Abstract
Management of patients with a major bleed while on vitamin K antagonist (VKA) is a common clinical challenge. Prothrombin Complex Concentrates (PCC) provide a rapid reversal of VKA induced coagulopathy. The aim of this systematic review is to describe the currently used PCC strategies and to present their efficacy in terms of target INR achievement and clinical outcome.
MEDLINE and EMBASE databases were searched for studies reporting the use of PCC for emergency reversal of VKA therapy. Additional inclusion criteria were the reporting of PCC dosing strategy, data on target INR or any clinical outcome or safety parameters, prospective patient enrollment, and a full text publication. All PCC studies in non-VKA patients, case-reports (N<5), duplicates, retrospective studies, and studies on activated PCC were excluded. The quality of selected studies was evaluated using two quality assessment tools which are described by Downs (J Epidemiol Community Health, 1998), and Thomas (McMaster University, 2008).
A total of 27 studies was included in which the majority was single cohort (N=18, 67%), open label (N=27, 100%), and/or nonrandomized (N=23, 85%). The total number of included patients was 2410, ranging from 5 to 686 patients per study. One of the included studies was scored as having a strong, 12 a moderate and 14 a weak design. The median quality assessment score was 16 out of 26 [range 10-22]. A large heterogeneity in study parameters was observed including 6 different primary endpoints with 12 different definitions.
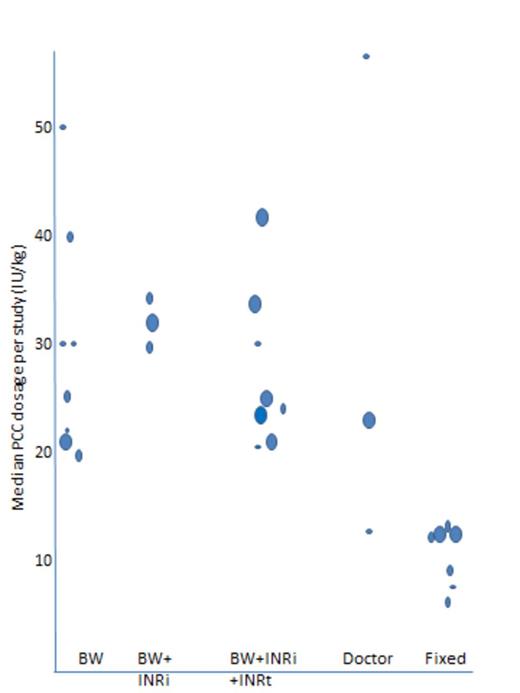
Fifteen PCC protocols were identified in which the PCC dose ranged from 8 to 50 IU of factor IX/kg or a fixed dose protocol of 200, 500, 1000, or 1500 IU of factor IX/patient. These dosing strategies were based on five principals, namely based on bodyweight (BW), bodyweight and initial INR (BW+INRi), bodyweight and initial INR and target INR (BW+INRi+INRt), individual doctors decision (doctor) or a fixed dose (fixed). The actual infused dosage is depicted in figure 1.
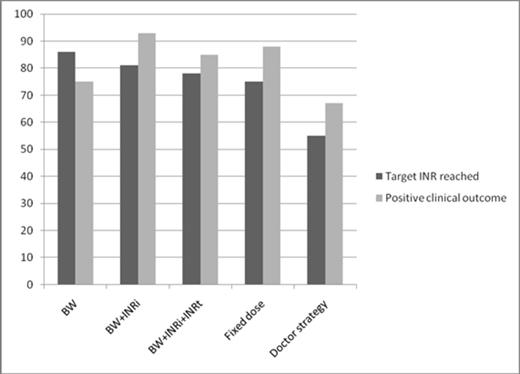
Results on target INR and clinical outcome per strategy. Estimated relative risks with 95% confidence intervals for the study period are shown. VTE: venous thromboembolism D: dabigatran R: rivaroxaban A: apixaban
Results on target INR and clinical outcome per strategy. Estimated relative risks with 95% confidence intervals for the study period are shown. VTE: venous thromboembolism D: dabigatran R: rivaroxaban A: apixaban
Evaluating the used dosing strategy, target INR was reached in 86%, 81%, 78% and 75% of patient in BW, BW+INRi, BW+INRi+INRt and fixed, respectively and was lower (55%) in doctor strategy. Of note, results of the doctor strategy are based on two studies.
Clinical outcome was positive for 75%, 93%, 85%, 88% and 67% of patients in strategy BW, BW+INRi, BW+INRi+INRt, fixed, and doctor strategy respectively. Of note, only one study reported on the clinical outcome in the BW+INRi strategy and two in doctor strategy.
While our review shows a great diversity on PCC dosing strategies among published data, the same applies to current PCC guidelines in which the ACCP leaves the dosing to the discretion of the physician, the French guidelines recommend a bodyweight adjusted dosing regardless of the INR, the Canadian guidelines recommend three different fixed doses stratified by initial INR, and the Australian guidelines recommend a range of bodyweight adjusted doses from which the physician should decide.
Apart from the different dosing strategies, considerable heterogeneity in assessing the impact of PCC treatment was noticed indicating the lack of consensus regarding different aspects of emergency reversal of VKA treatment e.g. optimal target INR, clinical outcome definition. Furthermore, PCC is predominantly studied in small, single-arm and open label settings using the INR to measure its effect rather than clinical outcome. In addition, results from our quality assessment showed that most study designs were at most moderately robust. Evidence gained from the included studies should therefore be interpreted with caution.
In conclusion, this review shows that the worst results are reported when a predefined dosing protocol is absent (doctors strategy), while with the use of any treatment protocol good outcome results of PCC treatment are obtained (target INR reached ³ 75%, positive clinical response ³ 75%). A fixed dose strategy seems to be the most simple treatment, with a high potential for optimal clinical outcome while the lowest PCC dosages are infused. Good quality studies with consistent endpoints are needed to guide clinical use.
Actual median dose infused in each study(arm). Dots represent the included studies(cohorts) with large, average and small amount of included patients
Khorsand:Sanquin BV, Amsterdam: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal