Abstract
In utero hematopoietic cell transplantation (IUHCTx) is a promising strategy to treat congenital disorders as the fetal host can potentially be tolerized to transplanted cells early in gestation. However, levels of engraftment have been low and fetal host conditioning strategies to increase space in hematopoietic niches have not been widely explored. We hypothesized that depletion of fetal host hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) using an antibody against the c-kit receptor (ACK2), a strategy which selectively depletes HSC by disrupting stem cell factor (SCF) signaling, would improve engraftment after HSC transplantation.
Fetal C57B6.CD45.2 (B6) mice were injected with increasing doses of ACK2 (2.5-50 µg/fetus) or isotype control antibody on E14.5 and surviving pups were transplanted with congenic B6.CD45.1 fetal liver mononuclear cells (2.5×106 cells/pup) on day of life 1 (P1, 7 days after in utero injection), allowing post-transplantation host monitoring. Host HSC depletion and residual serum ACK2 concentration were examined on P1. Peripheral blood chimerism, defined as donor/(donor+host) CD45 cells, as well as the lineage distribution of chimeric cells, were determined beginning 4 weeks after transplantation.
Survival to birth among fetuses injected with 2.5, 5, or 10 µg of ACK2 was similar to controls (control: 74%; 2.5 µg: 80%; 5 µg: 71%; 10 µg: 60%, p=0.2 by chi-square test, n≥45/group) but was significantly lower at higher concentrations (20 µg: 37%; 50 µg: 31%, p<0.001 vs. control, n≥70/group). Transient anemia and leukopenia were observed on P1 with doses ≥ 5 µg which resolved by P7 (n=17). Four of 19 pups previously treated with ACK2 (2.5-10 µg) and observed long-term had patchy coat discoloration, possibly a manifestation of disruption of C-kit+ melanocyte migration.
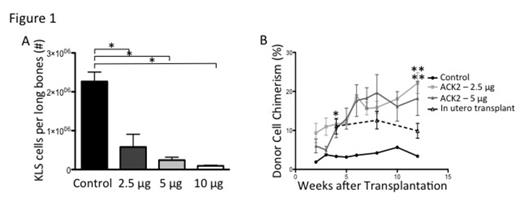
In utero ACK2 treatment resulted in significant and dose-dependent depletion of host HSCs (defined as Lin-Sca-1+C-kit+, KLS) in the bone marrow of treated animals by P1 (Figure 1A). There was no depletion of KLS cells in the liver. Residual ACK2 antibody was undetectable in the serum by P1, validating our strategy of in utero depletion and neonatal transplantation.
(A) Absolute number of KLS cells in long bones of animals treated with ACK2 or control on E14.5 and harvested on P1. * p<0.001, n=5-18/group. (B) Levels of donor peripheral blood CD45 cell chimerism in treated animals after in utero ACK2 treatment and neonatal transplantation, or in utero transplantation alone. * p<0.05 between control and all doses, n≥4/group, * * p<0.05 between 2.5 µg or 5 µg and in utero transplant at 12 weeks, n≥4/group.
(A) Absolute number of KLS cells in long bones of animals treated with ACK2 or control on E14.5 and harvested on P1. * p<0.001, n=5-18/group. (B) Levels of donor peripheral blood CD45 cell chimerism in treated animals after in utero ACK2 treatment and neonatal transplantation, or in utero transplantation alone. * p<0.05 between control and all doses, n≥4/group, * * p<0.05 between 2.5 µg or 5 µg and in utero transplant at 12 weeks, n≥4/group.
In animals receiving neonatal transplantation, ACK2 depletion resulted in a significant increase in levels of engraftment 4 weeks after transplantation compared to controls (control: 3.3±0.3%; 2.5 µg: 13±1.4%; 5 µg: 10±2.4%; 10 µg: 11±2.0%, p<0.05 for each dose vs control by ANOVA). Accordingly, we detected an increased number total bone marrow KLS cells 7 days after transplantation in ACK2 treated animals compared to controls (412±45.9 vs. 933±112 cells, p=0.01, n≥3/group). Moreover, levels of chimerism increased over time in treated animals (Figure 1B; 12 weeks: 2.5 µg: 190%; 5 µg: 170%; 10 µg: 160%) while they remained unchanged in controls. Overall, levels of chimerism achieved with ACK2 treatment were significantly higher than that observed in animals that received in utero transplantation without ACK2 depletion.
Lineage analysis of peripheral blood for granulocytes, B cells, and T cells indicated an equal increase in all lineages, suggesting ACK2 depletes true HSCs and not committed progenitors. Interestingly, ACK2 depletion at doses 2.5-10 µg did not result in engraftment of allogeneic BALB/c cells (n=11), indicating that allogeneic neonatal transplantation, unlike in utero transplantation, is limited by a host immune response which is unaffected by ACK2.
We have demonstrated that fetal HSC depletion using ACK2 can lead to clinically relevant levels of donor cell engraftment with minimal toxicity. In previous studies with this antibody, host HSC depletion required either immunodeficient animals or concurrent irradiation, whereas we achieved depletion in wild-type fetal hosts, suggesting differences in fetal vs. adult HSC sensitivity to SCF signaling. Future studies should explore this strategy to improve engraftment in large animals models of IUHCTx.
Weissman:Amgen, Systemix, Stem cells Inc, Cellerant: Consultancy, Employment, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal