Abstract
Introduction: End of treatment FDG-PET/CT activity is a powerful predictor of survival outcome in patients with Hodgkin, Diffuse large B cell and Follicular lymphomas. The predictive value of interim PET/CT scan on survival in Hodgkin lymphoma is also well established. To date, there are limited data regarding the prognostic significance of interim and end of treatment FDG-PET/scan results in adult patients with Burkitt lymphoma (BL), mainly due to the rarity of this entity. In this single-center retrospective study we analyzed the survival outcomes of patients with BL according to the findings on interim and end of treatment FDG-PET/CT scans using the Deauville criteria.
Methods: We thoroughly reviewed the clinical records of all BL patients who were treated in our medical center between 2005-2014. Thirty three patients and 104 scans were included in our final analysis. Interim PET/CT scan was performed before starting the 3rd cycle of the therapy. PET/CT scans were scored as positive or negative based on the five-point scale: scores 1-3 represented complete metabolic response (CMR) and scores 4-5 defined persistent or progressive disease. Response and survival outcomes were defined according to the Lugano Classification. Survival was calculated with the Kaplan-Meier method and survival comparison was analyzed with the Log-Rank test.
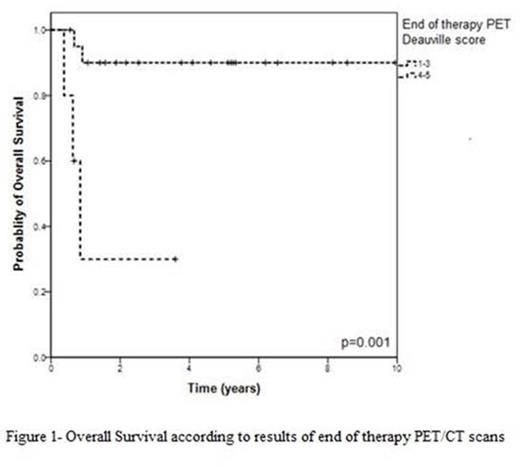
Results: Twenty four (73 %) were males and median age was 48 years (22-78). Two patients were HIV positive. Twenty four patients (73%) had stage 3 or 4 disease and 25 patients (76%) had high-intermediate or high risk disease according to the International Prognostic Index. All patients received intensive regimens, and the majority of them (78%) were treated according to the GMALL-B-ALL/NHL2002 protocol. Rituximab was part of treatment in 28 (85%) patients. After a median follow-up of 1.92 years (yrs) (0.08-9.58), 7 patients (21%) have died: six due to advanced BL and one from treatment related toxicity. The overall (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) at 3-yrs for all patients were 76% and 70%, respectively. Importantly, OS was predicted by the results of end of treatment PET/CT scans: patients in CMR (n=21) had OS of 90% while those with positive PET/CT (n=5) had OS of 30% at 3 years (Figure 1, p=0.001). Early-interim PET/CT results did not predict either PFS or OS at 3 years (OS - 85% for patients in CMR and 60% for patients with positive PET, p=0.27).
Conclusions: The current retrospective study indicates that adult patients with BL, who receive rituximab-based intensive regimens, such as the GMALL-B-ALL/NHL2002 protocol, have a favorable outcome. End of treatment PET activity strongly predicted survival outcomes while interim PET result did not correlate with prognosis. Based on our data, it appears that changing treatment in adult patients with BL only on the basis of interim PET/CT results is not advised, unless there is clear evidence of progression.
*Authors EP, MK & TD equally contributed to this study.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal