RNA levels of tumor-challenged mice (n = 2-4 per group) were calculated as described in “RNA extraction and RT-PCR.” (H) In vivo blockage of the LTβR signaling pathway by treatment of tumor cell recipient mice with 100 μg LTβR-Ig (n = 13) intraperitoneally in 5-day intervals starting on day −1, or control mouse IgG1 (MOCP21; n = 9), as described. Ten to 13 days after tumor challenge (1 × 105 Eμ-Myc GFP tumor cells), tumor load in spleen and LNs was assessed by flow cytometry. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. *P ≤ .05.
LTα-LTβR signaling enhances expression of CCL19 and CCL21 and supports Eμ-Myc lymphoma progression. (A) A total of 2 × 104 Wt Eμ-Myc GFP tumor cells were intravenously transferred into LTα−/− recipients (n = 4) and Wt controls (n = 5). At day 15, splenic tumor load was compared and expressed as splenic weight. Error bars represent mean ± SD of 2 independent experiments. *P ≤ .05. (B) A total of 2 × 104 Wt (n = 6) or LTα−/− Eμ-Myc tumor cells (n = 7) were intravenously transferred into congenic Wt recipients. At days 15-18 after tumor challenge, tumor load in the spleen was assessed by flow cytometry. Error bars represent mean ± SD of 2 independent experiments. *P ≤ .05. (C) A total of 2 × 104 Wt (n = 7) or LTα−/− Eμ-Myc tumor cells (n = 6) were intravenously transferred into LTa−/− recipients. At days 14-18 after tumor challenge, tumor load in the spleen was expressed as splenic weight. Error bars represent mean ± SD of 2 independent experiments. *P ≤ .05. (D) A total of 5 × 104 Wt (n = 3) or LTα−/− Eμ-Myc tumor cells (n = 3) were intravenously transferred into Rag−/− recipients. At day 17 after tumor challenge, tumor load in the spleen was expressed as splenic weight. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. *P ≤ .05. In one of the 2 experiments performed in panels B to D, splenic CCL19 and CCL21 mRNA expression of tumor challenged Wt or KO recipients was analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR (E-G). Open bars represent basal splenic CCL19 and CCL21 level of Wt (E), LTα−/− (F), and Rag−/− (G) mice. The relative CCL19 and CCL21 RNA levels of tumor-challenged mice (n = 2-4 per group) were calculated as described in “RNA extraction and RT-PCR.” (H) In vivo blockage of the LTβR signaling pathway by treatment of tumor cell recipient mice with 100 μg LTβR-Ig (n = 13) intraperitoneally in 5-day intervals starting on day −1, or control mouse IgG1 (MOCP21; n = 9), as described. Ten to 13 days after tumor challenge (1 × 105 Eμ-Myc GFP tumor cells), tumor load in spleen and LNs was assessed by flow cytometry. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. *P ≤ .05.
When LTα-deficient lymphoma cells were injected into Rag−/− mice, which lack lymphocytes and the gp38+ FRC network, a decreased splenic tumor load compared with transfer of Wt Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells was obtained (Figure 7D). In summary, LTα production by tumor cells and surrounding host lymphocytes contributes to lymphoma growth.
Because LTβR signaling increases production of homeostatic chemokines by stromal cells (ie, gp38+ FRCs), we compared CCL19 and CCL21 mRNA levels in spleens of tumor challenged mice with untreated controls (Figure 7E-G). Chemokine gene expression levels in untreated LTα−/− and Rag−/− compared with Wt mice were much lower. However, when Wt, LTα−/−, and Rag−/− mice were challenged with Wt Eμ-Myc cells, they exhibited enhanced gene expression of both chemokines compared with their respective untreated controls. In the recipient strains, gene expression for both chemokines was much lower when LTα−/− lymphoma cells were transplanted instead of Wt tumor cells (Figure 7E-G). When LTα−/− and Rag−/− mice were used as recipients of LTα−/− lymphomas, tumor-induced expression of CCL19 and CCL21 was almost completely abolished (Figure 7F-G). Thus, LTα, which is produced by lymphoma B cells and host lymphocytes, induces production of CCL19 and CCL21 in stroma cells.
In support of a reciprocal cross-talk mediated by LTα-LTβR interaction, in vitro coculture of freshly isolated lymphoma B cells and FRCs induced an up-regulation of VCAM-1 on stroma cells (supplemental Figure 5A). Furthermore, transfer of Wt, but not LTα-deficient Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells, into mice stimulated CCL21 gene expression in splenic FRCs (supplemental Figure 5B). Both gene expressions, VCAM-1 and CCL21, are indicative of LTβR signaling in FRCs.19,33,34 To address the consequences of an interruption in the LTα-LTβR signaling pathway in this lymphoma transfer model, Wt recipients were given the decoy receptor protein LTβR-Ig or mouse monoclonal IgG1 (MOPC21). When challenged with Wt lymphoma cells, analysis of tumor cell load in spleen and LNs exhibited a significant growth delay of the LTβR-Ig–treated group (Figure 7H; P < 0.05). Effective LTβR-Ig serum levels were confirmed by ELISA (supplemental Figure 6).
Taken together, interference with the LTβR signaling pathway leads to growth reduction of Eμ-Myc lymphomas, most likely through inhibition of a lymphoma cell–stroma cross-talk.
Discussion
In our report, we establish the link between CCR7 governed lymphoma homing and a LT-promoted cross-talk of tumor B-cells and T-cell zone stromal cells.
Applying a genetically defined mouse model, we found that the chemokine receptor CCR7 has a pivotal role in consecutive steps of lymphoma cell dissemination. First, in the absence of CCR7, spontaneous onset of disease in Eμ-Myc transgenic mice is delayed. In transfer models, recipients of CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells exhibited extended disease-free survival, decreased tumor burden, and a characteristic spatial positioning within spleen and LNs. Although CCR7−/− lymphoma cells were excluded from the T-cell zone, Wt lymphoma B cells lodged within the T-cell zone stroma in close proximity to the CCL19/CCL21 providing gp38+ cell population.35 Thus, this transfer model is suitable to resolve the conditions necessary for the earliest pathogenetic steps in lymphoma cell survival. On the contrary, despite a significant delay in spontaneous lymphoma development in CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc mice, proliferation and apoptosis status were similar in such Wt and CCR7−/− lymphomas, indicating that in a final disease stage Myc-induced hyperproliferation overcomes microenvironmental constraints. Localization of this B cell–derived lymphoma population is reminiscent of our former observations on classic Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes. These tumor cells localize to the paracortical T-cell zone areas of the LNs as well.9
In principle, Wt Eμ-Myc tumors arising in the B-cell compartment of an individual animal are widely considered a clonal entity.36,37 Loss of the dominant tumor suppressor activity, as mediated by p53, has been observed in high frequency in Wt Eμ-Myc lymphomas. Although p53 defects favor genomic instability, ensuing secondary genomic heterogeneity occurs within the primary transformed Eμ-Myc lymphoma; however, these effects do not alter the clonality of an individual lymphoma.5,25,38 From the levels of phospho-p53 and total p53 protein expression in 9 CCR7−/− Eμ-Myc lymphoma clones used here for transfer experiments, we infer that these lymphomas had no selective proapoptosis advantage over Wt lymphomas. Essentially, all CCR7−/− lymphomas grew with substantial delay, and transplantability was maintained even at low cell numbers (1-2 × 104; A.R. and U.E.H., data not shown).
The LTαβ-LTβR system controls the embryonic development of SLOs, whereas in the adult the microarchitecture needs to be maintained.39 Activation of LTβR on stromal cells, including FRCs, by B cell– or CD4+ T cell–displayed LTαβ40 maintains homeostatic chemokine expression, foremost CCL21 within the T-cell zone, thus creating a microenvironment that routes T lymphocytes reciprocally into this niche. Consistent with a survival-promoting function of the T-cell zone stroma, transfer of CD4+ T cells into Rag−/− recipients supported the formation of the gp38+ stromal network and allowed faster progression of Eμ-Myc lymphoma growth. We suggest that in this process T cells fulfill a dual function. They can present LTαβ necessary for LTβR activation on stromal cells, followed by stroma cell differentiation. Second, they can directly provide B-cell help through CD40L (CD154) expression. CD40 triggering can regulate a multitude of essential B-cell functions, including cell proliferation, survival, differentiation, antibody production, and development of humoral immune responses.41,42 Moreover, CD40 signals in B lymphocytes also enhance LT and TNF expression. Although we did not dissect CD40 signaling effects in more detail, antibody-mediated CD40L blockade in vivo revealed lymphoma growth inhibition. This effect would be consistent with a counterbalance of antiapoptotic and growth signals delivered via CD40, as seen in human NHL.43
Further support for a survival-promoting function of the T-cell zone stroma is indicated when Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells were transferred into LTα−/− recipients because tumor load in these mice was significantly decreased compared with Wt recipients. In addition, transfer of LTα-deficient lymphoma cells into Wt recipient mice delayed lymphoma progression.
Two recent reports proposed the importance of LTβR signaling and LTαβ production for tumor pathogenesis. In hepatocellular carcinoma, sustained hepatic LT expression in mice causes a sequel of events, including acute and chronic liver inflammation, eventually followed by hepatocellular carcinoma.44 Therapeutic LTβR inhibition was able to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma formation. In a prostate cancer model, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes stimulated castration-resistant growth of prostate cancer allografts.45 LTβ ablation in adoptively transferred B cells delayed growth of tumors. Taken together, both models provide a striking link between immune cell infiltration, chronic inflammation, and tumor pathogenesis.46 Molecularly, this link is dependent on LTβR- and nuclear factor-κB signaling.
In our model, tumor-bearing mice exhibited an expansion of the gp38+/CD45− FRC stroma cell population. This population could be derived from the conversion of mesenchymal stem cells under the influence of LTα and TNF, as has been shown in vitro for human B-cell NHL.47 The presence of gp38+/CD45− stromal cells conferred a selective survival advantage to Eμ-Myc lymphoma B cells. We suggest that FRC stromal structures exert a dual function. First, they release chemoattractants, including CCL19 and CCL21, which would allow lymphoma B cells to migrate into the T-cell zone. Second, we show that FRCs provide prosurvival signals, foremost the Hh ligand Ihh. This conclusion is in agreement with a previous paper by Diercks et al,31 where it was shown that LN and spleen-derived stromal cells supported Eμ-Myc lymphoma progression. Although this report convincingly demonstrated the tumor-promoting function of Hh signaling, stromal cell types involved in specific Hh provision remained elusive. Physiologically, Hh proteins induce signaling by binding to their receptor, Patched 1, which leads to Patched 1 inactivation and prevents it from inhibiting the receptor Smo. Smo activates GLI transcription factors, which regulate the expression of target genes involved in cell growth, survival, and proliferation.48 Consistent with a leading role of Hh signaling in lymphoma cell survival, in vitro we could reverse the prosurvival function of gp38+ stroma cells by inclusion of the Smo inhibitor cyclopamine.
In a reciprocal cross-talk, Eμ-Myc lymphoma B cells stimulate LTβR signaling through release of soluble or surface-bound LTαβ ligands. In vivo, we demonstrate that LTα-positive lymphoma cells enhance CCR7-ligand production in spleen, which could attract even more CCR7+ lymphoma B cells into the T-cell zone. Furthermore, the aggressive lymphoma progression on the expense of other SLO autochthonous cell populations might preclude the development of a CCL21-controlled regulatory immune cell recruitment. Notably, we observed a loss of CD3+ T cells and no gain of immunoregulatory myeloid derived suppressor cells.49
Inhibition of LTβR signaling using an IgG-coupled decoy receptor has provided a powerful tool in the amelioration of autoimmune diseases in murine disease models.50 Based on the identification of a strong T-cell zone stromal dependence of Eμ-Myc B-cell lymphomas, we took advantage of recombinant LTβR-Ig in our adoptive transfer model, presuming that adult stromal cells were also subject to LTβR signaling inhibition.51 Application of this immunomodulatory fusion protein led to a delay in lymphoma growth, which in a few extreme cases almost abrogated the emergence of tumor cells in spleen and LNs.
In conclusion, we provide the first in vivo genetic model for chemokine receptor-dependent lymphoma dissemination to and within SLOs. We dissect kinetic and spatial aspects of CCR7-dependent lymphoma cell lodging, a process that is intimately linked with lymphoma cell access to survival niches within the T-cell zone. In these niches, lymphoma cells engage LTβR signaling on stromal cells. In a reciprocal fashion, stromal cells enhance CCL19/CCL21 chemoattractant release. We show that targeting of the T-cell stroma-lymphoma interaction could provide a new strategy to control nodal B-cell lymphoma homing and expansion.
An Inside Blood analysis of this article appears at the front of this issue.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank J. L. Browning (Biogen Idec, Cambridge, MA) and S. Cayeux (Max-Delbrück-Center for Molecular Medicine, Berlin, Germany) for providing essential reagents, C. A. Schmitt (Charité, Berlin) for helpful suggestions, and K. Krüger, K. Räbel, H. Schwede, and M. Wiegand for excellent technical assistance.
This work was supported by the Deutsche Krebshilfe (grant 107749) and Berliner Krebsgesellschaft (U.E.H., A.R.).
Authorship
Contribution: A.R., A.M., K.S., K.G., S. Wittstock, S. Winter, G.B., and U.E.H. performed the experiments; A.R. and U.E.H. designed the study, analyzed the data, and wrote the paper; B.D. and M.L. edited the manuscript; and all authors discussed and commented on the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Uta E. Höpken, Max-Delbrück-Center for Molecular Medicine, 13125 Berlin, Germany; e-mail: uhoepken@mdc-berlin.de; and Armin Rehm, Max-Delbrück-Center for Molecular Medicine, 13125 Berlin, Germany; e-mail: arehm@mdc-berlin.de.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal