Abstract
Background: De-regulation of microRNA (miRNA) has been extensively investigated in both Hodgkin (HL) and non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL), however, little is known about the roles of miRNAs in T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma (T-LBL). To understand the involvement of miRNAs in the development and treatment of (T-LBL), miRNA profiles were compared between tumor and corresponding non-tumor tissues.
Methods: miRCURY LNA array was used to generate miRNA expressing profile. Real-time quantitative PCR and immunohistochemistry (IHC) were applied to detect the expression of miR-374b, AKT1 and Wnt16 in T-LBL samples. Dual-luciferase reporter assay was conducted to confirm target associations of miR-374b. The tumor suppressive effect of miR-374b was determined by both in-vitro and in-vivo studies.
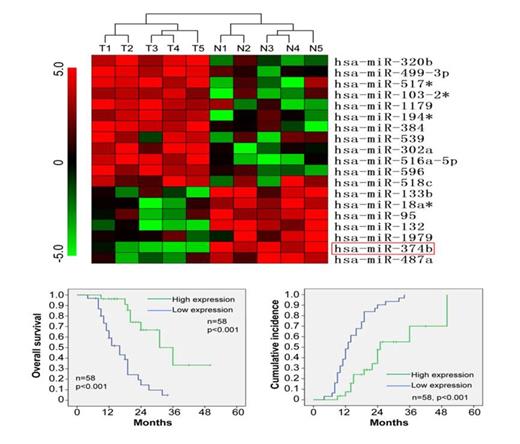
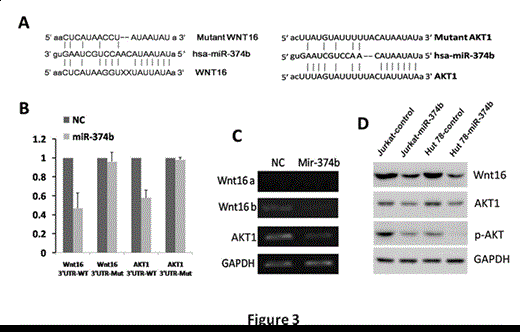
Results: The expression of 380 miRNAs was evaluated in five human T-LBL tissues and correspondence normal peripheral blood T-cells by microRNA microarrays. The down-regulation of miR-374b was frequently detected in primary T-LBL tissues, which was significantly associated with patients worse overall survival (P<0.001) and increasing risk of recurrence (P=0.012). Functional assays demonstrated that miR-374b could suppress T-NHL cells proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, miR-374b could also sensitize cells to both serum starvation- and chemotherapeutic agent-induced apoptosis. Significantly, subsequent investigation characterized two AKT pathway associated molecules, AKT1 and Wnt16, as direct targets of miR-374b and account for the effect of miR-374b in T-NHL cells. Consistently, in tissues of our T-LBL patients, AKT1 and Wnt16 expression was inversely correlated with miR-374b levels, and could also be independent predictors of recurrence and survival of these patients.
Conclusions: Our data highlight the molecular etiology and clinical significance of miR-374b in T-LBL. Targeting miR-374b may represent a new therapeutic strategy to improve the therapy effect and survival for T-LBL patients.
Down-regulation of miR-374b is associated with poor prognosis of T-LBL
ectopic expression of miR-374b suppress T-NHL cells proliferation and sensitize cells to both serum starvation- and chemotherapeutic agent-induced apoptosis
ectopic expression of miR-374b suppress T-NHL cells proliferation and sensitize cells to both serum starvation- and chemotherapeutic agent-induced apoptosis
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal