Abstract
Epigenome deregulation in cancer cells affects transcription of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. BET Bromodomain proteins recognize chromatin modifications and act as epigenetic readers contributing to gene transcription. BET Bromodomain inhibitors showed promising pre-clinical activity in hematological and solid tumors and are currently in phase I studies. The mechanism of action and relevant affected genes are not fully characterized and there are no established response predictors. We have shown activity of BET Bromodomain OTX015 in lymphoma cell lines (ASH 2012; ICML 2013). This study aimed at elucidating pathways and genes affecting response/resistance to BET Bromodomain inhibitors in lymphomas.
Baseline gene expression profiles (GEP) were obtained in 38 cell lines [22 diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), 8 anaplastic large T-cell lymphoma, 4 mantle cell lymphoma, 3 splenic marginal zone lymphoma, 1 chronic lymphocytic leukemia] with Illumina HumanHT-12 v4 Expression BeadChip. Genetic and biologic information were collected from literature. GEP/IC50 correlation (ASH 2012; ICML 2013) was assessed by Pearson correlation. Associations in two-way tables were tested for statistical significance using either chi-square or Fisher exact test, as appropriate. Differential expression analysis was performed using LIMMA, followed by multiple test correction using the BH method. Enrichment of functionally-related genes was evaluated by GSEA. For combination studies, 3 germinal center B-cell (GCB) and 2 activated B-cell (ABC) DLBCL were exposed to increasing doses of OTX015 alone or in combination with increasing doses of targeted agents for 72 hours, followed by MTT assay. Synergy was assessed by Chou-Talalay combination index (CI) with Synergy R package.
Transcripts associated with resistance to OTX015 were significantly enriched of genes involved in cell cycle regulation, DNA repair, chromatin structure, early B-cell development, E2F/E2F2 target genes, IL6-dependent genes, and mRNA processing. Conversely, transcripts associated with OTX015 sensitivity were enriched of hypoxia-regulated genes, interferon target genes, STAT3 targets, and involved in glucose metabolism. Genes associated with OTX015 sensitivity included LDHA, PGK1 (glucose metabolism) and VEGFA (hypoxia), while BCL2L1/BCLXL, BIRC5/survivin (anti-apoptosis), ERCC1 (DNA repair), TAF1A and BRD7 (transcription regulation) were correlated with reduced sensitivity.
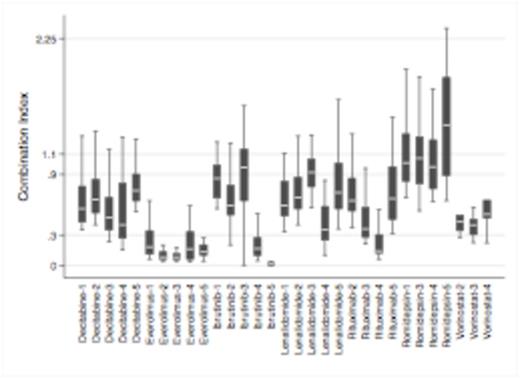
GEP identified 50 transcripts differentially expressed, including IL6, HCK, SGK1, MARCH1 and TRAFD1, between cells undergoing or not apoptosis after OTX015 exposure. GSEA showed significant enrichment of genes involved in IL-10 signaling pathway. While there was no association between response to OTX015<500nM and presence of translocated MYC, analysis of genetic and biologic features identified the ABC phenotype (P=.008) and presence of concomitant somatic mutations in MYD88 and CD79B or CARD11 genes and wild type TP53 (P=.027) as associated with apoptosis. Based on these observations and since mutated MYD88 interacts with BTK and MYD88/CD79B mutations have been associated with clinical responses with the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib, we evaluated OTX015 combination with this compound. Synergy was observed in particular in ABC-DLBCL with a median CI of .04 (range .02-.1). The demonstrated down-regulation of the MYD88/JAK/STAT pathway after OTX015 treatment, as shown by additional GEP, highlighted the importance of this pathway for OTX015 activity. Other targeted agents (everolimus, lenalidomide, rituximab, decitabine, vorinostat) appeared to synergize with OTX015 (Fig 1). The mTOR inhibitor everolimus presented a very strong synergism with a median CI of .11 (.1-.2), in accordance with the association between OTX015 sensitivity to high glucose metabolism and high levels of SGK1 in cells undergoing apoptosis.
OTX015 combinations in DLBCL cell lines showing additive effect or synergism in most instances. Y-axis: CI<0.3, strong synergism; 0.3-0.9, synergism; 0.9-1.1 additive effect. X-axis: drugs combined with OTX015 in GCB (1 DOHH2; 2 Karpas422; 3 SUDHL6) and ABC-DLBCL (4 U2932; 5 TMD8).
OTX015 combinations in DLBCL cell lines showing additive effect or synergism in most instances. Y-axis: CI<0.3, strong synergism; 0.3-0.9, synergism; 0.9-1.1 additive effect. X-axis: drugs combined with OTX015 in GCB (1 DOHH2; 2 Karpas422; 3 SUDHL6) and ABC-DLBCL (4 U2932; 5 TMD8).
Our study identified genetic mechanisms contributing to the response to BET Bromodomain inhibitors and promising combination schemes, such as OTX015/everolimus, to be further investigated.
Stathis:Oncoethix: NCT01713582 PI Other. Herait:Oncoethix: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees. Noel:Oncoethix: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees. Inghirami:Oncoethix: Research Funding. Bertoni:Oncoethix: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal