Abstract
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K) is an RNA and DNA binding protein that regulates critical pathways controlling differentiation and proliferation programs. While alterations in hnRNP K expression are associated with neoplastic malignancies, we currently do not understand how changes in hnRNP K expression contribute to tumor phenotypes in vivo. Previous biochemical and cell line studies demonstrate that hnRNP K transcriptionally regulates p53-dependent activities, suggesting it functions as a potential tumor suppressor. However, hnRNP K has also been shown to positively regulate c-Myc expression, indicating it may behave as an oncogene.
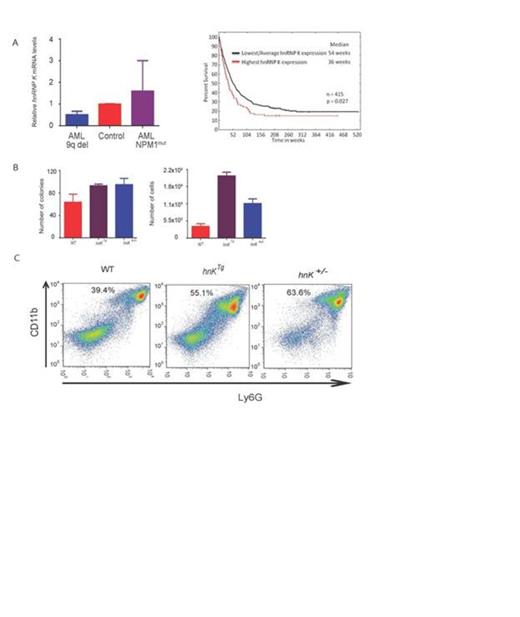
The HNRNP K gene maps to a region of chromosome 9 (9q21.32), which is lost in a subset of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). RNA expression analyses of patient samples with AML that harbor 9q21.32 deletions revealed a significant reduction in HNRNP K expression compared to wild type control samples, supporting the notion that hnRNP K acts as a tumor suppressor (Figure 1A). However, patients with AML who do not harbor a 9q21.32 deletion displayed a significant increase in hnRNP K expression (Figure 1A). Thus, to examine the association between altered hnRNP K expression and disease status in patients with AML, we performed reverse phase protein array (RPPA) analysis on CD34+ bone marrow cells from 415 de novo AML patient as well as healthy donor controls. Interestingly, we observed a significant correlation between elevated hnRNP K levels and poor outcomes, which supports the idea that hnRNP K has oncogenic potential (Figure 1A). Together, these observations indicate that any change in hnRNP K expression may contribute to the etiology of AML and supports the idea that hnRNP K may potentially act as either a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor or oncogene in AML.
To directly interrogate these possibilities in vivo, we generated mouse models that either harbor a deletion of one hnRNP K allele (hnRNP K+/-) or overexpressed hnRNP K (hnRNP KTg) in the hematological compartment. Western blot analyses demonstrated that hnRNP K haploinsufficiency results in a significant reduction in hnRNP K expression while tissue-specific activation of hnRNP K resulted in overexpression of hnRNP K.
Similar to our observation in AML patients, either hnRNP K haploinsufficiency or overexpression resulted in similar phenotypes in vitro and in vivo. Lin-CD117+ hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) from hnRNP K+/- and hnRNP KTg mice had significant increases in differentiation and proliferation potential as determined by colony formation assays. In these experiments, we observed a significant increase in the number of total colonies and number of cells per colony in both hnRNP K+/- and hnRNP KTg HSCs as compared to wild type HSCs (Figure 1B). In vivo analyses of the hnRNP K+/- and hnRNP KTg mice revealed a significant increase in myeloid hyperplasia in the peripheral blood and bone marrow, increased tumor formation, genomic instability, and decreased survival compared to wild type mice (Figure 1C). Interestingly, both increased and decreased hnRNP K expression resulted in alterations in similar pathways that regulate differentiation and proliferations potential (e.g.; p53 and c-Myc pathways and alterations in C/EBP expression).
Together, these clinical and animal model studies illustrate that either over-expression or under-expression of hnRNP K lead to strikingly similar phenotypes that directly impact the etiology of AML. Furthermore, these data not only implicate that hnRNP K behaves as both a tumor suppressor and oncogene, but also suggest that it functions as a master toggle that dictates the proliferation and differentiation potential of HSCs. We are currently using Whole Transcriptome Shotgun Sequencing (RNA-Seq) and ChIP-Seq to evaluate the mechanisms by which increased and decreased hnRNP K expression impact hematologic malignancies.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal