Key Points
High mortality rates are observed in patients with XIAP deficiency treated with myeloablative conditioning regimens for hematopoietic cell transplantation.
Abstract
There have been no studies on patient outcome after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) in patients with X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) deficiency. To estimate the success of HCT, we conducted an international survey of transplantation outcomes. Data were reported for 19 patients. Seven patients received busulfan-containing myeloablative conditioning (MAC) regimens. Eleven patients underwent reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) regimens predominantly consisting of alemtuzumab, fludarabine, and melphalan. One patient received an intermediate-intensity regimen. Survival was poor in the MAC group, with only 1 patient surviving (14%). Most deaths were from transplantation-related toxicities, including venoocclusive disease and pulmonary hemorrhage. Of the 11 patients who received RIC, 6 are currently surviving at a median of 570 days after HCT (55%). Preparative regimen and HLH activity affected outcomes, and of RIC patients reported to be in remission from HLH, survival is 86% (P = .03). We conclude that MAC regimens should not be used for patients with XIAP deficiency. It is possible that the loss of XIAP and its antiapoptotic functions contributes to the high incidence of toxicities observed with MAC regimens. RIC regimens should be pursued with caution and, if possible, efforts should be made to ensure HLH remission before HCT in these patients.
Introduction
Deficiency of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) is associated with X-linked lymphoproliferative disease (XLP) and familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHLH) phenotypes. Traditionally, patients with inherited immune deficiencies that cause HLH have been treated with allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) because of the life-threatening nature of HLH. There is extensive experience with transplantation in patients with FHLH. Over the past 10 years, survival has generally approximated 60% with myeloablative conditioning (MAC) regimens.1-7 More recently, improvements have been made with reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) protocols, and current survival rates are as high as 80%.8-11 There is less experience with transplantation in patients with XLP because of SLAM-associated protein (SAP) deficiency, but survival is generally accepted to be greater than 70% regardless of the intensity of the conditioning protocol.12-14
To date, little has been published concerning the outcomes of HCT for patients with XIAP deficiency. XIAP deficiency was first discovered in 2006,15 and is associated with XLP, FHLH, and colitis phenotypes.15-18 Patients with XIAP deficiency are unique compared with patients with the other genetic forms of HLH because, as the name suggests, XIAP is an inhibitor of apoptosis that is widely expressed outside of the immune system.19 Thymocytes from XIAP-deficient mice have been shown to have normal apoptotic responses to a variety of apoptotic stimuli,20 but hepatocytes are more sensitive to death induced by treatment with cross-linked Fas ligand.21 XIAP-deficient mouse embryonic fibroblasts are also more sensitive to death after infection with MHV-68.22 In addition, there is increasing experience with the use of XIAP inhibitors in conjunction with traditional cancer treatment. In this setting, XIAP inhibitors generally increase the susceptibility of cancer cells to undergo apoptosis.23,24 Because of the importance of XIAP in preventing apoptosis, patients with XIAP deficiency may be at increased risk of treatment-related toxicities because of increased sensitivity to chemotherapeutic agents.
To investigate whether deficiency of XIAP adversely affects the survival of patients undergoing allogeneic HCT, we conducted an international survey to collect information regarding the transplantation outcomes of patients confirmed to have XIAP deficiency.
Methods
Data collection
Approval for this retrospective study was granted by the Cincinnati Children's Hospital Institutional Review Board. A spreadsheet questionnaire was sent to physicians who provided treatment for patients with XIAP deficiency who underwent allogeneic HCT. Physicians were identified through contact with our center, our review of the literature regarding XIAP deficiency, or a request made to all members of the Histiocyte Society.
Patients
Only patients with a confirmed XIAP/BIRC4 (baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis repeat containing protein 4) mutation or with a sibling with a confirmed mutation were included in this study (Table 1), which was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Supplemental lymphocyte protein analysis was performed in some patients using either Western blot or intracellular flow cytometric analysis.15-17,25
Patient characteristics
| Patient no . | Age at initial presentation . | EBV HLH before HCT . | Non-EBV HLH before HCT . | HLH not in full remission before HCT . | Colitis before HCT . | Other . | XIAP mutation . | Protein expression . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 mo | − | + | − | − | 1443_1449 delins 24 (P482fsX508) | NE* | |
| 2 | 2 mo | − | + | + | − | 1443_1449 delins 24 (P482fsX508) | NE | |
| 3 | 2 mo | − | + | − | − | 563 G → A (G188E) | Reduced | |
| 4 | Asymptomatic (symptomatic brother) | − | − | − | − | 563 G → A (G188E) | Reduced | |
| 5 | 15 mo | − | − | − | + | Recurrent enterocutaneous fistulas; multiple episodes of polymicrobial sepsis | 608G → A (C203Y) | Reduced |
| 6 | 9 mo | − | + | − | − | E99KfsX129 | Absent | |
| 7 | 9 y | + | − | − | − | 497G → T, R166I | NE | |
| 8 | 7 mo | − | + | + | − | 1141C → T (R381X) | Reduced | |
| 9 | Infancy | − | + | − | − | 1481 T → A (I494N) | NE | |
| 10 | 4 mo | − | + | + | − | 1445 C → G (P482R) | Reduced | |
| 11 | 1 y | + | − | + | − | Repeated infections: pneumonia, otitis media, history of paracentesis, mastoidectomy | 1189 delA (I397fsX414) | Absent |
| 12 | 1 y | + | − | + | − | 387_390del (D130fsX140) | Not reported | |
| 13 | 3 mo | − | + | − | − | Gross Deletion Exons 1-5 | Absent | |
| 14 | 1 y | − | − | − | + | Recurrent fevers; pneumococcal sepsis. | 758 C → G (S253X) | Absent |
| 15 | 3 y | − | + | − | − | Ventricular septal defect | 356_359del (N119fs384) | NE |
| 16 | 7 y | + | + | − | − | 1141C → T (R381X) | Reduced | |
| 17 | 8 y | + | − | + | − | 310 C → T (Q104X) | Absent | |
| 18 | Infancy | − | + | − | − | Liver failure in infancy required liver transplantation; nodular lung disease; positive CMV and fungal elements | Gross deletion exon 6 | Truncated (robust detection of a smaller molecular weight protein by Western blot) |
| 19 | 17 y | + | − | − | − | 894_898 del 5 (K299fsX307) | Absent |
| Patient no . | Age at initial presentation . | EBV HLH before HCT . | Non-EBV HLH before HCT . | HLH not in full remission before HCT . | Colitis before HCT . | Other . | XIAP mutation . | Protein expression . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 mo | − | + | − | − | 1443_1449 delins 24 (P482fsX508) | NE* | |
| 2 | 2 mo | − | + | + | − | 1443_1449 delins 24 (P482fsX508) | NE | |
| 3 | 2 mo | − | + | − | − | 563 G → A (G188E) | Reduced | |
| 4 | Asymptomatic (symptomatic brother) | − | − | − | − | 563 G → A (G188E) | Reduced | |
| 5 | 15 mo | − | − | − | + | Recurrent enterocutaneous fistulas; multiple episodes of polymicrobial sepsis | 608G → A (C203Y) | Reduced |
| 6 | 9 mo | − | + | − | − | E99KfsX129 | Absent | |
| 7 | 9 y | + | − | − | − | 497G → T, R166I | NE | |
| 8 | 7 mo | − | + | + | − | 1141C → T (R381X) | Reduced | |
| 9 | Infancy | − | + | − | − | 1481 T → A (I494N) | NE | |
| 10 | 4 mo | − | + | + | − | 1445 C → G (P482R) | Reduced | |
| 11 | 1 y | + | − | + | − | Repeated infections: pneumonia, otitis media, history of paracentesis, mastoidectomy | 1189 delA (I397fsX414) | Absent |
| 12 | 1 y | + | − | + | − | 387_390del (D130fsX140) | Not reported | |
| 13 | 3 mo | − | + | − | − | Gross Deletion Exons 1-5 | Absent | |
| 14 | 1 y | − | − | − | + | Recurrent fevers; pneumococcal sepsis. | 758 C → G (S253X) | Absent |
| 15 | 3 y | − | + | − | − | Ventricular septal defect | 356_359del (N119fs384) | NE |
| 16 | 7 y | + | + | − | − | 1141C → T (R381X) | Reduced | |
| 17 | 8 y | + | − | + | − | 310 C → T (Q104X) | Absent | |
| 18 | Infancy | − | + | − | − | Liver failure in infancy required liver transplantation; nodular lung disease; positive CMV and fungal elements | Gross deletion exon 6 | Truncated (robust detection of a smaller molecular weight protein by Western blot) |
| 19 | 17 y | + | − | − | − | 894_898 del 5 (K299fsX307) | Absent |
Not examined.
Transplantation procedures
Patients received transplantation at centers in the United States (n = 12), Europe (n = 6), and Japan (n = 1) between the years 2001-2011. Transplantation procedures were carried out per institutional standard practices. Conditioning regimens and graft characteristics are listed in Table 2. Conditioning regimens were classified as MAC if they contained an alkylating agent (busulfan) or total body irradiation (TBI) at a dose that would not allow autologous BM recovery.26 Conditioning regimens were classified as RIC if they did not meet the definition of MAC regimen.26 If there was uncertainty regarding the intensity of the regimen (n = 1, patient 8), it was classified as an intermediate-intensity regimen. Neutrophil engraftment was considered to be the day the neutrophil count reached 0.5 × 109/L. Engraftment studies were done using either XY FISH for sex-mismatched donors or variable number of tandem repeat analysis for same-sex donors. Mixed chimerism was defined as having 5% or more host-derived cells in the whole blood on more than 1 occasion. Acute and chronic GVHD were assessed by standard criteria.27,28 Patients received GVHD prophylaxis per institutional standard practices. Other routine transplantation care, such as antimicrobial prophylaxis, IV Ig replacement, and fluid and nutrition supplementation when needed, were also provided per institutional standard practices.
Transplantation procedures
| Patient no . | Age at HCT, y . | Type of conditioning . | Conditioning regimen . | Graft HLA match* . | Graft source . | Relationship . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.42 | MAC | Bu, Mel, ATG | 5/6 | Cord | Unrelated |
| 2 | 0.58 | MAC | Bu, Cy, ATG, Etop | 6/6 | Cord | Unrelated |
| 3 | 1 | MAC | Bu, Cy, ATG | 7/8 | BM | Unrelated |
| 4 | 4 | MAC | Bu, Cy, ATG | 10/10 | BM | Unrelated |
| 5 | 5 | MAC | Bu, Flu, ATG | 6/6 | Cord | Unrelated |
| 6 | 10 | MAC | Bu, Cy, ATG | 6/6 | BM | Unrelated |
| 7 | 14 | MAC | Bu, Cy, ATG, Etop | 7/8 | PBSCs | Unrelated |
| 8 | 1 | Intermediate | TBI (6 Gy), Flu, Cy, Mel (80 mg/m2) | 7/8 | Cord | Unrelated |
| 9 | 0.40 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Mel | 8/8 | BM | Unrelated |
| 10 | 0.98 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Mel | 9/10 | BM | Unrelated |
| 11 | 2 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Mel | 9/10 | BM | Unrelated |
| 12 | 3 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Mel | 9/10 | Cord | Unrelated |
| 13 | 3 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Mel | 8/8 | BM | Unrelated |
| 14 | 3 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Mel | 10/10 | BM | Unrelated |
| 15 | 4 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Mel | 8/8 | PBSCs | Maternal |
| 16 | 7 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Treo, Thio | 10/10 | PBSCs | Unrelated |
| 17 | 9 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Mel | 7/8 | BM | Unrelated |
| 18 | 11 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Mel | 8/8 | BM | Unrelated |
| 19 | 19 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Mel | 10/10 | BM | Sibling |
| Patient no . | Age at HCT, y . | Type of conditioning . | Conditioning regimen . | Graft HLA match* . | Graft source . | Relationship . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.42 | MAC | Bu, Mel, ATG | 5/6 | Cord | Unrelated |
| 2 | 0.58 | MAC | Bu, Cy, ATG, Etop | 6/6 | Cord | Unrelated |
| 3 | 1 | MAC | Bu, Cy, ATG | 7/8 | BM | Unrelated |
| 4 | 4 | MAC | Bu, Cy, ATG | 10/10 | BM | Unrelated |
| 5 | 5 | MAC | Bu, Flu, ATG | 6/6 | Cord | Unrelated |
| 6 | 10 | MAC | Bu, Cy, ATG | 6/6 | BM | Unrelated |
| 7 | 14 | MAC | Bu, Cy, ATG, Etop | 7/8 | PBSCs | Unrelated |
| 8 | 1 | Intermediate | TBI (6 Gy), Flu, Cy, Mel (80 mg/m2) | 7/8 | Cord | Unrelated |
| 9 | 0.40 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Mel | 8/8 | BM | Unrelated |
| 10 | 0.98 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Mel | 9/10 | BM | Unrelated |
| 11 | 2 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Mel | 9/10 | BM | Unrelated |
| 12 | 3 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Mel | 9/10 | Cord | Unrelated |
| 13 | 3 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Mel | 8/8 | BM | Unrelated |
| 14 | 3 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Mel | 10/10 | BM | Unrelated |
| 15 | 4 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Mel | 8/8 | PBSCs | Maternal |
| 16 | 7 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Treo, Thio | 10/10 | PBSCs | Unrelated |
| 17 | 9 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Mel | 7/8 | BM | Unrelated |
| 18 | 11 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Mel | 8/8 | BM | Unrelated |
| 19 | 19 | RIC | Alem, Flu, Mel | 10/10 | BM | Sibling |
Bu indicates busulfan; Mel, melphalan; ATG, antithymocyte globulin; Cy, cyclophosphamide; Etop, etoposide; Flu, fludarabine; Alem, alemtuzumab; Treo, treosulfan; Thio, thiotepa; and PBSCs, peripheral blood stem cells.
Six to 10 alleles (HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C, HLA-DRB1, or HLA-DQB1).
Statistical analysis
Survival was analyzed using Kaplan-Meier curves created with XLSTAT 2011 software (Addinsoft). Comparison of survival curves was done using the log-rank test. For multivariate analysis of survival time and the impact of preparative regimen (MAC vs RIC), donor match, (full match vs mismatch), and HLH activity (remission vs nonremission), Cox proportional hazard regression model analysis was used. The patient who received the intermediate-intensity regimen was excluded from these analyses. Statistical significance was considered as P < .05.
Results
Patients
Nineteen patients with XIAP deficiency underwent allogeneic HCT between 2001 and 2011 at a median age of 3 years (range, 0.4-19). Patient characteristics before HCT and XIAP/BIRC4 mutations are listed in Table 1. Approximately one-third of patients had developed EBV-related HLH before HCT, and approximately two-thirds of patients had developed non-EBV HLH before HCT. Six of these patients were reported to have either active HLH or HLH in partial remission just before HCT. Two patients with colitis were diagnosed and treated as having Crohn disease before the diagnosis of XIAP deficiency.
Transplantation procedures
Graft characteristics and conditioning regimens are shown in Table 2. Seven patients received a MAC protocol.26 Most patients received busulfan, cyclophosphamide, and antithymocyte globulin with or without etoposide (n = 5). The remaining 2 patients received busulfan with either fludarabine or melphalan and antithymocyte globulin. Eleven patients received a RIC protocol.26 Ten RIC patients received alemtuzumab, fludarabine, and melphalan, and 1 patient received alemtuzumab, fludarabine, treosulfan, and thiotepa. The remaining patient (patient 8) received an intermediate protocol consisting of TBI (6 Gy), fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and melphalan (80 mg/m2).
Eleven patients received fully matched related (n = 2) or unrelated (n = 9) grafts based on typing of 6-10 HLA antigens (HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C, HLA-DRB1, and HLA-DQB1). Eight patients received a single allele mismatched graft. The stem cell source was BM in 11 patients, cord blood in 5 patients, and peripheral blood stem cells in 3 patients.
Engraftment
All patients engrafted with a median of 15 days (range, 8-22) except for patient 11, who died before engraftment on day +13.
Toxicities
There was a high incidence of conditioning-related toxicities among MAC patients (Table 3). There were 3 cases of hepatic venoocclusive disease (VOD), which contributed to deaths on days +17, +50, and +144 in patients 6, 2, and 1, respectively. Two of these patients also developed pulmonary hemorrhage. One patient (patient 3) developed pulmonary hypertension of uncertain etiology with pulmonary hemorrhage after transplantation and died on day +170. This patient had received MAC after having previously undergone HCT twice with RIC.
Toxicities and complications
| Patient no . | VOD . | Pulmonary hemorrhage . | Acute VHD . | Pneumonitis or ARDS . | Confirmed bacteremia/sepsis . | Fungal infection . | Viremia with EBV, CMV, adenovirus, or HHV6 . | BK virus hemorrhagic cystitis . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | + | + | − | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| 2 | + | − | − | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| 3 | − | + (shown by autopsy, not clinically) | II | − | + (S marcescens) | − | + (EBV, adenovirus) | − |
| 4 | − | + (related to fungal septic thrombosis of the pulmonary veins and pulmonary artery) | III | − | − | + (fungal septic thrombosis of the pulmonary veins and pulmonary artery) | + (EBV, adenovirus) | + |
| 5 | − | − | I | − | + (K oxytoca, Enterococcus sp, P aeruginosa) | − | + (CMV, adenovirus, HHV6) | − |
| 6 | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 7 | − | − | III | + | − | − | − | − |
| 8 | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − |
| 9 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + (adenovirus) | − |
| 10 | − | − | − (+ after DLI) | − | + (K oxytoca, S maltophilia, P aeruginosa) | − | − | − |
| 11 | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − |
| 12 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + |
| 13 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + (adenovirus) | − |
| 14 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + (EBV, CMV) | − |
| 15 | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − |
| 16 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + (adenovirus) | − |
| 17 | − | − | I | − | + (S aureus) | − | + (adenovirus) | − |
| 18 | − | − | − | − | + (S aureus) | − | + (CMV) | − |
| 19 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Patient no . | VOD . | Pulmonary hemorrhage . | Acute VHD . | Pneumonitis or ARDS . | Confirmed bacteremia/sepsis . | Fungal infection . | Viremia with EBV, CMV, adenovirus, or HHV6 . | BK virus hemorrhagic cystitis . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | + | + | − | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| 2 | + | − | − | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| 3 | − | + (shown by autopsy, not clinically) | II | − | + (S marcescens) | − | + (EBV, adenovirus) | − |
| 4 | − | + (related to fungal septic thrombosis of the pulmonary veins and pulmonary artery) | III | − | − | + (fungal septic thrombosis of the pulmonary veins and pulmonary artery) | + (EBV, adenovirus) | + |
| 5 | − | − | I | − | + (K oxytoca, Enterococcus sp, P aeruginosa) | − | + (CMV, adenovirus, HHV6) | − |
| 6 | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 7 | − | − | III | + | − | − | − | − |
| 8 | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − |
| 9 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + (adenovirus) | − |
| 10 | − | − | − (+ after DLI) | − | + (K oxytoca, S maltophilia, P aeruginosa) | − | − | − |
| 11 | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − |
| 12 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + |
| 13 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + (adenovirus) | − |
| 14 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + (EBV, CMV) | − |
| 15 | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − |
| 16 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + (adenovirus) | − |
| 17 | − | − | I | − | + (S aureus) | − | + (adenovirus) | − |
| 18 | − | − | − | − | + (S aureus) | − | + (CMV) | − |
| 19 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
ARDS indicates acute respiratory distress syndrome; NR, not reported; and DLI, donor lymphocyte infusion.
There were no cases of hepatic VOD or pulmonary hemorrhage in patients who received RIC. However, 1 patient (patient 11) developed multiorgan failure and cardiac toxicity with asystole and died at day +13. A second patient (patient 15) suffered an unexpected death related to idiopathic pneumonitis and respiratory failure at day +125.
Patient 8, who received the intermediate preparative regimen (consisting of TBI, fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and melphalan), suffered posttransplantation cytokine storm syndrome with acute respiratory distress syndrome and died on day +22.
GVHD
Three patients developed acute GVHD of grade 2 or greater (Table 3). One additional patient developed acute GVHD after receiving a donor lymphocyte infusion that was administered as an intervention for declining donor contribution to hematopoiesis. Two patients developed chronic GVHD (limited, n = 1, and extensive, n = 1).
Infections
Most patients experienced an infectious complication of HCT (Table 3). Common viral complications included EBV viremia (n = 3, all patients received rituximab), CMV viremia (n = 3, all patients received CMV-directed therapy), and adenovirus viremia (n = 7, 4 patients received adenovirus-directed therapy). Other reported viral complications included human herpesvirus 6 (HHV6) viremia and encephalitis (n = 1), varicella zoster (n = 1), and BK virus hemorrhagic cystitis (n = 2).
Reported bacterial infections included pneumonias, bacteremias and episodes of sepsis (n = 5) related to Serratia marcescens, Klebsiella oxytoca, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Enterococcus sp, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Staphylococcus aureus. One patient developed fatal fungal septic thrombosis of the pulmonary veins and pulmonary artery.
Donor contribution to hematopoiesis
Six patients were reported to develop mixed donor and recipient chimerism (< 95% donor cells detected in peripheral blood) at a median of 37 days after HCT. All of these patients had received RIC. Patient 12 was reported to lose the graft by 35 days after HCT. For the remaining 5 patients (patients 9, 10, 13, 18, and 19), the lowest observed donor contributions to hematopoiesis ranged from 13.8%-92%. Three patients received a stem cell boost and/or donor lymphocyte infusion(s). At the time of last follow-up at a median of 867 days after HCT (range, 139-1706), all 5 patients possessed greater than 90% donor contribution to hematopoiesis and remained free of disease.
Survival and outcome
Only 1 of the 7 patients who received MAC is currently surviving, 414 days after HCT (Table 4). The other 6 patients died at a median of 97 days after HCT (range, 17-247) from toxicities and complications including VOD, pulmonary hemorrhage, pulmonary hypertension, GVHD, sepsis, multiorgan failure, and fungal septic thrombosis of pulmonary veins and pulmonary artery with pulmonary hemorrhagic necrosis.
Patient outcomes
| Patient no . | Follow-up, d . | Outcome . | Cause of death . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 144 | Died | VOD and pulmonary hemorrhage |
| 2 | 50 | Died | VOD and MOF |
| 3 | 170 | Died | Pulmonary hypertension |
| 4 | 247 | Died | Fungal septic thrombosis of pulmonary veins and pulmonary artery with pulmonary hemorrhagic necrosis |
| 5 | 414 | Alive and well; limited skin GVHD | |
| 6 | 17 | Died | Pulmonary hemorrhage, VOD |
| 7 | 50 | Died | GVHD, MOF |
| 8 | 22 | Died | ARDS, posttransplantation cytokine storm syndrome |
| 9 | 1765 | Alive and well | |
| 10 | 285 | Died | Drug-resistant P aeruginosa sepsis |
| 11 | 13 | Died | Cardiac toxicity, MOF, asystole |
| 12 | 140 | Died | Encephalitis, HLH with CNS involvement |
| 13 | 1057 | Alive and well | |
| 14 | 149 | Alive and well | |
| 15 | 125 | Died | Pneumonitis and respiratory failure |
| 16 | 273 | Alive and well | |
| 17 | 416 | Died | Pneumonia and respiratory failure; chronic extensive GVHD |
| 18 | 867 | Alive and well | |
| 19 | 139 | Alive and well |
| Patient no . | Follow-up, d . | Outcome . | Cause of death . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 144 | Died | VOD and pulmonary hemorrhage |
| 2 | 50 | Died | VOD and MOF |
| 3 | 170 | Died | Pulmonary hypertension |
| 4 | 247 | Died | Fungal septic thrombosis of pulmonary veins and pulmonary artery with pulmonary hemorrhagic necrosis |
| 5 | 414 | Alive and well; limited skin GVHD | |
| 6 | 17 | Died | Pulmonary hemorrhage, VOD |
| 7 | 50 | Died | GVHD, MOF |
| 8 | 22 | Died | ARDS, posttransplantation cytokine storm syndrome |
| 9 | 1765 | Alive and well | |
| 10 | 285 | Died | Drug-resistant P aeruginosa sepsis |
| 11 | 13 | Died | Cardiac toxicity, MOF, asystole |
| 12 | 140 | Died | Encephalitis, HLH with CNS involvement |
| 13 | 1057 | Alive and well | |
| 14 | 149 | Alive and well | |
| 15 | 125 | Died | Pneumonitis and respiratory failure |
| 16 | 273 | Alive and well | |
| 17 | 416 | Died | Pneumonia and respiratory failure; chronic extensive GVHD |
| 18 | 867 | Alive and well | |
| 19 | 139 | Alive and well |
MOF indicates multiorgan failure; and ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Patient 8, who received an intermediate-conditioning regimen, also died, on day +22, of posttransplantation cytokine storm syndrome with acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Of the patients who received RIC, 6 of 11 are currently alive and well at a median of 570 days after HCT (55%). All but 1 survivor were given a Lansky or Karnofsky score of 100 at the time of last follow-up. Patients 10, 11, 12, 15, and 17 died at a median of 140 days after HCT (range, 13-416). Reported causes of death were heterogeneous and included pneumonitis with respiratory failure, cardiac toxicity with asystole and multiorgan failure, encephalitis, and ongoing CNS HLH (with loss of graft), sepsis, and pneumonia with respiratory failure (Table 4).
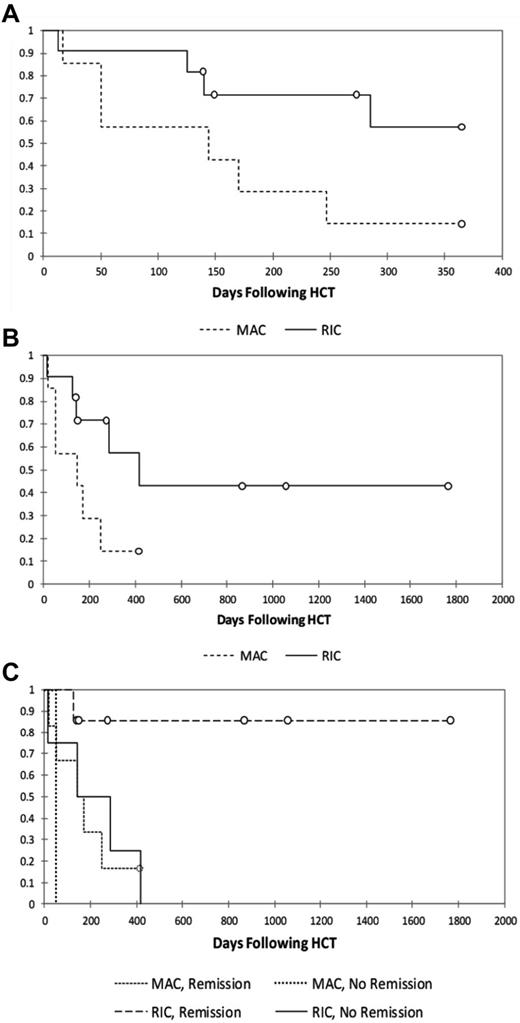
The 1-year probabilities of survival for MAC and RIC patients are 14% and 57%, respectively (Figure 1A), with long-term probabilities of survival of 14% and 43%, respectively (Figure 1B).
Kaplan-Meier survival analyses. Shown are analyses of 1-year survival (A), long-term survival (B), and survival stratified by reported HLH status at the time of transplantation (C; P = .035) in patients treated with MAC or RIC regimens.
Kaplan-Meier survival analyses. Shown are analyses of 1-year survival (A), long-term survival (B), and survival stratified by reported HLH status at the time of transplantation (C; P = .035) in patients treated with MAC or RIC regimens.
Influences on survival
We examined the significance of multiple factors known to influence transplantation outcomes including preparative regimen (MAC vs RIC),11 donor match,29 and HLH disease status at the time of transplantation.2-4 HLH disease status at the time of transplantation was based on the judgment of the treating/contributing physician who reported HLH to be in remission, in partial remission, or active. The patient who received the intermediate-intensity regimen (patient 8) was excluded from the analysis. Although there are a limited number of patients in our series, it is notable that of the surviving patients (n = 7), all were reported to be in remission of HLH at the time of HCT. Of the deceased patients (n = 12), half were reported to be in partial remission or have active disease at the time of HCT. It is also notable that of the 7 surviving patients, all but 1 received grafts from HLA-matched donors, whereas of the 12 deceased patients, only 3 received grafts from HLA-matched donors. Multivariate analysis suggested that MAC regimens and HLH that was not in remission conveyed statistically significant negative influences on survival (Figure 1C and Table 5). Match was significant in univariate analysis (data not shown), but was not significant once controlled for conditioning regimen and HLH remission status. Survival for patients receiving RIC who were reported to be in remission from HLH is 86% (P = .03; Figure 1C).
Cox proportional hazard regression model analysis
| Variable . | P . | HR . | HR 95% CI . | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | ||||
| Conditioning (MAC vs RIC) | .0251 | 7.524 | 1.287 | 44.000 |
| Match (match vs mismatch) | .2744* | 0.471 | 0.122 | 1.816 |
| HLH activity (not in remission vs remission) | .0806 | 4.322 | 0.837 | 22.330 |
| B | ||||
| Conditioning (MAC vs RIC) | .0181 | 6.348 | 1.371 | 29.394 |
| HLH activity (not in remission vs remission) | .0218 | 5.301 | 1.275 | 22.046 |
| Variable . | P . | HR . | HR 95% CI . | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | ||||
| Conditioning (MAC vs RIC) | .0251 | 7.524 | 1.287 | 44.000 |
| Match (match vs mismatch) | .2744* | 0.471 | 0.122 | 1.816 |
| HLH activity (not in remission vs remission) | .0806 | 4.322 | 0.837 | 22.330 |
| B | ||||
| Conditioning (MAC vs RIC) | .0181 | 6.348 | 1.371 | 29.394 |
| HLH activity (not in remission vs remission) | .0218 | 5.301 | 1.275 | 22.046 |
In part A of the table, multivariate analysis included preparative regimen, match, and HLH activity; in part B, the effects of preparative regimen and HLH activity were analyzed with removal of the nonsignificant match effect.
HR indicates hazard ratio; and CI, confidence interval.
The effect of match was statistically significant in univariate analysis.
Because XIAP functions as an inhibitor of apoptosis and is widely expressed, we also sought to determine whether residual protein expression may offer some protective benefit for survival after allogeneic HCT. Twelve patients were reported to have had analysis of XIAP protein expression. Of 5 patients with no detectable XIAP, 2 are alive and well (40%). Of 7 patients with detectable decreased or truncated protein expression, 3 are alive and well (43%). We conclude that in this limited cohort, the presence of detectable XIAP does not appear to confer a survival advantage.
Discussion
Deficiency of XIAP is a newly recognized disorder, and the results of the present study survey reveal that transplantation outcomes overall appear poor compared with the outcomes typically expected of patients with XLP and FHLH. There was a high incidence of conditioning-related toxicity, which may be related to the lack of ubiquitously expressed XIAP and the resultant loss of its antiapoptotic and other functions. In particular, only 1 patient treated with MAC is currently surviving (14%). This is in sharp contrast to the typical survival rates in other forms of HLH, which are generally greater than 50%.1-7,11-13 There was a preponderance of hepatic VOD and pulmonary hemorrhage in MAC patients. Although VOD has been reported in patients with HLH who undergo MAC regimens, it appears that the 50% incidence of VOD in this series is high compared with previous reports of 20%-30%.3,4 However, because of the small number of patients included in the present study, it is difficult to conclude definitively that XIAP deficiency predisposes patients to an increased risk of liver and pulmonary toxicity. In addition, a high proportion of MAC patients received grafts from HLA-mismatched donors or had HLH that was not in remission at the time of transplantation, which may have contributed to the poor outcomes. Regardless, based on the poor survival outcomes, MAC protocols should be cautioned against and avoided in patients with XIAP deficiency.
With regard to the RIC cohort, the overall survival of just over half of patients appears to be decreased compared with the relatively high survival rates expected for HLH patients undergoing RIC HCT, which are typically greater than 80%.10,11 However, the causes of death among the patients with XIAP deficiency were heterogeneous and we found no clear evidence to suggest that the deaths were related to deficiency of XIAP. The survival of RIC patients reported to be in remission from HLH was 86%, and the impact of HLH status was significant. This suggests that RIC transplantation outcomes for patients with XIAP deficiency who are in remission from HLH may be equivalent to that of other forms of XLP and FHLH. Infectious complications were common after HCT in both MAC and RIC patients. These complications do not appear to be increased compared with reports of transplantation outcomes for patients with HLH.9,11
Given our findings, the question of whether to pursue allogeneic RIC HCT is somewhat difficult to answer and is further complicated by the limited amount of information regarding outcomes of patients with XIAP deficiency not treated with transplantation. In the largest published series to date (N = 30), approximately 40% of patients with XIAP deficiency died at a mean age of 16 years predominantly because of HLH, colitis, or complications of allogeneic HCT.30 Overall, the small numbers of patients make it difficult to draw a firm conclusion regarding recommendations for RIC HCT for patients with XIAP deficiency. At this time, based on the available information, it is the our opinion that RIC protocols should be pursued with caution in young patients with XIAP deficiency who have a compelling clinical history and for whom a good stem cell donor is available. Preferably, patients should have no active lymphoproliferative disease or HLH and aggressive efforts should be made to ensure remission of HLH. The outcomes of all patients with XIAP deficiency should be monitored to further support evidence-based decisions regarding optimal treatment strategies.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Histiocyte Society for distributing our request for participation in this study to the members of the Society; Denise Bellman, Laura Hart, Linda Bierman, Angie Bonavita, and Christine Sper; Kejian Zhang and the molecular genetics laboratory at Cincinnati Children's Hospital; the patients and their families; and all of the physicians, nurses, and staff who provided care for patients.
R.A.M. is supported by a grant from the Clinical Immunology Society.
Authorship
Contribution: R.A.M. and K.R. designed the study, collected and analyzed the patient data, and wrote the manuscript; P.K., K.L., I.M., A.F., S.L., P.S., V.B., K.H., H.K., S.M., D.A.M., D.D., J.C., D.N.D., P.J.A., P.V., A.R.K., M.B.J., and J.J.B. collected the patient data and edited the manuscript; D.L. and M.K. performed the statistical analyses; and A.H.F. designed and oversaw the study and edited the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Rebecca A. Marsh, MD, Division of Bone Marrow Transplantation and Immune Deficiency, Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, 3333 Burnet Ave, Cincinnati, OH 45229; e-mail: rebecca.marsh@cchmc.org.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal