Abstract
The palmitoylation/depalmitoylation cycle of posttranslational processing is a potential therapeutic target for selectively inhibiting the growth of hematologic cancers with somatic NRAS mutations. To investigate this question at the single-cell level, we constructed murine stem cell virus vectors and assayed the growth of myeloid progenitors. Whereas cells expressing oncogenic N-RasG12D formed cytokine-independent colonies and were hypersensitive to GM-CSF, mutations within the N-Ras hypervariable region induced N-Ras mislocalization and attenuated aberrant progenitor growth. Exposing transduced hematopoietic cells and bone marrow from Nras and Kras mutant mice to the acyl protein thioesterase inhibitor palmostatin B had similar effects on protein localization and colony growth. Importantly, palmostatin B-mediated inhibition was selective for Nras mutant cells, and we mapped this activity to the hypervariable region. These data support the clinical development of depalmitoylation inhibitors as a novel class of rational therapeutics in hematologic malignancies with NRAS mutations.
Introduction
Ras proteins regulate cell fate by cycling between active GTP-bound and inactive GDP-bound conformations (Ras-GTP and Ras-GDP). RAS genes encode 4 proteins (N-Ras, H-Ras, K-Ras4A, and K-Ras4B) that have identical guanine nucleotide and effector binding domains but diverge substantially within the hypervariable region (HVR).1,2 Prenylation of the C-terminal cysteine and palmitoylation of other cysteines within the HVR of H-Ras and N-Ras induce a dynamic cycle of depalmitoylation and repalmitoylation that regulates subcellular trafficking. By contrast, K-Ras4B localizes to the plasma membrane (PM) by a mechanism that does not involve palmitoylation.1 Perturbation of palmitate turnover leads to a nonspecific distribution of H- and N-Ras to endomembranes and decreases signaling from the PM.3 This observation suggests that interfering with depalmitoylation might selectively reduce the growth of cancer cells with NRAS mutations, as normal K-Ras4B function would be preserved. Inhibiting oncogenic N-Ras signaling is particularly relevant in hematologic malignancies where NRAS is mutated more frequently than KRAS.4-9
Acyl protein thioesterase 1 (APT1) catalyzes Ras depalmitoylation.10 Dekker et al10 recently developed palmostatin B, a small molecule inhibitor with activity against APT1 that disrupted normal H-Ras subcellular localization and attenuated signaling in fibroblasts transformed with oncogenic Hras. Here we present genetic, cell biologic, and biochemical data with in vitro studies of palmostatin B that support targeting the depalmitoylation/repalmitoylation cycle in hematologic cancers characterized by oncogenic NRAS mutations.
Methods
Nras and Kras alleles containing an N terminal green fluorescent protein (GFP) marker were cloned into the murine stem cell virus (MSCV) vector with expression driven by the internal ribosomal entry site.11,12 Retrovirally transduced E14.5 fetal liver cells from inbred C57Bl/6 mice were plated in methylcellulose medium to assess CFU-GM growth as described previously.1,11,12 Biochemical analyses were performed on cultured macrophages that were differentiated from transduced GFP+ fetal liver cells in 50 ng/mL M-CSF.11,12 Cells were analyzed by confocal microscopy 7 days after differentiation using the Zeiss LSM 510 NLO Meta. Mx1-Cre; LSL-NrasG12D and Mx1-Cre; LSL-KrasG12D mice were injected with a single dose of polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid to induce Kras/Nras expression as previously described.13,14 Bone marrow cells from Mx1-Cre, LSL-NrasG12D and Mx1-Cre, LSL-KrasG12D mice with myeloproliferative disease (MPD) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) were harvested, and colony assays were performed as described.14-16 Mice with MPD were generated in the C57Bl/6 strain background, and the AML cells were generated by insertional mutagenesis in which C57Bl/6 × 129/Sv F1 mice were infected with the MOL4070LTR retrovirus.14,15 Palmostatin B was synthesized and suspended as described.10
Results and discussion
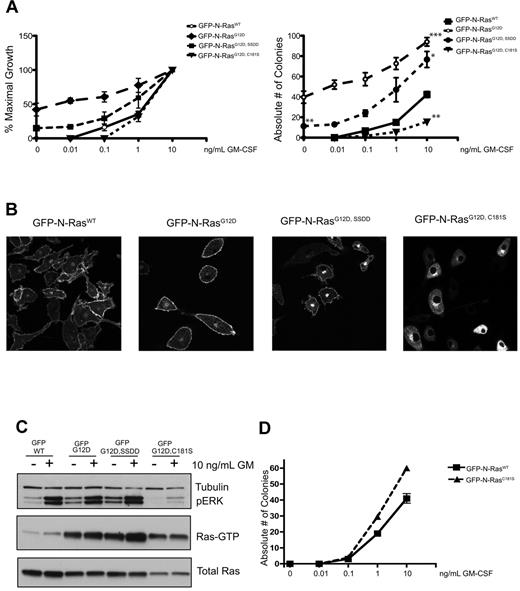
We generated MSCV vectors encoding N-terminal GFP fusions of wild-type (WT) N-Ras, N-RasG12D, N-RasG12D, C181S, and N-RasG12D, SSDD, which lacks a conserved SSDD (serine-serine-aspartic acid-aspartic acid) motif in the HVR domain that promotes stable palmitoylation.17 After transduction and sorting, CFU-GM growth from GFP+ mouse fetal liver cells was assessed over a range of GM-CSF concentrations. In all experiments, the growth of cells infected with an “empty” MSCV-internal ribosomal entry site–GFP vector was also assessed and was consistently similar to cells expressing WT N-Ras (supplemental Figure 1, available on the Blood Web site; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article). N-RasG12D expression induced cytokine-independent CFU-GM growth and conferred pronounced GM-CSF hypersensitivity (Figure 1A). Fetal liver cells expressing N-RasG12D, SSDD formed fewer colonies in the absence of GM-CSF and were less hypersensitive at low cytokine doses (Figure 1A). The C181S substitution abrogates the palmitoylation site in the N-Ras HVR. Cells expressing this mutant protein unexpectedly formed fewer CFU-GM colonies than control cells, suggesting dominant negative effects on hematopoietic growth (Figure 1A).
Functional analysis of N-RasG12D mutant proteins. (A) CFU-GM growth of GFP+ fetal liver cells expressing WT N-Ras, N-RasG12D, and N-RasG12D HVR mutant proteins over a range of GM-CSF concentrations. The data are shown as percentage of maximal growth (left panel) and the absolute number of colonies (right panel) for each construct. The data presented are from 3 independent experiments. Asterisks on the right panel indicate statistically significant differences in colony growth: *P < .05; **P < .005; ***P < .0005. Cytokine-independent CFU-GM growth was only observed in cells expressing N-RasG12D, SSDD or N-RasG12D, and was significantly lower for the SSDD mutant. For statistical analyses, the number of CFU-GM colonies that formed in cells expressing WT N-Ras in the presence of a saturating concentration of GM-CSF (10 ng/mL) was compared with all 3 mutants. Cells expressing N-RasG12D, SSDD or N-RasG12D formed significantly more colonies, whereas cells expressing N-RasG12D, C181S formed significantly fewer. (B) Confocal imaging of macrophages differentiated from GFP+ fetal liver cells. Note that the SSDD mutant protein accumulates in the Golgi and that the C181S mutant is absent from the plasma membrane. The confocal images were acquired on the Zeiss LSM 510 NLO Meta using the Plan-APOCHROMAT 63×/1.4 aperture oil objective. Images were taken on live cells grown on Lab-Tek chambered coverglass w/cvr at 25°C. We used GFP as the fluorochrome, and fluorescent signals were detected using photomultiplier tubes. We used the acquisition software LSM 510 and no further manipulation of the images was performed. (C) Biochemical analysis of cultured GFP+ fetal liver cells differentiated into macrophages in vitro. The cells were deprived of serum overnight and stimulated with 10 ng/mL GM-CSF for 20 minutes. The 3 G12D mutant proteins accumulate in the GTP-bound conformation, and both total Ras expression and ERK activation are severely attenuated by the C181S substitution. (D) CFU-GM growth of fetal liver cells expressing WT N-Ras and WT N-Ras with the C181S mutation over a range of GM-CSF concentrations. The data presented are from 3 independent experiments.
Functional analysis of N-RasG12D mutant proteins. (A) CFU-GM growth of GFP+ fetal liver cells expressing WT N-Ras, N-RasG12D, and N-RasG12D HVR mutant proteins over a range of GM-CSF concentrations. The data are shown as percentage of maximal growth (left panel) and the absolute number of colonies (right panel) for each construct. The data presented are from 3 independent experiments. Asterisks on the right panel indicate statistically significant differences in colony growth: *P < .05; **P < .005; ***P < .0005. Cytokine-independent CFU-GM growth was only observed in cells expressing N-RasG12D, SSDD or N-RasG12D, and was significantly lower for the SSDD mutant. For statistical analyses, the number of CFU-GM colonies that formed in cells expressing WT N-Ras in the presence of a saturating concentration of GM-CSF (10 ng/mL) was compared with all 3 mutants. Cells expressing N-RasG12D, SSDD or N-RasG12D formed significantly more colonies, whereas cells expressing N-RasG12D, C181S formed significantly fewer. (B) Confocal imaging of macrophages differentiated from GFP+ fetal liver cells. Note that the SSDD mutant protein accumulates in the Golgi and that the C181S mutant is absent from the plasma membrane. The confocal images were acquired on the Zeiss LSM 510 NLO Meta using the Plan-APOCHROMAT 63×/1.4 aperture oil objective. Images were taken on live cells grown on Lab-Tek chambered coverglass w/cvr at 25°C. We used GFP as the fluorochrome, and fluorescent signals were detected using photomultiplier tubes. We used the acquisition software LSM 510 and no further manipulation of the images was performed. (C) Biochemical analysis of cultured GFP+ fetal liver cells differentiated into macrophages in vitro. The cells were deprived of serum overnight and stimulated with 10 ng/mL GM-CSF for 20 minutes. The 3 G12D mutant proteins accumulate in the GTP-bound conformation, and both total Ras expression and ERK activation are severely attenuated by the C181S substitution. (D) CFU-GM growth of fetal liver cells expressing WT N-Ras and WT N-Ras with the C181S mutation over a range of GM-CSF concentrations. The data presented are from 3 independent experiments.
We next performed confocal microscopy on macrophages grown from GFP+ fetal liver cells. WT N-Ras and N-RasG12D showed similar distributions to the PM and perinuclear Golgi (Figure 1B). Loss of the SSDD motif reduced PM targeting and increased the intensity of perinuclear Golgi staining, whereas the nonpalmitoylated N-RasG12D, C181S protein showed a complete lack of PM localization (Figure 1B).
To analyze Ras signaling, cultured macrophages were deprived of M-CSF and serum for 16 hours followed by stimulation with GM-CSF. Cells expressing WT N-Ras displayed low basal levels of Ras-GTP and phosphorylated ERK (pERK), which increased on GM-CSF stimulation (Figure 1C). By contrast, N-RasG12D and N-RasG12D, SSDD expression resulted in elevated basal Ras-GTP and pERK levels, which increased further in response to GM-CSF. Although the N-RasG12D, C181S mutant protein also accumulated in the GTP-bound conformation, basal and cytokine-induced pERK levels were greatly attenuated. Moreover, total Ras levels were markedly lower in macrophages expressing N-RasG12D, C181S relative to the other 3 proteins (Figure 1C). These biochemical data are consistent with the adverse effects of N-RasG12D, C181S on CFU-GM growth (Figure 1A). To further address how N-RasG12D, C181S expression affects normal Ras signaling and progenitor growth, we generated the C181S mutation in WT N-Ras. This mutant did not alter CFU-GM growth (Figure 1D), which supports the hypothesis that GTP-bound N-RasG12D, C181S functions in a dominant negative manner by sequestering effectors.
To investigate the therapeutic potential of interfering with subcelluar N-RasG12D localization, we assessed the effects of palmostatin B10 on the growth of primary hematopoietic cells. We first assayed the effects of palmostatin B on CFU-GM growth from fetal liver cells transduced with GFP-N-RasG12D and K-Ras4BG12D. Importantly, palmostatin B promoted a dose-dependent reduction in cytokine-independent CFU-GM growth that was selective for cells expressing GFP-N-RasG12D (Figure 2A). Similar effects were observed in the presence of a sub-saturating concentration of GM-CSF (0.1 ng/mL; Figure 2A). We next generated vectors in which the HVR domains of N-RasG12D and K-Ras4BG12D were exchanged (GFP-N-RasG12D, KHVR and GFP-K-Ras4BG12D, NHVR). Studies of progenitors expressing these fusion proteins confirmed the importance of the N-Ras HVR in conferring sensitivity to palmostatin B as cells expressing K-Ras4BG12D, NHVR were highly responsive to the drug, whereas cells transduced with the GFP-N-RasG12D, KHVR were not (Figure 2B). Confocal microscopy showed that treatment with palmostatin B increased endomembrane localization of N-RasG12D and K-Ras4BG12D, NHVR, whereas PM targeting of K-Ras4BG12D and N-RasG12D, KHVR was unaffected (Figure 2C).
Effects of palmostatin B on CFU-GM and blast colony growth. (A-B) CFU-GM were grown from fetal liver cells expressing N-RasG12D, K-RasG12D, N-RasG12D, KHVR, and K-RasG12D, NHVR at 0 and 0.1 ng/mL GM-CSF in the presence palmostatin B. As in Figure 1, the data presented are from 3 independent experiments. Asterisks indicate statistically significant reductions in colony growth compared with untreated cells that were transduced with the same vector and plated in parallel: *P < .05; ***P < .0005. Only cells infected with MSCV vectors encoding proteins containing the N-Ras HVR are sensitive to treatment. (C) Confocal imaging of differentiated macrophages from GFP+ fetal liver cells after treatment with 10μM palmostatin B for 15 minutes. Proteins containing the N-Ras HVR show reduced localization at the plasma membrane by palmostatin B treatment. The confocal images were acquired on the Zeiss LSM 510 NLO Meta using the Plan-APOCHROMAT 63×/1.4 aperture oil objective. Images were taken on live cells grown on Lab-Tek chambered coverglass w/cvr at 25°C. We used GFP as the fluorochrome, and fluorescent signals were detected using photomultiplier tubes. We used the acquisition software LSM 510 and no further manipulation of the images was performed. (D) Effects of palmostatin B on cytokine-independent CFU-GM growth from the bone marrows of 3-month-old Mx1-Cre; LSL-NrasG12D/+, Mx1-Cre; LSL-KrasG12D/+, Mx1-Cre; LSL-NrasG12D/G12D mice as well as from 6-month-old Mx1-Cre, LSL-NrasG12D/G12D mice. One mouse of each genotype was analyzed in 2 independent experiments. Asterisks indicate statistically significant reductions in CFU-GM growth compared with untreated cells of the same genotype: *P < .05; **P < .005; ***P < .0005. (E) Recipient mice that were transplanted with Mx1-Cre, LSL-NrasG12D and Mx1-Cre, LSL-KrasG12D AML cells died of aggressive leukemia (leukocyte counts > 100 000/mm3). Blast colony growth was assessed from bone marrow cells plated in 10 ng/mL GM-CSF with or without palmostatin B. The growth of CFU-GM colonies from a WT mouse was compared with blast colony growth from the same Kras mutant AML and from 2 Nras AMLs in 2 independent experiments. Asterisks indicate statistically significant reductions in CFU-GM growth compared with untreated cells from the same mice: *P < .05; **P < .005.
Effects of palmostatin B on CFU-GM and blast colony growth. (A-B) CFU-GM were grown from fetal liver cells expressing N-RasG12D, K-RasG12D, N-RasG12D, KHVR, and K-RasG12D, NHVR at 0 and 0.1 ng/mL GM-CSF in the presence palmostatin B. As in Figure 1, the data presented are from 3 independent experiments. Asterisks indicate statistically significant reductions in colony growth compared with untreated cells that were transduced with the same vector and plated in parallel: *P < .05; ***P < .0005. Only cells infected with MSCV vectors encoding proteins containing the N-Ras HVR are sensitive to treatment. (C) Confocal imaging of differentiated macrophages from GFP+ fetal liver cells after treatment with 10μM palmostatin B for 15 minutes. Proteins containing the N-Ras HVR show reduced localization at the plasma membrane by palmostatin B treatment. The confocal images were acquired on the Zeiss LSM 510 NLO Meta using the Plan-APOCHROMAT 63×/1.4 aperture oil objective. Images were taken on live cells grown on Lab-Tek chambered coverglass w/cvr at 25°C. We used GFP as the fluorochrome, and fluorescent signals were detected using photomultiplier tubes. We used the acquisition software LSM 510 and no further manipulation of the images was performed. (D) Effects of palmostatin B on cytokine-independent CFU-GM growth from the bone marrows of 3-month-old Mx1-Cre; LSL-NrasG12D/+, Mx1-Cre; LSL-KrasG12D/+, Mx1-Cre; LSL-NrasG12D/G12D mice as well as from 6-month-old Mx1-Cre, LSL-NrasG12D/G12D mice. One mouse of each genotype was analyzed in 2 independent experiments. Asterisks indicate statistically significant reductions in CFU-GM growth compared with untreated cells of the same genotype: *P < .05; **P < .005; ***P < .0005. (E) Recipient mice that were transplanted with Mx1-Cre, LSL-NrasG12D and Mx1-Cre, LSL-KrasG12D AML cells died of aggressive leukemia (leukocyte counts > 100 000/mm3). Blast colony growth was assessed from bone marrow cells plated in 10 ng/mL GM-CSF with or without palmostatin B. The growth of CFU-GM colonies from a WT mouse was compared with blast colony growth from the same Kras mutant AML and from 2 Nras AMLs in 2 independent experiments. Asterisks indicate statistically significant reductions in CFU-GM growth compared with untreated cells from the same mice: *P < .05; **P < .005.
To evaluate the effects of palmostatin B on cells expressing oncogenic N- and K-Ras from their endogenous loci, we grew CFU-GM colonies from Mx1-Cre, LSL-NrasG12D and Mx1-Cre, LSL-KrasG12D mice. In contrast to Mx1-Cre, LSL-KrasG12D/+ mice,13 heterozygous Nras mutant (Mx1-Cre, LSL-NrasG12D/+) mice do not develop MPD during the first 6 months of life on an inbred C57Bl/6 strain background, and the bone marrow contains rare cytokine-independent CFU-GM.14,18 However, consistent with a recent report,19 mice that are homozygous for the NrasG12D allele developed overt MPD by 3 months of age (supplemental Figure 3), and bone marrow cells from these animals and from Mx1-Cre, LSL- KrasG12D/+ mice formed large numbers of CFU-GM colonies in the absence of GM-CSF. Palmostatin B reduced cytokine-independent CFU-GM growth from heterozygous and homozygous Nras mutant bone marrow but had no effect on Kras mutant cells (Figure 2D). We also cultured cells from Mx1-Cre, LSL-NrasG12D/+ and Mx1-Cre, LSL-KrasG12D/+ mice that developed AML after retroviral mutagenesis.14,15 The growth of blast colonies from 2 independent Nras leukemias was reduced by approximately 50% in response to 30μM palmostatin B. Importantly, this drug concentration has no effect on colony growth from a Kras mutant AML or from WT marrow (Figure 2E).
Cuiffo and Ren recently reported that mutating the palmitoylation site at cysteine 181 in N-RasG12D inhibited PM localization in fibroblasts and prevented the development of MPD in a transduction/transplantation model.20 However, our observation that exogenous expression of the C181S substitution has dominant negative effects in primary progenitors precludes drawing therapeutic inferences from these data. We therefore expressed N-RasG12D, SSDD and demonstrated that this protein does not interfere with either normal Ras signaling or CFU-GM growth. Importantly, the SSDD mutation reduced N-Ras trafficking to the PM and attenuated the effects of oncogenic N-RasG12D on progenitor growth. Treatment with palmostatin B had similar effects, and studies in which we created N-Ras and K-Ras4B fusion proteins localized the inhibitory effects to the N-Ras HVR. Palmostatin B also showed selective efficacy in bone marrow cells from mice in which NrasG12D is expressed from the endogenous locus.
Palmostatin B locks N-Ras and H-Ras in the palmitoylated form, which results in entropy-driven diffusion throughout the cell via membrane exchange processes.21 Developing palmitoyl transferase inhibitors is an alternative strategy for selectively inhibiting oncogenic N-Ras signaling; however, this is challenging because of the existence of more than 20 known family members.22 Together, our data support investigating inhibitors of depalmitoylation in hematologic cancers characterized by oncogenic NRAS mutations.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (grant R37 CA72614, and an American Recovery and Reinvestment Act supplement to this award; grant K08 CA134649), the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society (Specialized Center of Research award), the Frank A. Campini Foundation, and the American Cancer Research Society (Post-Doctoral Fellowship award, J.X.). K.S. is an American Cancer Society Research Professor.
National Institutes of Health
Authorship
Contribution: J.X. designed experiments, performed research studies, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript; F.J.D. and C.H. synthesized and characterized palmostatin B and assisted in writing and editing the manuscript; Q.L. generated and characterized Mx1-Cre, NrasG12D knockin mice, generated the Kras and Nras mutant AMLs used in these studies, and assisted in writing and editing the manuscript; K.M.H. developed NrasG12D knockin mice and assisted in writing and editing the manuscript; E.H. generated reagents and assisted J.X. with some of the research studies; H.W. designed and supervised the work leading to the synthesis and characterization of palmostatin B and assisted in writing and editing the manuscript; and K.S. designed experiments, reviewed the data, and wrote the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Kevin Shannon, Helen Diller Family Cancer Research Bldg, University of California–San Francisco, 1450 3rd St, Rm 240, San Francisco, CA 94158-9001; e-mail: shannonk@peds.ucsf.edu.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal