Abstract
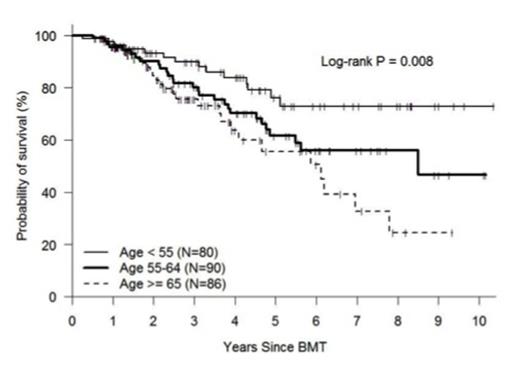
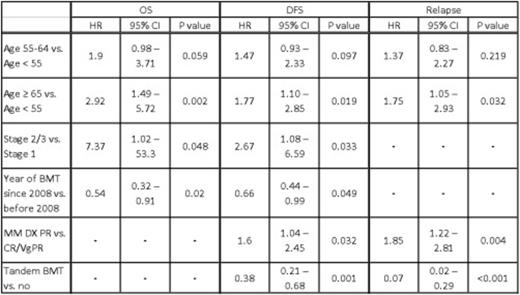
Multiple myeloma is the second most common hematological malignancy in the United States. The risk of developing multiple myeloma increases with age; with approximately 85% of patients are over age 55 and 62% over age 65. Through improved supportive care, increased access to hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, and introduction of new biologic agents, survival has increased over the past 20 years. Currently, autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) is the standard of care after primary therapy for eligible patients. Research has suggested a greater survival benefit after ASCT for patients < 60 years, but the role of ASCT in older individuals remains less clear. In order to better understand the impact of age on the outcome of myeloma patients receiving ASCT, we analyzed the presenting features and outcomes of 256 consecutive patients at our institution that received a first ASCT between January 2004 and December 2013. Patient characteristics were: median age 61 (range 32-76), Sex: M=55% F=45%, Immunochemical subtype: IgG=59%, IgA =21%, Light chain=16%, Other=4%, Durie-Salmon System (DSS) stage at diagnosis: Stage I=9%, Stage II=20%, Stage III=68%, Unknown=4%, Disease status at transplant: CR/sCRsp=18%, VgPR=27%, PR=49%, Stable=6%, Melphalan preparative dose: 200mg/m2=93%, 140mg/m2=7%. Second ASCT was eventually performed in 60 (23%) of patients, with 39 (15%) of these being planned tandem ASCT. Patient survival and disease status were collected prospectively as part of our comprehensive database. For purposes of analysis, patients were divided by age into three groups: age<55 (n=80), age 55-64 (n=90), age ≥ 65 (n=86). Groups were similar in regards to disease subtype, stage, status at the time of transplant, comorbidity index, and year of transplant; differences included more second transplants and tandem transplants in the youngest age group and more reduced dose melphalan in the oldest age group. At day +100 post-transplant, disease response was CR, VGPR, PR, and <PR in 35%, 24%, 39%, and 2%, respectively and did not differ statistically by age group. Non-relapse mortality at one-year post-transplant was 1%, and did not differ among the <55, 55-64, and ≥ 65 age-groups (0%, 3%, and 0%, respectively). With a median follow-up of 39 months, the estimated 4-year OS, DFS, and relapse incidence (RI) was 73%, 43%, and 48%, respectively. Survival and RI were significantly better in the younger age group (4-yr OS 84%, 70%, 64%; DFS 58%, 35%, 39%; RI 34%, 53%, 53%, respectively in the <55, 55-64, and ≥ 65 age-groups; see figure). Outcomes were extremely favorable in patients <55 years of age transplanted in CR or VGPR with a 4-yr OS, DFS, and RI of 96%, 75%, and 21%, respectively. Even in the older age groups, median overall survival had not been reached by 5 years, suggesting that all age groups benefit from ASCT. There were no statistically significant differences in measured outcomes between patients age 55-64 years and those age ≥ 65 years, confirming that age ≥ 65 years should not be used to determine transplant eligibility. In multivariate analysis, variables predictive of OS included age, disease stage, and year of transplant; whereas for DFS, predictive variables also included disease status at transplant and planned tandem ASCT (see table). This analysis builds on a growing body of evidence suggesting improved outcomes in patients with multiple myeloma. Patients regardless of age appear to benefit from ASCT, with median survival now exceeding 5 years in all age groups. Patients less than 55 years of age and particularly those achieving at least a VGPR prior to ASCT seem to represent a patient population with an extremely favorable prognosis post-transplant.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal