Abstract
Abstract 451
Chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) represent a potent strategy to target T cells against selected tumor antigens. Ongoing clinical trials indicate that autologous T cells expressing CARs targeting CD19, a B cell-associated antigen, can induce complete remission and B cell aplasia in patients with B cell malignancies. Donor CD19-CAR+ T cells could potentially be used to treat recipients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT), but the risk of alloreactivity mediated by endogenous T cell receptors (TCR) triggering an acute GVHD is not known. This is partly due to the absence of in vivo models to study the relative effects of CAR and endogenous TCR signaling. For the first time, we have evaluated the relative effects of CD19-targeted donor T cells on the elimination of CD19+ B cells and endogenous TCR-mediated alloreactivity in mouse models of allo-HSCT.
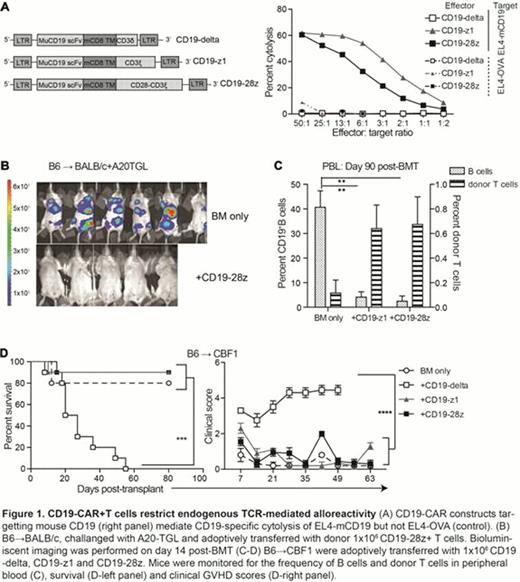
We generated a panel of retroviral vectors encoding mouse CD19-specific CARs: as a control, CD19-delta, a tail-less CAR lacking the CD3ζ signaling domain; CD19z1, which signals through its CD3ζ endodomain; and CD19-28z, which signals through CD28 and CD3ζ (Figure 1A). CD19z1+ and CD19-28z+ T cells mediated specific lysis of CD19-expressing tumors in vitro, while CD19-delta+ T cells did not. In order to assess the anti-tumor capacity of CD19-CAR+ T cells in vivo, we transferred the transduced B6 donor T cells into lethally irradiated BALB/c recipients that were administered T cell-depleted allografts and CD19+ lymphoma A20-TGL (B6–> BALB/c+A20-TGL). CD19-CAR+ T cells (CD19z1 and CD19-28z) mediated clearance of A20 tumor cells visualized by in vivo imaging of luciferase-expressing tumor cells (Figure 1B and data not shown) and significantly improved tumor free survival. CD19-CAR+ B6 T cells could sustain prolonged B cell hypoplasia when adoptively transferred into lethally irradiated haploidentical CBF1 recipients of T cell-depleted allografts (B6–> CBF1, Figure 1C). These data indicate that under alloreactive conditions, donor CD19-CAR+ T cell signaled through the CAR leading to specific elimination of CD19+ tumors and B lineage cells.
In order to determine the risk of GVHD, we transferred the donor CD19-CAR+ T cells into haploidentical HSCT recipients. Interestingly, CD19-CAR+ T cells mediated significantly less acute GVHD, resulting in improved survival and lower GVHD scores (Figure 1D). Donor CD19-delta+ T cells however mediated lethal GVHD, indicating that the endogenous TCR mediated strong alloreactivity in the absence of CAR signaling. Similar results were obtained from experiments using MHC-mismatched (B6–> BALB/c) models. It is known that signaling through endogenous TCR is accompanied by down-regulation of surface TCR expression. We found significant decreases in surface CD3ϵ, TCRβ and CD90 expressions in donor CD19-delta+ T cells under alloreactive conditions. In contrast, donor CD1928z+ T cells failed to down-regulate surface TCR expression under similar conditions, suggesting that endogenous TCR function was altered in CAR-activated T cells. In the context of allo-HSCT, preferential CAR signaling at the expense of alloreactive endogenous TCR signaling may thus lead to reduced alloreactivity and attenuation of GVHD. These results provide the first pre-clinical evidence suggesting that CAR-modified, unselected donor T cells may be safely applied in an allogeneic context.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal