Abstract
Abstract 267
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a prothrombotic disorder mediated by platelet, monocyte, and endothelial cell-activating antibodies (Abs) against ultralarge complexes of platelet factor 4 (PF4) and heparin. Laboratory testing plays a key role in the diagnosis of HIT, but is associated with important shortcomings. Immunoassays such as the PF4/heparin ELISA frequently yield false-positive results due to their inability to discriminate cellular activating-Abs from their non-pathogenic counterparts. Functional assays such as the 14C-serotonin release assay (SRA) are more specific, but are unfeasible for most clinical laboratories due to the requirement for radioisotope and fresh platelets from reactive donors.
KKO is a monoclonal Ab that causes a HIT-like thrombocytopenic disorder in a mouse model. Binding of KKO to immobilized PF4/heparin is inhibited by human HIT plasma, but not by plasma from patients with non-pathogenic anti-PF4/heparin Abs.1 We exploited this property of KKO to develop a KKO-inhibition (KKO-I) ELISA to detect platelet-activating Abs. We recently described a system to measure cell activation by HIT Abs: DT40 (chicken B lymphocyte) cells transfected with human FcgRIIa coupled to a luciferase reporter.2 We hypothesized that this system (DT40-luc) could be used to identify cell-activating anti-PF4/heparin Abs without need for donor platelets or radioactivity. Here we describe the KKO-I and DT40-luc assays and compare their performance to two commercially available immunoassays and the SRA in samples from 58 patients with suspected HIT and circulating anti-PF4/heparin Abs.
Patient samples consecutively referred to a clinical coagulation laboratory for HIT laboratory testing that tested positive by polyspecific anti-PF4/heparin ELISA were included. In addition to the polyspecific ELISA, citrated plasma samples from all patients were tested by an IgG-specific PF4/heparin ELISA, an in-house SRA, and the investigational KKO-I and DT40-luc assays. A 4Ts score to estimate the clinical likelihood of HIT was determined for each subject. The investigator performing 4Ts scoring was blinded to the results of HIT laboratory assays. Investigators performing the KKO-I and DT40-luc assays were blinded to the 4Ts score and the results of the SRA and anti-PF4/heparin ELISA.
The KKO-I and DT40-luc assays were performed as previously described.1,2 HIT was defined as the combination of an intermediate or high probability 4Ts score (≥4) and a positive SRA. The performance of each assay with respect to this reference standard was evaluated by receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. Areas under the ROC curves (AUCs) were calculated and compared using the Delong method for correlated samples.
Fifty-eight subjects were enrolled, 21 of whom met prespecified criteria for HIT. There were no significant differences in demographic characteristics between the 21 HIT-positive and 37 HIT-negative subjects.
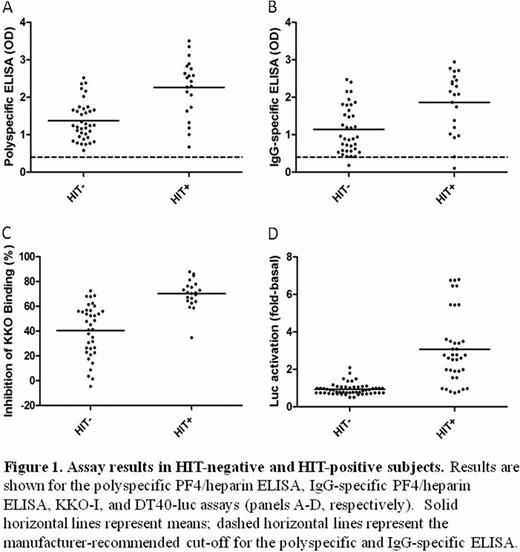
The ability of the polyspecific ELISA, IgG-specific ELISA, KKO-I, and DT40-luc assay to discriminate HIT-positive from HIT-negative subjects is shown in Figure 1. HIT-positive plasma showed significantly greater mean inhibition of KKO binding than HIT-negative plasma (70.1%, 95% CI 64.8–75.4 vs. 40.4%, 33.5–47.4, p<0.0001) (Figure 1C). Plasma from HIT-positive subjects also induced significantly greater luciferase activity (3.14, 2.25–4.03 vs. 0.96, 0.85–1.07, p<0.0001) in the DT40-luc assay (Figure 1D).
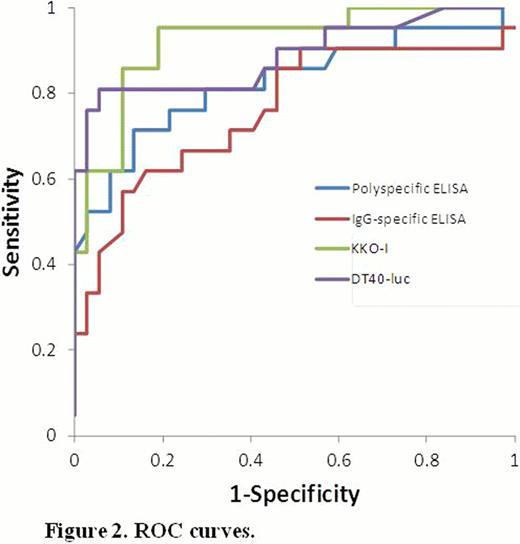
ROC curves for each assay are shown in Figure 2. The AUC for KKO-I (0.92, 0.85–1.00) was significantly greater than the AUC for the polyspecific (0.82, 0.70–0.95) and IgG-specific (0.76, 0.62–0.90) ELISAs (p<0.05 for both comparisons). The AUC for DT40-luc (0.89, 0.79–0.99) was significantly greater than the AUC for the IgG-specific (p=0.046), but not the polyspecific ELISA (p=0.28).
KKO-I and DT40-luc showed better discrimination than commercially available ELISAs in a small cohort of patients with suspected HIT and anti-PF4/heparin Abs. These assays are simple to perform, do not require donor platelets or radioactivity, and hold promise for improving the specificity and feasibility of HIT laboratory testing. Further evaluation in a larger cohort of patients is required.
Cuker:Baxter: Consultancy, Research Funding; Bayer: Consultancy; Canyon: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Stago: Research Funding. Arepally:Teva Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding. Cines:Amgen: Consultancy; GSK: Consultancy; Eisai: Consultancy; T2 Biosystems: Research Funding.
References
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal