Abstract
Abstract 1544
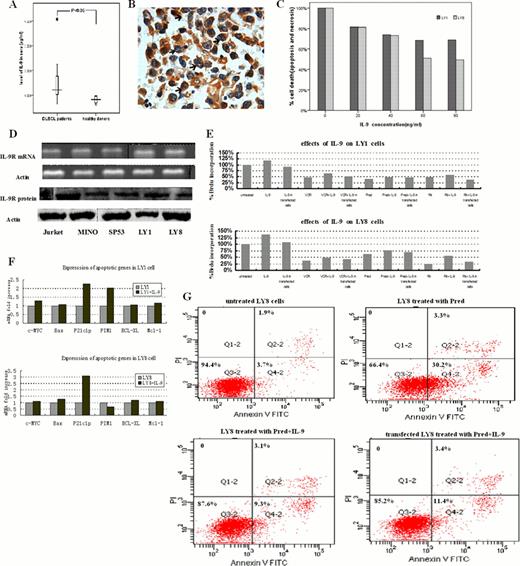
Diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is known as an aggressive malignancy arising from B lymphocytes. Despite its greatly improved prognosis as a result of chemotherapy and immunotherapy with monoclonal antibodies, the exact molecular etiology of DLBCL is not well understood. Interleukin-9 (IL-9) is initially described as a growth factor secreted by activated Th2 cells. Various observations have demonstrated its diverse actions in immune disorders. Recent years, the determination of its growth-proliferative and anti-apoptotic activities on multiple transformed cells implies a potential role of this cytokine in tumorigenesis but there are still no reports about its oncogenic activities in DLBCL. Our study is aimed to test the expression of IL-9 and its receptor (IL-9R) in DLBCL patients and illustrate its pathogenic effect on DLBCL cell lines in vitro.
Blood samples and araffin-embedded tissues from twenty DLBCL patients were collected prior to therapeutic interventions. Serums from healthy volunteers served as normal control. IL-9 levels in sera were quantified using human ELISA kits. The expression of IL-9R protein in DLBCL tissues and lymphoma cell lines (LY1, LY8, SP53, Mino and Jurket) was determined by immunohistochemical staining and western-blot, respectively. IL-9R genes were knocked down in DLBCL cell lines LY1 and LY8 by lentivirus-mediated gene silencing (interference sequence 5'- GCTCGTGCCATCTGACAATTT -3'). LY1, LY8 and the stable transfected cells were treated with IL-9 alone and in synergy with rituximab (10ug/ml).
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal