Key Points
Brentuximab vedotin was active in DLBCL across a range of CD30 expression levels, and objective responses occurred in 44% of patients.
Abstract
Several non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) subtypes, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), variably express CD30. This phase 2, open-label study evaluated the efficacy of brentuximab vedotin, an anti-CD30 antibody-drug conjugate, in relapsed/refractory CD30+ NHL. This planned subset analysis of B-cell NHLs includes 49 patients with DLBCL and 19 with other B-cell NHLs. Objective response rate was 44% for DLBCL, including 8 (17%) complete remissions (CRs) with a median duration of 16.6 months thus far (range, 2.7 to 22.7+ months). There was no statistical correlation between response and level of CD30 expression; however, all responding patients had quantifiable CD30 by computer-assisted assessment of immunohistochemistry. DLBCL patients were generally refractory to first-line (76%) and most recent therapies (82%), and 44% of these refractory patients responded (15% CRs). Patients with other B-cell lymphomas also responded: 1 CR, 2 partial responses (PRs) of 6 with gray zone, 1 CR of 6 with primary mediastinal B-cell, and 1 CR of 3 with posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder. Adverse events were consistent with known toxicities. The combination of brentuximab vedotin with rituximab was generally well tolerated and had activity similar to brentuximab vedotin alone. Overall, significant activity with brentuximab vedotin was observed in relapsed/refractory DLBCL, and responses occurred across a range of CD30 expression. This study was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT01421667.
Introduction
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL).1 First-line treatment with rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone (R-CHOP) results in long-term disease-free survival in 33% to 96% of patients, depending on several prognostic variables; however, about 30% of patients with DLBCL eventually succumb to the disease.2 A fraction of DLBCL patients (∼25%) who recur after or are refractory to first-line therapy are eligible for and will be cured by salvage chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation (SCT). There is no standard therapy for patients for whom salvage regimens fail or who are ineligible for transplant. Response rates are poor in this setting, and novel approaches are needed.3-7 Similarly, effective salvage therapies are lacking for subsets of DLBCL, such as the mediastinal variant of DLBCL, and other aggressive NHLs, such as gray zone lymphomas (B-cell lymphoma unclassifiable with features intermediate between DLBCL and classical Hodgkin lymphoma [HL]) and posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders (PTLDs).8-12
CD30 is expressed in a variety of malignancies13,14 and is present in 14% to 25% of DLBCL patients, depending on the cutoff used to assign positivity.15-17 Hu et al reported a unique gene expression profile for de novo DLBCL expressing CD30 in greater than 20% of cells.15 Although this study suggested that CD30 expression imparts a more favorable prognosis with first-line R-CHOP therapy, other studies have not universally confirmed this finding and the prognostic implications of CD30 expression at relapse are unclear.17,18
Brentuximab vedotin (ADCETRIS) is a CD30-directed antibody-drug conjugate (ADC). After binding to CD30 on the tumor cell surface, preclinical data suggest that the ADC internalizes leading to release of monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) via proteolytic cleavage and induction of cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis.19 This study (NCT01421667) was initiated to evaluate the efficacy and safety of single-agent brentuximab vedotin in relapsed/refractory mature T-cell and B-cell lymphomas with variable CD30 expression. Results from the T-cell cohort were published previously.20 The protocol was amended to include an additional group of DLBCL patients to be treated with brentuximab vedotin and rituximab with the intent of assessing the safety of this combination.
Patients and methods
This is a phase 2, open-label, multicenter study designed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of brentuximab vedotin in relapsed/refractory NHL, including both World Health Organization classifications of mature T-cell and/or natural killer–cell and B-cell neoplasms.21 The results for the planned subset analysis of patients with CD30+ B-cell lymphomas, including DLBCL and other B-cell lymphomas, are presented.
This study was conducted in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki, the International Conference on Harmonization Good Clinical Practices, and the applicable US Food and Drug Administration regulations. Approval from the institutional review board was received for each site, and all patients gave written informed consent prior to study participation.
Eligibility
Patients could have any subtype of histologically confirmed B-cell lymphoma with CD30 expression detectable by visual assessment of immunohistochemistry (IHC) on a biopsy of the most recent relapsed/refractory disease per institutional laboratory. All eligible patients had bidimensionally measurable disease of ≥1.5 cm in greatest transverse diameter and no history of another active invasive malignancy within the previous 3 years. Patients had to be age 12 years or older and have an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of ≤2. Previous allogeneic SCT was allowed if >100 days had elapsed since SCT and there was no active graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) at the time of screening. Patients were required to have adequate baseline laboratory values for eligibility as previously reported.20 Exclusion criteria included prior treatment with brentuximab vedotin, evidence of cerebral/meningeal disease, or prior progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Patients with pre-existing peripheral neuropathy were eligible.
Study design
The study was designed to enroll approximately 65 patients with CD30+ relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphomas, including approximately 50 DLBCL patients. Patients received 1.8 mg/kg brentuximab vedotin intravenously every 3 weeks. Those who achieved stable disease (SD) or better could receive continued treatment until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or study closure. The primary objective was objective response rate (ORR) as determined by the investigator per the Revised Response Criteria for Malignant Lymphoma.22 Secondary end points included safety, correlation of CD30 expression with response, duration of objective response, and progression-free survival (PFS).
Dose reduction to 1.2 mg/kg and treatment delay of up to 3 weeks was allowed, depending on the type and severity of toxicity, including peripheral neuropathy. Support with platelet and/or red blood cell transfusion or granulocyte colony-stimulating factors was allowed. Low-dose prednisone (≤20 mg per day or other steroid equivalent) was permitted prior to study entry for GVHD and other indications unrelated to treatment of lymphoma. Immunosuppressive therapy (any dose level) was permitted for the prevention of transplant rejection or management of GVHD.
A separate cohort of patients (approximately 15 planned) received brentuximab vedotin 1.8 mg/kg intravenously in combination with rituximab (375 mg/m2) on day 1 of each 3-week cycle. The primary objective was to assess the safety of brentuximab vedotin when given in combination with rituximab. Patients who completed 8 cycles of combination therapy or those who had unacceptable toxicity to rituximab prior to completion of 8 cycles could receive brentuximab vedotin, 1.8 mg/kg, as a single agent on day 1 of each cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
For patients who received at least 1 dose of brentuximab vedotin, disease status and survival were observed every 3 months for the first 2 years and per institutional standard of care thereafter until study closure or withdrawal of consent. For patients who discontinued study drug for any reason other than disease progression or initiation of a nonprotocol therapy, radiographic assessments were done every 6 months for the first year and per institutional standard of care thereafter.
Study assessments
Response assessments were performed by using computed tomography and positron emission tomography scans of the neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis at baseline, after cycles 2 and 4, and every 3 cycles thereafter while on study treatment, at end-of-treatment, and during follow-up as described above. Restaging assessments were performed by using only computed tomography scans of diagnostic quality if disease was not fluorodeoxyglucose-avid at baseline. Clinical response per the Revised International Working Group Response Criteria for Malignant Lymphoma 2007 was determined by the investigator.22 Progressive disease (PD) included both disease progression by radiographic assessment and clinical disease progression as determined by the investigator. Safety and tolerability were assessed from first dose until approximately 30 to 37 days after the last dose of study drug. The National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 4.0.3 was used for grading adverse events (AEs). Other study assessments included pharmacokinetic (PK) analyses.
CD30 expression and soluble CD30
For eligibility, CD30 positivity on lymphoma cells was determined by the institutional laboratory by visual assessment of routine IHC staining using the anti-CD30 BerH2 antibody. Tissue samples were also sent to the central pathology laboratory (Quest Diagnostics) for an independent quantification of CD30 expression by IHC. Central laboratory definition of CD30 positivity was ≥1% expression on neoplastic cells.
For exploratory purposes, further analyses of the same samples was performed to quantify CD30 expression by computer-assisted methods using pixel-based image processing techniques to detect CD30 expression on all cells (Flagship Biosciences).
Soluble CD30 (sCD30) concentrations were measured in a commercial bead-based sandwich fluoroimmunoassay modified to eliminate interference by brentuximab vedotin; assays were performed on a Bio-Plex 200 system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.) with appropriate calibrators and controls.
Statistical analysis
Pathology was classified as DLBCL or other B-cell lymphomas according to World Health Organization 2008 criteria. Patient disposition, demographics, disease characteristics, safety, disease response, and exposure to study drug were analyzed by disease diagnosis, including DLBCL and other B-cell lymphomas. Primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma (PMBL) was included in other B-cell lymphomas because the natural history and treatment for PMBL can differ from that for other DLBCLs.23,24
ORR was defined as the proportion of patients with complete response (CR) or partial response (PR) as best clinical response according to the Revised Response Criteria for Malignant Lymphoma.22 For the primary objective for the DLBCL subgroup, observation of 10 or more objective responses (≥20% ORR) in efficacy-evaluable patients allowed rejection of the null hypothesis and a claim that the true ORR is greater than 10% (with a one-sided significance level of 0.05). The efficacy-evaluable analysis set included all patients who received any amount of brentuximab vedotin or combination therapy and who had both a baseline and at least one postbaseline disease assessment (radiographic response assessment or clinical disease progression) up to the closure of the study or prior to the start of new anti-cancer treatment. No formal hypothesis was specified for the other B-cell lymphoma subgroup.
The medians and two-sided 95% confidence intervals for duration of response, duration of CR, and PFS were estimated by using Kaplan-Meier methodology. Duration of response for this study was defined as the time from start of the first documentation of objective response (CR or PR) to the first documentation of tumor progression or to death as a result of any cause. PFS was defined as the time from start of study treatment to first documentation of tumor progression or death as a result of any cause. Patients who initiated a nonprotocol antitumor treatment prior to documented PD or death (excluding stem cell transplant) were censored at the date of the last disease assessment prior to start of new therapy. The correlation of CD30 expression with response was assessed by using a generalized linear model. The PK parameters of brentuximab vedotin, MMAE, and total antibody were estimated and summarized with descriptive statistics.
No formal hypotheses were specified for combination therapy. The intent of this cohort was to describe the type, incidence, severity, seriousness, and relatedness of AEs and laboratory abnormalities in patients treated with brentuximab vedotin in combination with rituximab.
Results
Patients
Sixty-eight patients with B-cell lymphomas (49 DLBCL and 19 other B-cell lymphomas) were treated between August 2011 and August 2013 at 26 sites in the United States. Patient demographics, baseline disease characteristics, and prior cancer-related therapies are presented in Table 1. Most patients had stage III or IV disease, and 12 DLBCL patients (24%) had transformed disease from a prior indolent NHL. More than half of all patients had received 3 or more prior systemic therapies (range, 1 to 19 therapies), and nearly all had received prior rituximab. Most patients had refractory disease defined by less than CR or relapse from CR within 3 months of completion of first-line therapy or lack of an objective response with most recent therapy in patients who had received more than 1 prior therapy. Thirteen (19%) of the 68 patients had a prior SCT. Patients who had not undergone prior SCT were considered by the treating investigator to be ineligible for SCT on the basis of age, comorbidities, and/or lack of response.
Demographics and baseline disease characteristics
| . | Single-agent brentuximab vedotin . | Brentuximab vedotin + rituximab . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DLBCL (n = 49) . | Other B-cell lymphoma (n = 19) . | DLBCL (n = 16) . | ||||
| No. . | % . | No. . | % . | No. . | % . | |
| Age, y | ||||||
| Median | 62 | 36 | 62 | |||
| Range | 17-85 | 16-68 | 22-78 | |||
| Male | 28 | 57 | 11 | 58 | 12 | 75 |
| Baseline ECOG performance status | ||||||
| 0 | 17 | 35 | 8 | 42 | 9 | 56 |
| 1 | 28 | 57 | 7 | 37 | 7 | 44 |
| 2 | 4 | 8 | 3 | 16 | 0 | |
| IPI score | ||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 0 | |
| 1 | 9 | 18 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 25 |
| 2 | 11 | 22 | 6 | 32 | 6 | 38 |
| 3 | 14 | 29 | 4 | 21 | 3 | 19 |
| 4 | 8 | 16 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Unknown | 6 | 12 | 7 | 37 | 3 | 19 |
| DLBCL | ||||||
| DLBCL-NOS | 43 | 88 | 0 | 16 | 100 | |
| EBV-positive DLBCL of the elderly | 5 | 10 | 0 | 0 | ||
| T-cell-rich B-cell lymphoma | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Other B-cell lymphomas | ||||||
| Gray zone lymphoma | 0 | 6 | 32 | 0 | ||
| PMBL | 0 | 6 | 32 | 0 | ||
| Follicular lymphoma | 0 | 3 | 16 | 0 | ||
| PTLD | 0 | 3 | 16 | 0 | ||
| Plasmablastic lymphoma | 0 | 1 | 5 | 0 | ||
| Transformed disease | 12 | 24 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 31 |
| Bulky disease, ≥5 cm on at least one baseline index lesion | 19 | 39 | 8 | 42 | 4 | 25 |
| Time from diagnosis to first dose, months | ||||||
| Median | 14.0 | 13.2 | 16.6 | |||
| Range | 0.8-124.4 | 1.7-191.2 | 0.9-347.3 | |||
| % CD30+ malignant cells* | ||||||
| Median | 25 | 47.5 | 50 | |||
| Range | 0-100 | 4-100 | 1-100 | |||
| sCD30, ng/mL† | ||||||
| Median | 206.1 | 385.1 | 389.7 | |||
| Range | 35.6-9428.6 | 33.2-21277.7 | 62.9-1070.2 | |||
| Stage at initial diagnosis‡ | ||||||
| I-II | 12 | 24 | 4 | 21 | 4 | 25 |
| III-IV | 35 | 71 | 13 | 68 | 12 | 75 |
| Refractory to most recent prior therapy | 40 | 82 | 14 | 74 | 9 | 56 |
| Refractory to first-line therapy | 37 | 76 | 17 | 89 | 10 | 63 |
| No. of prior cancer-related systemic therapies | ||||||
| Median | 3 | 3 | 3 | |||
| Range | 1-6 | 1-19 | 1-5 | |||
| Patients with prior: | ||||||
| Rituximab exposure | 47 | 96 | 18 | 95 | 15 | 94 |
| Anthracycline-containing regimen | 45 | 92 | 17 | 89 | 14 | 88 |
| Platinum-based systemic therapy | 34 | 65 | 12 | 63 | 10 | 63 |
| Cancer-related radiotherapy | 14 | 29 | 6 | 32 | 5 | 31 |
| Stem cell transplant | 10 | 20 | 3 | 16§ | 4 | 25 |
| Autologous | 10 | 20 | 2 | 11 | 4 | 25 |
| Allogeneic | 0 | 2 | 11 | 0 | ||
| . | Single-agent brentuximab vedotin . | Brentuximab vedotin + rituximab . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DLBCL (n = 49) . | Other B-cell lymphoma (n = 19) . | DLBCL (n = 16) . | ||||
| No. . | % . | No. . | % . | No. . | % . | |
| Age, y | ||||||
| Median | 62 | 36 | 62 | |||
| Range | 17-85 | 16-68 | 22-78 | |||
| Male | 28 | 57 | 11 | 58 | 12 | 75 |
| Baseline ECOG performance status | ||||||
| 0 | 17 | 35 | 8 | 42 | 9 | 56 |
| 1 | 28 | 57 | 7 | 37 | 7 | 44 |
| 2 | 4 | 8 | 3 | 16 | 0 | |
| IPI score | ||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 0 | |
| 1 | 9 | 18 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 25 |
| 2 | 11 | 22 | 6 | 32 | 6 | 38 |
| 3 | 14 | 29 | 4 | 21 | 3 | 19 |
| 4 | 8 | 16 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Unknown | 6 | 12 | 7 | 37 | 3 | 19 |
| DLBCL | ||||||
| DLBCL-NOS | 43 | 88 | 0 | 16 | 100 | |
| EBV-positive DLBCL of the elderly | 5 | 10 | 0 | 0 | ||
| T-cell-rich B-cell lymphoma | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Other B-cell lymphomas | ||||||
| Gray zone lymphoma | 0 | 6 | 32 | 0 | ||
| PMBL | 0 | 6 | 32 | 0 | ||
| Follicular lymphoma | 0 | 3 | 16 | 0 | ||
| PTLD | 0 | 3 | 16 | 0 | ||
| Plasmablastic lymphoma | 0 | 1 | 5 | 0 | ||
| Transformed disease | 12 | 24 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 31 |
| Bulky disease, ≥5 cm on at least one baseline index lesion | 19 | 39 | 8 | 42 | 4 | 25 |
| Time from diagnosis to first dose, months | ||||||
| Median | 14.0 | 13.2 | 16.6 | |||
| Range | 0.8-124.4 | 1.7-191.2 | 0.9-347.3 | |||
| % CD30+ malignant cells* | ||||||
| Median | 25 | 47.5 | 50 | |||
| Range | 0-100 | 4-100 | 1-100 | |||
| sCD30, ng/mL† | ||||||
| Median | 206.1 | 385.1 | 389.7 | |||
| Range | 35.6-9428.6 | 33.2-21277.7 | 62.9-1070.2 | |||
| Stage at initial diagnosis‡ | ||||||
| I-II | 12 | 24 | 4 | 21 | 4 | 25 |
| III-IV | 35 | 71 | 13 | 68 | 12 | 75 |
| Refractory to most recent prior therapy | 40 | 82 | 14 | 74 | 9 | 56 |
| Refractory to first-line therapy | 37 | 76 | 17 | 89 | 10 | 63 |
| No. of prior cancer-related systemic therapies | ||||||
| Median | 3 | 3 | 3 | |||
| Range | 1-6 | 1-19 | 1-5 | |||
| Patients with prior: | ||||||
| Rituximab exposure | 47 | 96 | 18 | 95 | 15 | 94 |
| Anthracycline-containing regimen | 45 | 92 | 17 | 89 | 14 | 88 |
| Platinum-based systemic therapy | 34 | 65 | 12 | 63 | 10 | 63 |
| Cancer-related radiotherapy | 14 | 29 | 6 | 32 | 5 | 31 |
| Stem cell transplant | 10 | 20 | 3 | 16§ | 4 | 25 |
| Autologous | 10 | 20 | 2 | 11 | 4 | 25 |
| Allogeneic | 0 | 2 | 11 | 0 | ||
EBV, Epstein-Barr virus; ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; IPI, International Prognostic Index; NOS, not otherwise specified.
Per visual central review; includes 44 patients with DLBCL and 18 patients with other B-cell lymphomas who were treated with monotherapy, and 12 patients who were treated with combination therapy.
Includes 46 patients with DLBCL and 18 patients with other B-cell lymphomas who were treated with monotherapy, and 12 patients who were treated with combination therapy.
Four patients had unknown disease stage at study entry including 2 patients with DLBCL and 2 patients with other B-cell lymphomas who were treated with single-agent therapy.
One patient had both a prior autologous and a prior allogeneic SCT.
Efficacy
For the 48 efficacy-evaluable DLBCL patients, the ORR was 44% (Table 2). Eight patients (17%) achieved a CR and 13 (27%) achieved a PR. One patient was excluded because the patient received a nonprotocol anticancer treatment prior to end-of-treatment restaging. The ORR was 44% in patients with refractory disease (15% CRs) and 38% in patients with relapsed disease (25% CRs) (Table 2). The ORR was 50% for the 12 DLBCL patients with transformed disease (3 CRs and 3 PRs).
Best clinical response to single-agent brentuximab vedotin
| . | DLBCL . | Other B-cell . | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refractory (n = 39) . | Relapsed (n = 8) . | Total (n = 48)* . | Total (n = 19)† . | |||||||||
| No. . | % . | 95% CI‡ . | No. . | % . | 95% CI‡ . | No. . | % . | 95% CI‡ . | No. . | % . | 95% CI‡ . | |
| Objective response rate | 17 | 44 | 27.8 to 60.4 | 3 | 38 | 8.5 to 75.5 | 21 | 44 | 29.5 to 58.8 | 5 | 26 | 9.1 to 51.2 |
| Best clinical response§ | ||||||||||||
| CR | 6 | 15 | 2 | 25 | 8 | 17 | 3 | 16 | ||||
| PR | 11 | 28 | 1 | 13 | 13 | 27* | 2 | 11 | ||||
| SD | 8 | 21 | 3 | 38 | 11 | 23 | 7 | 37 | ||||
| PD | 14 | 36 | 2 | 25 | 16 | 33 | 6 | 32 | ||||
| Disease control rate|| | 25 | 64 | 6 | 75 | 32 | 67 | 12 | 63 | ||||
| . | DLBCL . | Other B-cell . | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refractory (n = 39) . | Relapsed (n = 8) . | Total (n = 48)* . | Total (n = 19)† . | |||||||||
| No. . | % . | 95% CI‡ . | No. . | % . | 95% CI‡ . | No. . | % . | 95% CI‡ . | No. . | % . | 95% CI‡ . | |
| Objective response rate | 17 | 44 | 27.8 to 60.4 | 3 | 38 | 8.5 to 75.5 | 21 | 44 | 29.5 to 58.8 | 5 | 26 | 9.1 to 51.2 |
| Best clinical response§ | ||||||||||||
| CR | 6 | 15 | 2 | 25 | 8 | 17 | 3 | 16 | ||||
| PR | 11 | 28 | 1 | 13 | 13 | 27* | 2 | 11 | ||||
| SD | 8 | 21 | 3 | 38 | 11 | 23 | 7 | 37 | ||||
| PD | 14 | 36 | 2 | 25 | 16 | 33 | 6 | 32 | ||||
| Disease control rate|| | 25 | 64 | 6 | 75 | 32 | 67 | 12 | 63 | ||||
One patient was missing disease status, but had a response assessment and was included in the efficacy analysis.
One response was determined to be not evaluable because the patient had no measureable baseline lesions.
Two-sided 95% exact confidence intervals (CIs).
Per Cheson, as assessed by the investigator.
CR + PR + SD.
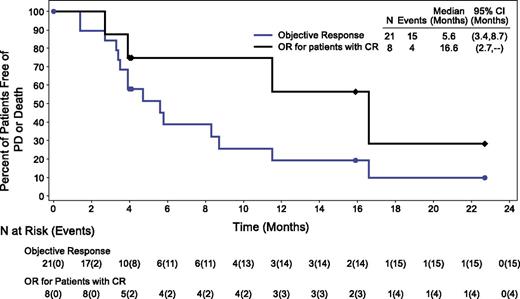
At the time of this analysis, the median follow-up time from first dose was 4.6 months (range, 0.6 to 29.5 months), and the median PFS for the DLBCL patients was 4 months (range, 0.6+ to 24+ months). The median duration of objective response was 5.6 months (range, 0+ to 22.7+ months) in all responders and 16.6 months (range, 2.7 to 22.7+ months) in patients with a CR (Figure 1). Median duration of PR was 3.9 months (range, 0+ to 8.7 months). Two patients who achieved an objective response discontinued treatment to proceed to transplant. One achieved a PR and underwent autologous SCT after 2 cycles of treatment, and the other patient achieved a PR and underwent allogeneic SCT after 7 cycles of treatment.
Duration of objective response (OR) and CR in DLBCL patients. Analyzed by using Kaplan-Meier methodology; censored patients are indicated.
Duration of objective response (OR) and CR in DLBCL patients. Analyzed by using Kaplan-Meier methodology; censored patients are indicated.
Five (26%) of the 19 efficacy-evaluable patients with other B-cell lymphomas had either CR or PR: 3 of 6 patients with gray zone lymphoma (1 CR and 2 PRs), 1 of 6 patients with PMBL (1 CR), and 1 of 3 patients with PTLD (1 CR) (see supplemental Table 1 available at the Blood Web site). One PTLD patient’s response was determined to be not evaluable because the patient had no measureable baseline lesions.
sCD30 and CD30 expression in responding DLBCL patients
A summary of baseline CD30 expression by visual central review and by computer-assisted methods as well as a summary of baseline sCD30 is presented in Table 3. Five CD30+ DLBCL patients per the enrolling institution were reclassified as having undetectable CD30 expression by central laboratory review and were included in analyses as having 0% CD30 expression. Five patients with DLBCL and 1 patient with PTLD had inadequate tissue for central review; these patients were excluded from analyses that required a quantitative CD30 expression level.
Summary of baseline CD30 expression in DLBCL by central review and computer-assisted methods and summary of baseline sCD30 for patients treated with single-agent brentuximab vedotin
| . | CR (n = 8) . | CR + PR (n = 21) . | Nonresponders (n = 27) . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. . | % . | No. . | % . | No. . | % . | |
| sCD30 expression at baseline, ng/mL* | ||||||
| Median | 103 | 121 | 223 | |||
| Range | 44-485 | 44-1341 | 36-9429 | |||
| % CD30+ malignant cells by visual central review | ||||||
| Median | 11 | 25 | 25 | |||
| Range | 0-90 | 0-90 | 0-100 | |||
| Patients with <10% CD30+ malignant cells by visual central review | 4 | 50 | 8 | 21 | 7 | 26 |
| % CD30+ in all cells by computer-assisted methods | ||||||
| Median | 58.5 | 37.4 | 20.7† | |||
| Range | 1-95 | 1-95 | 0-100 | |||
| . | CR (n = 8) . | CR + PR (n = 21) . | Nonresponders (n = 27) . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. . | % . | No. . | % . | No. . | % . | |
| sCD30 expression at baseline, ng/mL* | ||||||
| Median | 103 | 121 | 223 | |||
| Range | 44-485 | 44-1341 | 36-9429 | |||
| % CD30+ malignant cells by visual central review | ||||||
| Median | 11 | 25 | 25 | |||
| Range | 0-90 | 0-90 | 0-100 | |||
| Patients with <10% CD30+ malignant cells by visual central review | 4 | 50 | 8 | 21 | 7 | 26 |
| % CD30+ in all cells by computer-assisted methods | ||||||
| Median | 58.5 | 37.4 | 20.7† | |||
| Range | 1-95 | 1-95 | 0-100 | |||
Normal range, <29 ng/mL.
Patients with data available, n = 24; no data available, n = 3.
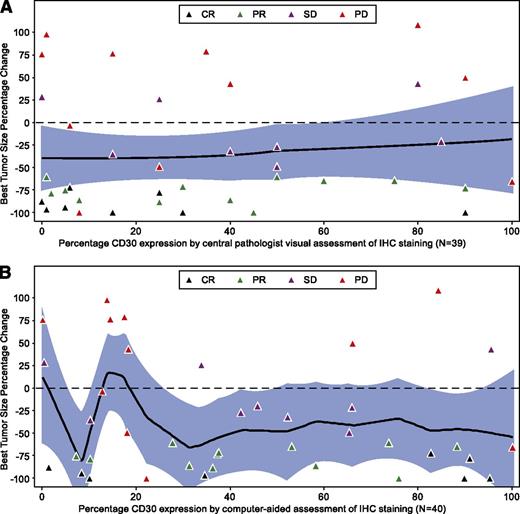
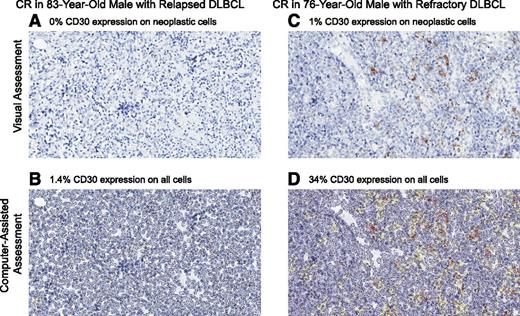
No statistical correlation was observed between response and CD30 expression as assessed by visual central review (Figure 2A) or by computer-assisted central review of IHC (Figure 2B), nor was there a correlation between CR and CD30 expression. There was also no statistical correlation between sCD30 and response or CR. However, all responding patients had elevated sCD30 at baseline, and all patients had quantifiable CD30 expression per computer-assisted assessment of IHC. As expected, the majority of patients had a higher CD30 expression level by computer-assisted analysis because this method detects low-intensity staining and analyzes all cells within the tumor whereas the central pathologist manually scores CD30 visual presence only on neoplastic cells. One DLBCL patient who achieved a CR was determined to have 0% CD30 expression by central visual review but had detectable CD30 expression (1.4%) by subsequent computer-assisted evaluation (Figure 3A-B). Another DLBCL patient who achieved a CR had 1% CD30 expression detected by visual central review but had 34% CD30 by computer-assisted methods (Figure 3C-D). Best clinical response, percentage of CD30 expression by visual assessment of neoplastic cells, percentage of CD30 expression by computer-assisted methods on all cells within tumor, and baseline sCD30 levels are shown for each of the responding DLBCL patients in supplemental Table 2.
Maximum tumor size reduction by quantitative CD30 expression in DLBCL patients. Blue-shaded area represents the 95% confidence band around the point estimates; solid line is a smooth curve based on nonparametric regression. Figure includes patients who have both postbaseline radiographic response assessments and CD30 IHC expression data. Maximum tumor size decrease by CD30 expression as assessed by (A) central visual review and (B) by computer-assisted methods.
Maximum tumor size reduction by quantitative CD30 expression in DLBCL patients. Blue-shaded area represents the 95% confidence band around the point estimates; solid line is a smooth curve based on nonparametric regression. Figure includes patients who have both postbaseline radiographic response assessments and CD30 IHC expression data. Maximum tumor size decrease by CD30 expression as assessed by (A) central visual review and (B) by computer-assisted methods.
CD30 expression per IHC assessed by visual and computer-assisted methods. An 83-year-old male with relapsed DLBCL achieved a CR after 2 cycles of treatment and had (A) 0% CD30 expression by visual central review and (B) 1.4% CD30 expression by computer-assisted methods. He discontinued treatment after 7 cycles of therapy as a result of grade 2 PSN and subsequently progressed (response duration ∼4 months). A 76-year-old male with refractory DLBCL achieved a CR after 2 cycles of treatment and had (C) 1% CD30 expression by visual central review and (D) 34% CD30 expression by computer-assisted methods. He discontinued treatment after 17 cycles of therapy as a result of PD (response duration ∼11 months).
CD30 expression per IHC assessed by visual and computer-assisted methods. An 83-year-old male with relapsed DLBCL achieved a CR after 2 cycles of treatment and had (A) 0% CD30 expression by visual central review and (B) 1.4% CD30 expression by computer-assisted methods. He discontinued treatment after 7 cycles of therapy as a result of grade 2 PSN and subsequently progressed (response duration ∼4 months). A 76-year-old male with refractory DLBCL achieved a CR after 2 cycles of treatment and had (C) 1% CD30 expression by visual central review and (D) 34% CD30 expression by computer-assisted methods. He discontinued treatment after 17 cycles of therapy as a result of PD (response duration ∼11 months).
Safety
All patients with B-cell lymphomas who received at least 1 dose of brentuximab vedotin were included in the safety analysis. Patients received a median of 4 cycles of treatment (range, 1 to 19 cycles). Neutropenia and peripheral sensory neuropathy were the primary AEs leading to dose modifications. Forty percent of patients had dose delays, and 13% had dose reductions. PD was the most common reason for treatment discontinuation (71%). Six DLBCL patients (12%) discontinued treatment because of AEs, including peripheral sensory neuropathy (PSN; n = 3), peripheral motor neuropathy, hypoxia, and elevated alanine aminotransferase (n = 1 each). Five of these 6 patients had CR and 1 had SD at the time treatment was discontinued. Three (20%) of the 15 patients with pre-existing PSN either experienced a worsening of the event on treatment or were dose reduced because of PSN. Two (33%) of the 6 patients in the combination cohort with pre-existing PSN experienced a worsening of the event on treatment. These patients did not require dose reduction.
Overall, the safety data in this study is comparable to the safety data reported in the pivotal phase 2 study of single-agent brentuximab vedotin treatment in systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL).25 Treatment-emergent AEs occurring in ≥25% of patients are shown in Table 4. Serious AEs (SAEs) of pyrexia and pneumonia were the most frequently occurring SAEs observed (10% and 9%, respectively). All 5 deaths within 30 days of the last study treatment were disease related.
Treatment-emergent AEs occurring in ≥25% of patients with B-cell lymphomas treated with single-agent brentuximab vedotin
| AE . | DLBCL (n = 49) . | Other B-cell lymphomas (n = 19) . | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1/2 . | Grade 3/4* . | Total . | Grade 1/2 . | Grade 3/4† . | Total . | |||||||
| No. . | % . | No. . | % . | No. . | % . | No. . | % . | No. . | % . | No. . | % . | |
| Fatigue | 21 | 43 | 6 | 12 | 27 | 55 | 5 | 26 | 0 | 5 | 26 | |
| Diarrhea | 18 | 37 | 3 | 6 | 21 | 43 | 4 | 21 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 26 |
| Neutropenia | 2 | 4 | 18 | 37 | 20 | 41 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 26 | 6 | 32 |
| Nausea | 13 | 27 | 6 | 12 | 19 | 39 | 4 | 21 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 26 |
| Decreased appetite | 11 | 22 | 4 | 8 | 15 | 31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Pyrexia | 13 | 27 | 1 | 2 | 15 | 31 | 5 | 26 | 0 | 5 | 26 | |
| Peripheral sensory neuropathy | 12 | 24 | 2 | 4 | 14 | 29 | 4 | 21 | 0 | 4 | 21 | |
| AE . | DLBCL (n = 49) . | Other B-cell lymphomas (n = 19) . | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1/2 . | Grade 3/4* . | Total . | Grade 1/2 . | Grade 3/4† . | Total . | |||||||
| No. . | % . | No. . | % . | No. . | % . | No. . | % . | No. . | % . | No. . | % . | |
| Fatigue | 21 | 43 | 6 | 12 | 27 | 55 | 5 | 26 | 0 | 5 | 26 | |
| Diarrhea | 18 | 37 | 3 | 6 | 21 | 43 | 4 | 21 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 26 |
| Neutropenia | 2 | 4 | 18 | 37 | 20 | 41 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 26 | 6 | 32 |
| Nausea | 13 | 27 | 6 | 12 | 19 | 39 | 4 | 21 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 26 |
| Decreased appetite | 11 | 22 | 4 | 8 | 15 | 31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Pyrexia | 13 | 27 | 1 | 2 | 15 | 31 | 5 | 26 | 0 | 5 | 26 | |
| Peripheral sensory neuropathy | 12 | 24 | 2 | 4 | 14 | 29 | 4 | 21 | 0 | 4 | 21 | |
All AEs were grade 3 with the exception of grade 4 neutropenia in 9 patients (18%).
All AEs were grade 3 with the exception of grade 4 neutropenia in 2 patients (11%).
Combination with rituximab
To explore the safety of combining brentuximab vedotin and rituximab, this study was amended in January 2013 to add approximately 15 patients with histologically confirmed DLBCL. Sixteen DLBCL patients were enrolled in this cohort, and 1 patient withdrew consent after only 1 dose of treatment and was replaced with an additional patient to ensure sufficient collection of safety data. Baseline disease characteristics in this cohort were similar to those of the DLBCL patients who received monotherapy (Table 1). Disposition and exposure are presented in supplemental Table 3. Treatment-emergent AEs occurring in ≥25% of patients were similar to those reported in the monotherapy cohort (Table 5). Neutropenia incidence appeared to be lower in patients treated with the combination potentially because of the better Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (Table 1), as well as a shorter duration of drug exposure (13% received >5 cycles vs 43% who received monotherapy). SAEs were consistent with what would be expected for the study agents and patient population (supplemental Table 4). For the efficacy-evaluable patients (n = 13), the ORR was 46% (2 CRs and 4 PRs) with a median follow-up of 2.8 months thus far (supplemental Table 5).
Treatment-emergent AEs occurring in ≥25% of DLBCL patients (n = 16) treated with brentuximab vedotin + rituximab
| Adverse event . | Grade 1/2 . | Grade 3/4 . | Total . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. . | % . | No. . | % . | No. . | % . | |
| Nausea | 6 | 38 | 0 | 6 | 38 | |
| Peripheral sensory neuropathy | 5 | 31 | 0 | 5 | 31 | |
| Vomiting | 5 | 31 | 0 | 5 | 31 | |
| Chills | 4 | 25 | 0 | 4 | 25 | |
| Headache | 4 | 25 | 0 | 4 | 25 | |
| Neutropenia | 1 | 6 | 3 | 19* | 4 | 25 |
| Pyrexia | 3 | 19 | 1 | 6† | 4 | 25 |
| Adverse event . | Grade 1/2 . | Grade 3/4 . | Total . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. . | % . | No. . | % . | No. . | % . | |
| Nausea | 6 | 38 | 0 | 6 | 38 | |
| Peripheral sensory neuropathy | 5 | 31 | 0 | 5 | 31 | |
| Vomiting | 5 | 31 | 0 | 5 | 31 | |
| Chills | 4 | 25 | 0 | 4 | 25 | |
| Headache | 4 | 25 | 0 | 4 | 25 | |
| Neutropenia | 1 | 6 | 3 | 19* | 4 | 25 |
| Pyrexia | 3 | 19 | 1 | 6† | 4 | 25 |
All grade 4.
All grade 3.
PK
PK parameters for monotherapy were determined by using concentrations of serum brentuximab vedotin ADC and plasma MMAE and actual sampling times relative to the start of infusion. The estimated area under the curve, maximum concentration, and time at which maximum concentration of brentuximab vedotin and MMAE occurred were consistent with those from historic data for brentuximab vedotin. On the basis of current analyses, there did not appear to be a significant correlation between response and exposure to ADC or MMAE.
Discussion
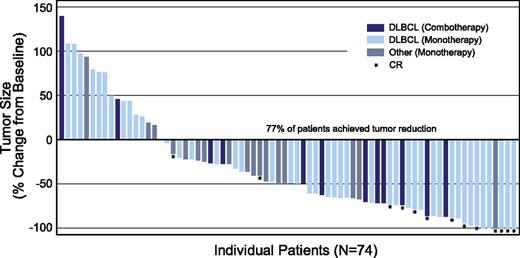
The cell surface antigen CD30 is a well-established target for the targeted delivery of MMAE to lymphoma cells via the ADC brentuximab vedotin as evidenced by an ORR of 86% (CRs, 59%) in patients with relapsed systemic ALCL and 75% (CRs, 34%) in patients with relapsed HL in pivotal studies.26,27 Both diseases are characterized by high CD30 expression. CD30 is also frequently expressed on other T- and B-cell malignancies, making brentuximab vedotin a potential therapeutic option in these diseases. In this phase 2 study of brentuximab vedotin, reduction in tumor volume was observed in the majority of enrolled patients who had B-cell NHLs with CD30 expression, as determined by standard IHC per local laboratory (Figure 4). In addition, 44% of all patients with DLBCL (27 of 61) regardless of treatment regimen (monotherapy or combination therapy) achieved an objective response (supplemental Table 4).
Maximum tumor size reduction from baseline. Includes patients with postbaseline tumor measurements (n = 74). Five patients are not included in the figure for the following reasons: 1 patient with plasmablastic lymphoma was determined to have clinical PD per investigator and had no postbaseline scans; 1 PTLD patient’s response was determined to be not evaluable because the patient had no measureable baseline lesions; and 3 patients in the combination therapy cohort were excluded because 1 patient received 1 cycle of treatment, then withdrew consent; 1 died as a result of related toxic epidermal necrolysis after 2 cycles with no response assessment; and 1 was excluded because of prohibited therapy prior to ending treatment of progression (no postbaseline scans).
Maximum tumor size reduction from baseline. Includes patients with postbaseline tumor measurements (n = 74). Five patients are not included in the figure for the following reasons: 1 patient with plasmablastic lymphoma was determined to have clinical PD per investigator and had no postbaseline scans; 1 PTLD patient’s response was determined to be not evaluable because the patient had no measureable baseline lesions; and 3 patients in the combination therapy cohort were excluded because 1 patient received 1 cycle of treatment, then withdrew consent; 1 died as a result of related toxic epidermal necrolysis after 2 cycles with no response assessment; and 1 was excluded because of prohibited therapy prior to ending treatment of progression (no postbaseline scans).
The ORR of single-agent brentuximab in DLBCL was 44% (21 of 48), including 8 (17%) CRs. CRs were durable with a median duration of 16.6 months. At a median follow-up time of 4.6 months, the median PFS in DLBCL patients was 4 months. Most DLBCL patients had refractory disease, and the ORR was no different in refractory DLBCL patients than in relapsed DLBCL patients. There was no correlation of disease or demographic characteristics with response to treatment.
Objective responses were observed in patients across a wide range of CD30 expression by central IHC. One unanticipated finding was that neither the degree of surface expression of CD30 nor levels of CD30 correlated with the likelihood of response. However, all responding DLBCL patients had elevated sCD30 at baseline and also proved to have a quantifiable level of CD30 expression by computer-assisted methods, even if the visual assessment of IHC on central review did not suggest CD30 expression. The lack of correlation between the level of surface CD30 or sCD30 and response have several possible explanations. CD30 expression within the tumor could be heterogeneous and not fully represented by random samples selected for IHC. Another possibility is that some minimal threshold of CD30 is required for response; this was not apparent in the pivotal studies in relapsed HL and ALCL, diseases with uniformly high CD30 expression, in which brentuximab vedotin can be an effective therapy.26,27 This would explain responses in patients with no CD30 expression by visual assessment of IHC but with low-level expression detected by optical methods. A bystander effect is also plausible, with uptake in the tumor microenvironment and subsequent release of MMAE to the tumor cells. To further understand the activity of brentuximab vedotin in patients with low levels of CD30 expression, this study was amended in July 2013 to evaluate the efficacy of monotherapy in DLBCL patients with undetectable CD30 expression by visual assessment of IHC. Results from this cohort are forthcoming.
Brentuximab vedotin was also active in other B-cell lymphomas. Three of the 6 patients with gray zone lymphoma achieved an objective response, and 1 patient with PTLD achieved a CR. One unexpected finding was the relatively low response rate in PMBL (1 CR in 6 patients; 17% ORR), which is typically characterized by high CD30 expression. However, given the small numbers of each of these B-cell NHL subtypes, it is difficult to establish meaningful conclusions on the activity of brentuximab vedotin in them.
The results of brentuximab vedotin monotherapy in CD30+ DLBCL are comparable to other agents studied in relapsed/refractory DLBCL. Lenalidomide alone or in combination with rituximab has ORRs of 33% to 40%, with a median duration of response of 8 to 10 months. The ORR differs by cell of origin and is 53% in the activated B-cell subtype (ABC) versus 9% in the germinal center B-cell (GCB) subtype.28-30 Similarly, ibrutinib had a single-agent ORR of 40% and PFS of 5.5 months in the ABC subtype but an ORR of only 5% in the GCB subtype.31 The combination of bendamustine and rituximab resulted in an ORR of 45.8% (CR, 15%; PR, 31%) in DLBCL. One limitation of that study, similar to limitations in our study, is that responses were not analyzed by cell of origin.32 Assessing responses to brentuximab vedotin by cell of origin of DLBCL would be an interesting exploratory analysis, although CD30 expression does not clearly correspond to the GCB or the ABC subtype of DLBCL.15-18 Other limitations of this study are the lack of a comparator arm, absence of central review of response, and lack of analysis of response by other potentially important prognostic markers, such as Bcl-2 or c-Myc. We also cannot exclude the possibility that relapsed CD30+ DLBCL has a better prognosis than relapsed CD30– DLBCL because there are no studies examining CD30 as a prognostic factor at relapse.
Brentuximab vedotin as a single agent and in combination with rituximab was generally well tolerated in these heavily pretreated patients with advanced disease. AEs were generally consistent with the known toxicity profile of brentuximab vedotin on the basis of prior studies.
In summary, brentuximab vedotin demonstrated noteworthy activity in relapsed/refractory DLBCL patients, and CRs were durable. Antitumor activity was not associated with CD30 expression levels by IHC or baseline sCD30. The activity of brentuximab vedotin in this study warrants further investigation. Additional combination studies are being considered for the treatment of relapsed/refractory DLBCL and for first-line treatment of DLBCL.
Presented in abstract form and as an oral presentation at the 55th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Hematology, New Orleans, LA, December 10, 2013.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is an Inside Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Tiffany Griffin (Seattle Genetics, Inc.) for assistance in manuscript preparation.
The study was supported by Seattle Genetics, Inc.
Authorship
Contribution: E.D.J. and N.L.B. contributed to the analysis and interpretation of data and wrote the manuscript; J.P.S., Y.O., R.H.A., J.N.W., C.M.B., and G.S. contributed to the acquisition of the data and critically reviewed the manuscript; M.C.P.-W., D.A.K., P.L., and J.Y. contributed to the analysis and interpretation of the data and critically reviewed the manuscript; all authors contributed to the concept and design of the study and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: Seattle Genetics, Inc. provided research funding to the institutions of E.D.J., J.P.S., Y.O., R.H.A., J.N.W., C.M.B., G.S., and N.L.B. N.L.B. and G.S. have acted as consultants for Seattle Genetics, Inc. C.M.B. has participated in a Seattle Genetics, Inc. speakers’ bureau. Seattle Genetics Inc. has provided J.P.S., R.H.A., and N.L.B. with funds for travel expenses. M.C.P.-W., D.A.K., P.L., and J.Y. are employees of and have equity ownership in Seattle Genetics, Inc.
Correspondence: Eric D. Jacobsen, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, 450 Brookline Ave, Rm MA221, Boston, MA 02215; e-mail: eric_jacobsen@dfci.harvard.edu.