Abstract
Introduction The prognosis for patients with high tumor burden follicular lymphoma (FL) continues to improve in the modern immunochemotherapy era. However there is still a subgroup of 20% of patients who progress within 2 years of first line R-CHOP, (rituximab, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone) and experience a poor outcome (Casulo JCO 2015). To date, early identification of these high risk patients has been unsatisfactory.
FDG-PET-CT (PET) is now the recommended imaging technique for staging and response assessment in FL and central scan review in a pooled analysis from three prospective studies has shown that post induction PET identifies a population with a high risk of death (Trotman, Lancet Haematol 2014). From this new pooled analysis we aimed to determine the prognostic impact of the total metabolic tumour volume (TMTV) measured on baseline PET and its added value to existing clinical prognostic indexes.
Material and Methods 161 FL patients who had measurable quantitative data on baseline PET were selected from PET-FL, n=84 (Dupuis, JCO 2012), PRIMA, n=36 (Trotman, JCO 2011) and FOLL05 studies, n=41 (Luminari, Ann Oncol 2014). All met criteria for treatment of symptomatic high tumour burden or advanced stage disease. They received R-CHOP (80%), R-CVP (17%) or R-FM (4%) induction therapy with 24% receiving Rituximab maintenance. TMTV was computed on baseline PET by summing the metabolic volumes of all nodal and extranodal lesions using the established 41% SUVmax thresholding method (Meignan, Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2013). Optimal cut-points for binary outcomes were determined using X-tile® and ROC analysis. Prognostic value was assessed using univariate analysis and Kaplan-Meier estimates of progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) and compared to other prognostic factors.
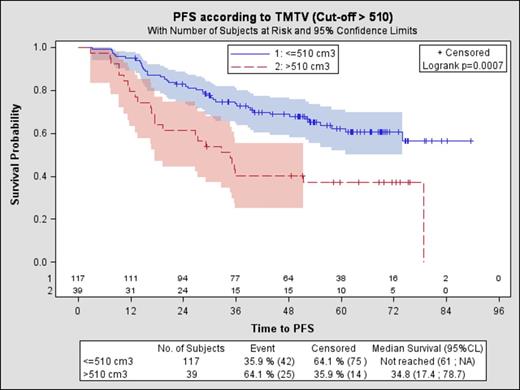
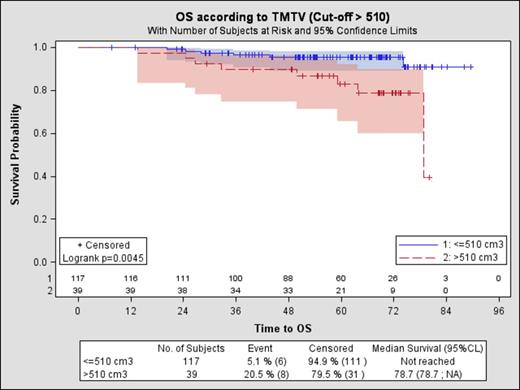
Results 156 patients with available survival data were analyzed. Median age was 56 years; 92% were stage III/IV; 38% had FLIPI 3-5; and 29% had FLIPI2 3-5. Median SUVmax was 10 (Q1-Q3: 7-14). Median TMTV was 260 cm3 (Q1-Q3: 131-513 cm3). With a median follow-up of 64 months, 5-yr PFS and OS were 56% and 92% respectively in the whole population. Using a cut-off of 510 cm3, 39 patients (25%) had a high TMTV (>510cm3). Patients with high TMTV (>510cm3) had a significantly shorter PFS (Figure 1) and OS (Figure 2) than those with low TMTV (≤510cm3), (5-yrs PFS was 37% vs 62% p=.0007, HR=2.3 and 5-yr OS 83% vs 95% p=.0045, HR=4.1). Median PFS was not reached for patients with low TMTV vs. 34.8 months for patients with high TMTV. Beta2 microglobulin (Β2Μ) >ULN and FLIPI2 3-5 were also predicted factor of poor PFS, whereas FLIPI and LDH were not. When combined, FLIPI2 and TMTV had a significant impact on PFS and OS . The 5-yr PFS was 67%, 45% and 27% respectively for patients with: low TMTV and FLIPI2 0-2, high TMTV or FLIPI2 3-5, and high TMTV and FLIPI2 3-5. Incorporating TMTV >510cm3 into the FLIPI2 instead of the longest diameter of the largest lymph node >6cm improved results for PFS and OS. Patients with 3-5 factors with this revised index had a significantly worse outcome than patients with 0-2 factors (5yr PFS 38% vs 66%, p=0.001, HR=2.62, 5yr OS 84% vs 97%, HR=4.98, p=0.013).
Conclusions In this pooled analysis from three prospective studies baselineTMTV is a strong predictor of outcome in high tumor burden FL. It adds value to existing pre-treatment prognostic indices in identifying a population for whom FL can no longer be characterized as indolent. The prognostic value of TMTV in stratifying patient outcomes needs to be validated in other populations treated with both R-CHOP +/- maintenance and R-Bendamustine.
Dupuis:ABBVIE: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; ROCHE: Speakers Bureau. Haioun:Roche: Honoraria. Salles:Celgene Corporation; Roche and Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; Calistoga Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Celgene Corporation; Genentech, Inc.; Janssen Pharmaceutica Products, L.P.; Roche: Consultancy; Celgene Corporation; Roche: Speakers Bureau. Luminari:Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Teva: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal