Abstract

Introduction: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) primarily affects older patients (pts) who often have medical comorbidities along with disease-related immunosuppression and myelosuppression. Although alkylating agents such as chlorambucil (clb) have been commonly used in these pts, novel therapies are needed. Ibrutinib (ibr) is a first-in-class, oral, covalent inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase FDA-approved for pts with CLL who received ≥1 prior therapy and for del17p CLL (including first-line). Ibr showed high activity in treatment-naïve pts age ≥65 years, with an overall response rate (ORR) of 84% (complete response [CR] in 23%) and 30-month progression-free survival (PFS) of 96% (Byrd et al. Blood 2015). We conducted a randomized, open-label phase 3 trial to evaluate efficacy and safety of single-agent ibr vs clb in treatment-naïve older pts with CLL/SLL.
Methods: Pts aged ≥65 years with treatment-naïve CLL/SLL were randomized 1:1 to receive 420 mg ibr daily until progression or clb 0.5 mg/kg (up to maximum of 0.8 mg/kg) on days 1 and 15 of a 28-day cycle for up to 12 cycles. Pts with del17p were excluded. Primary endpoint was independent review committee (IRC)-assessed PFS per iwCLL 2008 criteria, with 2012 clarification for treatment-related lymphocytosis. Secondary endpoints included overall survival (OS), ORR, event-free survival (EFS), rate of hematologic improvement, and safety. Pts with IRC-confirmed progression could transfer to an extension study where next-line therapy (including ibr) could be initiated if they had an iwCLL indication for treatment.
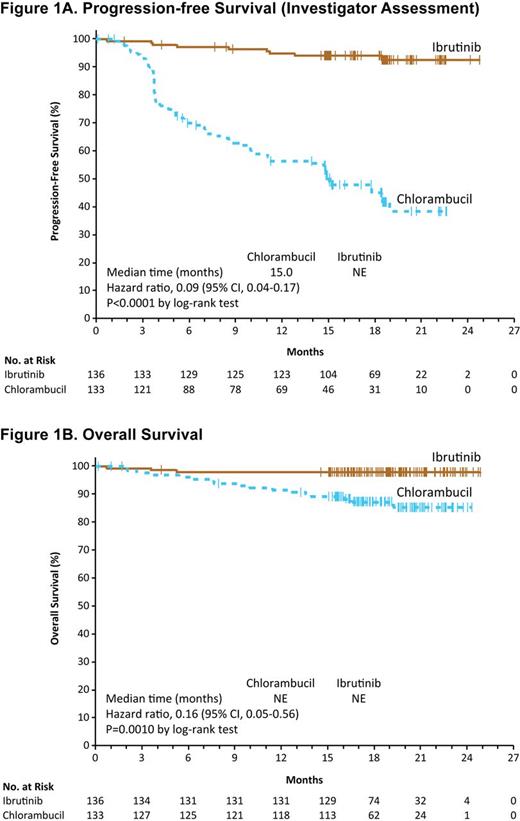
Results: Among 269 pts enrolled, median age was 73 years (70% ≥70 years). Baseline characteristics were balanced between arms; 45% had advanced Rai stage, 20% had del11q, and 69% had comorbidities at baseline including CIRS score >6, reduced creatinine clearance, or ECOG status of 2. For pts treated with clb, 40% completed 12 cycles of therapy (mean dose 0.6 mg/kg). At a median follow-up of 18.4 months (mos), ibr significantly prolonged IRC-assessed PFS vs clb (median not reached [NR] vs 18.9 mos; HR 0.16, 95% CI 0.09-0.28, P<0.0001); this was consistent within subgroups including age ≥70 years, del11q, and unmutated IGHV. As assessed by investigator, ibr reduced the risk of progression or death by 91% (HR 0.09; 95% CI, 0.04-0.17; P<0.0001; Figure 1A), with an 18-mo PFS of 93.9% vs 44.8%. Ibr significantly prolonged OS vs clb (median NR for either arm; HR 0.16, 95% CI 0.05-0.56, P=0.0010; Figure 1B); 24-mo OS was 97.8% vs 85.3%, respectively. Three deaths occurred on the ibr arm vs 17 deaths on clb arm. The IRC-assessed ORR was 86.0% with ibr (4.4% CR/CRi) vs 35.3% with clb (1.5% CR/CRi). ORR with ibr was higher than clb at all evaluated time points; at 8 mos, ORR was 84% and 31%, respectively. Investigator-assessed ORR was 90.4% (9.6% CR/CRi) vs 35.3% (4.5% CR/CRi), respectively. Median EFS was also prolonged with ibr (NR vs 12 mos; HR 0.17, 95% CI 0.10-0.26; P<0.0001). A ≥50% reduction in lymph node burden was observed in 91.2% vs 36.8% (P<0.0001), and reduction in spleen enlargement in 75.7% vs 39.1% (P<0.0001), for ibr and clb, respectively. Rates of sustained hematologic improvements were significantly higher with ibr vs clb, including in pts with baseline anemia (84% vs 45%; P<0.0001) or thrombocytopenia (77% vs 43%; P=0.0054). Median duration of treatment was 17.4 mos with ibr and 7.1 mos with clb. Most frequent (≥20% of pts) adverse events (AEs) with ibr included diarrhea, fatigue, cough and nausea. Most frequent AEs with clb included nausea, fatigue, neutropenia, anemia and vomiting. AEs leading to treatment discontinuation were less frequent with ibr (9% vs 23%). Atrial fibrillation occurred in 6% (6 pts grade 2 and 2 pts grade 3) with ibr and 1% with clb. Hypertension was noted more frequently on ibr, but was limited to grade 1-3 and managed without ibr dose modification or discontinuation. Major hemorrhage occurred in 4% (1 pt grade 2, 4 pts grade 3, 1 pt grade 4) with ibr over median follow-up of approximately 1.5 years, and in 2% with clb. At the time of study closure, 87% of pts randomized to ibr continue to receive ibr.
Conclusions: Treatment with single-agent ibr was superior to clb in terms of PFS, OS, ORR, EFS and hematologic improvement in treatment-naïve older CLL/SLL patients, with an 84% reduction in risk of death, and an acceptable safety profile.
Off Label Use: ibrutinib in first-line CLL (including non-del17p CLL). Barr:Gilead: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Consultancy, Research Funding. Robak:Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; MorphoSys AG: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Owen:Janssen: Honoraria; Lundbeck: Honoraria; Gilead: Honoraria; Roche: Honoraria. Ghia:Adaptive: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; GSK: Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy, Research Funding; Acerta Pharma BV: Research Funding. Hillmen:Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Roche Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Honoraria, Research Funding. Bartlett:Novartis: Research Funding; Millennium: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; MERC: Research Funding; Insight: Research Funding; Colgene: Research Funding; Medimmune: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Kite: Research Funding; Dynavax: Research Funding; Idera: Research Funding; Portola: Research Funding; Bristol Meyers Squibb: Research Funding; Infinity: Research Funding; LAM Theapeutics: Research Funding. Coutre:Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding. Quach:Celgene Corp, ONYX, Janssen, Takeda, Novartis, BMS: Honoraria, Research Funding. Janssens:Mundipharma: Speakers Bureau; Roche: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy. O'Dwyer:Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding. Hellmann:BMS: Consultancy, Other: funding of travel, accomodations or expenses, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Other: funding of travel, accomodations or expenses, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Schuh:Acerta Pharma BV: Research Funding. Siddiqi:Seattle Genetics: Speakers Bureau; Pharmacyclics/Jannsen: Speakers Bureau; Kite pharma: Other: attended advisory board meeting. Tam:AbbVie: Honoraria; Roche: Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Keating:Glaxo-Smith-Kline Inc.: Other: Advisory board; Celgene Corp.: Consultancy. Suri:Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Employment. Zhou:Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Employment. Clow:Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Employment. Styles:Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Employment. James:Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Employment. Kipps:Pharmacyclics Abbvie Celgene Genentech Astra Zeneca Gilead Sciences: Other: Advisor; Pharmacyclics Abbvie Celgene Genentech Astra Zeneca Gilead Sciences: Other: Advisor. Burger:Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal