Abstract
A better understanding of the biology of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) has led to significant advances in therapeutic strategies for patients with CLL. Chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) has been the standard first-line therapy for CLL. Age and comorbidities can help decide which patients may benefit from a CIT approach. FCR (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab) is the current standard treatment option for younger patients with CLL. For older patients and for patients with renal dysfunction, bendamustine and rituximab may be a better option. For older patients with comorbidities who may not be able to tolerate intensive CIT, the combination treatment of chlorambucil and obinutuzumab or ofatumumab is an option. For patients with del(17p), ibrutinib is the treatment of choice. Several ongoing phase 3 clinical trials with novel therapies will further refine the frontline therapy of CLL.
Introduction
Chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) has been the standard first-line treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).1 In the last several years, major strides have been made in understanding the biology of CLL, and fortunately, several of these discoveries are making their way into the clinics.2-5 These include novel CD20 monoclonal antibodies (mAb) (ofatumumab and obinutuzumab),6 Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors (ibrutinib),3 phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitors (idelalisib),5 Bcl-2 inhibitors (ABT-199), and several others.7 Lenalidomide, an immunomodulatory drug, has also been studied in CLL, both in the relapsed and in the first-line setting.8 In this review, we summarize the available clinical data, in the first-line setting, with both the chemotherapy and the targeted therapy approaches in patients with CLL.
Indications for treatment
Most patients with CLL do not need treatment at the time of the diagnosis of CLL. However, the majority will ultimately require treatment during their lifetime. Assessment of prognostic markers such as IGHV mutation status, fluorescence in situ hybridization, ZAP-70, CD38, and β2-microglobulin can guide in predicting the time to first anti-CLL treatment.9 The 2008 International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (IWCLL) criteria are the standard criteria, even in the current era of novel therapies, that should be used to identify patients who need first-line treatment of CLL.10
Patient stratification for first-line treatment
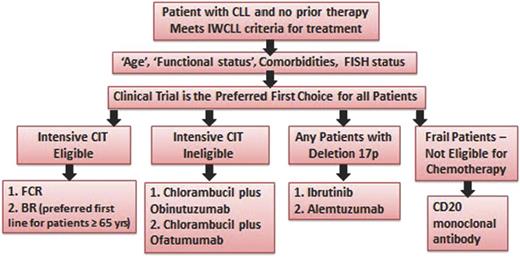
Patients with CLL who need first-line treatment can be categorized into several groups based on age, comorbidities, and performance status (see Figure 1). The German CLL Study Group (GCLLSG) has used a comorbidity index (Cumulative Illness Rating Scale [CIRS]) and kidney function to describe patients suitable for myelosuppressive CIT (CIRS ≤6 and creatinine clearance ≥70 mL/min).11 In the United States, age is most commonly used as a stratification factor with patients <65 years of age considered suitable for more intensive CIT. Patients 65 to 70 years of age with good performance status (0-1) and no significant comorbidities are also considered appropriate for more intensive CIT. Recent studies have shown that patients with del(17p), a high-risk disease subgroup, significantly benefit from nonchemotherapy approaches such as ibrutinib, and therefore, these patients, irrespective of age and comorbidities, should be offered treatment with novel targeted therapies. It is important to note that the median age of diagnosis of CLL in the United States is 72 years, and the average time to first treatment is 4 to 5 years from the time of diagnosis. However, most clinical trials in the first-line setting have enrolled younger patients.
Treatment algorithm for first-line therapy of CLL. FISH, fluorescence in situ hybridization.
Treatment algorithm for first-line therapy of CLL. FISH, fluorescence in situ hybridization.
First-line treatment
Intensive-CIT–eligible patients (non-del(17p))
The current standard first-line treatment of this group of patients is CIT with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR).12 Tam et al reported long-term outcomes of 300 patients treated first-line with FCR at the MD Anderson Cancer Center (MDACC).12,13 The median age was 57 years (range, 17-86). Fourteen percent of the patients were ≥70 years of age. A complete response (CR) rate of 72% with an overall response rate (ORR) of 95% was achieved. In patients with a partial response (PR) or better, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 80 months. Older age (≥70 years) was associated with a lower rate of achieving CR (51%). Twenty-six percent of patients did not complete the recommended 6 courses of FCR therapy.12 The major cause of premature discontinuation of therapy was persistent cytopenia (majority neutropenia), noted in almost half of the patients who discontinued therapy. Early discontinuation of therapy was significantly associated with advanced Rai stage, age >65 years, creatinine >1.4 mg/dL, hemoglobin <11 g/dL, and β2-microglobulin >4 mg/dL. Dose reductions were more common in patients older than 60 years of age.
The GCLLSG compared outcomes of FCR vs fludarabine and cyclophosphamide (FC) in a phase 3 trial (CLL8 trial). Patients needed to have a CIRS ≤6 and creatinine clearance ≥70 mL/min to be eligible. The median age was 61 years (range, 30-81). They reported a significantly improved CR rate (44% vs 22%, P < .0001), ORR (90% vs 80%, P < .0001), PFS (median PFS 52 months vs 33 months, P < .0001), and overall survival (OS) (3-year OS 87% vs 83%, P = .012) with the addition of rituximab.14 This trial established the role of an anti-CD20 mAb in the first-line therapy of CLL.
Bendamustine has also been evaluated as first-line treatment of patients with CLL. Fischer et al reported on the outcomes of 117 patients, median age 64 years (range, 34-78), with untreated CLL who received treatment with bendamustine and rituximab.15 Eligibility criteria included creatinine clearance >30 mL/min. Bendamustine was administered at a dose of 90 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 combined with 375 mg/m2 rituximab on day 0 of the first course and 500 mg/m2 on day 1 during subsequent courses, for up to 6 courses. The ORR was 88% with a CR rate of 23%. The median PFS was 34 months. Notably, 35% of the patients had a creatinine clearance ≤70 mL/min (these patients are typically excluded from the GCLLSG FCR-based studies), and these patients did equally well as compared with patients with a creatinine clearance >70 mL/min. There were 26% of the patients who were older than 70 years of age in this study, and their PFS was similar to that of the younger patient population, though ORR was lower for the older patient group.
The GCLLSG recently reported results of the randomized phase 3 study of FCR vs bendamustine/rituximab (BR) as first-line therapy for patients with CLL (CLL10 trial).16 This trial included patients with CLL (non-del(17p)) and good physical fitness (CIRS ≤6 and creatinine clearance ≥70 mL/min) who were randomized to receive FCR or BR. The primary end point of the study was noninferiority of BR vs FCR for PFS. A total of 282 patients received FCR, and 279 patients received BR. The median follow-up was 37 months. The FCR arm had a significantly higher CR/complete remission with incomplete blood count recovery (CRi) rate (39.7 vs 30.8, P = .03) with significantly improved PFS (median PFS 55.2 months vs 41.7 months, P < .001). OS was not different between the 2 groups. Not unexpectedly, patients on the FCR arm experienced more grade 3 or 4 neutropenia (84.2% vs 59%, P < .001), thrombocytopenia (21.5% vs 14.4%, P = .03), and increased risk of grade 3 or 4 infections (39.1% vs 26.8%, P < .001). However, the treatment-related mortality was similar in the 2 arms. The use of growth factors was not mandated in this study, and this may have contributed to the high rates of neutropenia and infections. In a subgroup analysis, the PFS improvement with FCR over BR was restricted to patients with an unmutated IGHV. That being said, the number of events (in either arm) in patients with mutated IGHV was low. Additionally, there was no improvement in PFS noted with FCR compared with BR in patients >65 years of age; there was, however, an increased risk of infections in the older patients (47.7% vs 20.6%, P < .001). Based on these data, FCR is the standard first-line CIT regimen for patients with CLL who are ≤65 years. However, for patients who are >65 years (and able to receive CIT), BR can be considered as the preferred first-line option. However, it is important to note that the CLL10 trial was not powered for subgroup analysis, and therefore, the lack of benefit of FCR over BR in older patients needs further assessment. In addition, in patients with impaired renal function (creatinine clearance 30-70 mL/min), FCR therapy can lead to more cytopenias, dose reductions and early treatment discontinuations,12 and therefore, BR may be a better alternative.
Several phase II studies have been reported with the intent of modifying the FCR regimen either by dose-intensifying rituximab,17 adding mitoxantrone,18,19 adding alemtuzumab,20 or adding granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor,21 but these studies have not shown superior results as compared with those seen with the standard FCR regimen. Brown et al recently reported results of a nonrandomized, parallel-cohort phase 1b study of obinutuzumab-bendamustine (G-B) or obinutuzumab-fludarabine-cyclophosphamide (G-FC) for the therapy of previously untreated fit patients with CLL (GALTON trial).22 Patients received up to 6 cycles of G-B (n = 20) or G-FC (n = 21). Infusion-related reactions (88%; grade 3-4, 20%) were the most common adverse event (AE). Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia was seen in 55% of patients on G-B and 48% of patients on G-FC. In a preliminary efficacy analysis in this small series of patients, the ORR for G-B and G-FC was 90% and 62%, respectively. Besides FCR and BR, several other chemotherapy regimens have been explored in the first-line setting including the use of fludarabine-rituximab,23,24 lower doses of FCR (FCR-lite),25,26 an alternate purine analog (pentostatin),27,28 and an alternate anti-CD20 mAb (ofatumumab)29,30 in patients with CLL (see Table 1 for details). Foon et al examined the role of lower doses of FC and higher dose of rituximab followed by rituximab maintenance (FCR-lite) as initial therapy of patients with CLL.25,26 A total of 65 CLL patients (median age, 58 years; range, 36-85 years) were treated with an ORR of 94% and a CR rate of 73%. It is important to note that majority of the patients treated on this trial had Rai stage I or II disease (80%), making them a more favorable group of patients than is usually treated on clinical trials. Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia occurred in only 11% of total cycles of FCR-lite; however, prophylactic growth factor support was routinely used. Bouvet et al reported a retrospective analysis of the dose intensity of FCR as initial therapy for patients with CLL.31 They noted that a >20% dose reduction of CIT led to a significantly lower PFS.
First-line CIT trials for CLL
| Regimen and trial . | No. of patients . | Median age (y) . | Older patents (%) . | Creatinine clearance <70 mL/min (%) . | CR% . | ORR% . | PFS (mo) . | Comments . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCR | ||||||||
| MDACC12,13 | 300 | 57 | 14% (≥70 y) | NR (creatinine ≥2 excluded) | 72 | 95 | 80 | Lower CR rate in older patients |
| CLL8 trial (FCR arm)14 | 408 | 61 | 11% (≥70 y) | Excluded | 44 | 90 | 52 | Patients (≥65 y) had similar CR and PFS as younger patients; however, there was more hematologic toxicity and bacterial infections in older patients |
| 31% (≥65 y) | ||||||||
| CLL10 trial (FCR arm)16 | 282 | 61 | 31% (≥65 y) | Excluded | 40 | 95 | 55 | |
| FCR-lite25,26 | 63 | 58 | 15% (≥70 y) | NR (creatinine ≥1.8 excluded) | 73 | 94 | 70 | |
| BR | ||||||||
| GCLLSG phase 215 | 117 | 64 | 26% (>70 y) | 35% | 23 | 88 | 34 | ORR inferior for older patients but similar PFS; patients with lower GFR had a response and PFS similar to those with GFR ≥70 mL/min |
| CLL10 trial (BR arm)16 | 279 | 62 | 39% (≥65 y) | Excluded | 31 | 96 | 42 | |
| FR | ||||||||
| CALGB 971223,24 | 104 | 63 | NR | NR (creatinine >1.5 × ULN excluded) | 47 | 84 | 42 | |
| PCR | ||||||||
| Kay27,28 | 64 | 63 | 28% (≥70 y) | 40% | 41 | 91 | 33 | No difference in PFS between older and younger or between those with poor renal function and normal renal function |
| FCO | ||||||||
| Wierda29 | 61 | 56 | 18% (≥65 y) | NR (creatinine > 1.5 × ULN excluded) | 41 | 75 | ∼70% at 1 y | |
| PCO | ||||||||
| Shanafelt30 | 48 | 65 | 38% (≥70 y) | NR (creatinine > 1.5 × ULN excluded) | 46 | 96 | NR | |
| G-FC | ||||||||
| Brown22 | 21 | 58 | NR | NR (creatinine clearance ≤ 60 mL/min excluded) | 24 | 62 | 100% at a median follow-up of 20.7 mo | |
| G-B | ||||||||
| Brown22 | 20 | 62 | NR | NR | 45 | 90 | 100% at a median follow-up of 23.5 mo |
| Regimen and trial . | No. of patients . | Median age (y) . | Older patents (%) . | Creatinine clearance <70 mL/min (%) . | CR% . | ORR% . | PFS (mo) . | Comments . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCR | ||||||||
| MDACC12,13 | 300 | 57 | 14% (≥70 y) | NR (creatinine ≥2 excluded) | 72 | 95 | 80 | Lower CR rate in older patients |
| CLL8 trial (FCR arm)14 | 408 | 61 | 11% (≥70 y) | Excluded | 44 | 90 | 52 | Patients (≥65 y) had similar CR and PFS as younger patients; however, there was more hematologic toxicity and bacterial infections in older patients |
| 31% (≥65 y) | ||||||||
| CLL10 trial (FCR arm)16 | 282 | 61 | 31% (≥65 y) | Excluded | 40 | 95 | 55 | |
| FCR-lite25,26 | 63 | 58 | 15% (≥70 y) | NR (creatinine ≥1.8 excluded) | 73 | 94 | 70 | |
| BR | ||||||||
| GCLLSG phase 215 | 117 | 64 | 26% (>70 y) | 35% | 23 | 88 | 34 | ORR inferior for older patients but similar PFS; patients with lower GFR had a response and PFS similar to those with GFR ≥70 mL/min |
| CLL10 trial (BR arm)16 | 279 | 62 | 39% (≥65 y) | Excluded | 31 | 96 | 42 | |
| FR | ||||||||
| CALGB 971223,24 | 104 | 63 | NR | NR (creatinine >1.5 × ULN excluded) | 47 | 84 | 42 | |
| PCR | ||||||||
| Kay27,28 | 64 | 63 | 28% (≥70 y) | 40% | 41 | 91 | 33 | No difference in PFS between older and younger or between those with poor renal function and normal renal function |
| FCO | ||||||||
| Wierda29 | 61 | 56 | 18% (≥65 y) | NR (creatinine > 1.5 × ULN excluded) | 41 | 75 | ∼70% at 1 y | |
| PCO | ||||||||
| Shanafelt30 | 48 | 65 | 38% (≥70 y) | NR (creatinine > 1.5 × ULN excluded) | 46 | 96 | NR | |
| G-FC | ||||||||
| Brown22 | 21 | 58 | NR | NR (creatinine clearance ≤ 60 mL/min excluded) | 24 | 62 | 100% at a median follow-up of 20.7 mo | |
| G-B | ||||||||
| Brown22 | 20 | 62 | NR | NR | 45 | 90 | 100% at a median follow-up of 23.5 mo |
FCO, fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and ofatumumab; FR, fludarabine and rituximab; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; NR, not reported; PCO, pentostatin, cyclophosphamide, and ofatumumab; PCR, pentostatin, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab; ULN, upper limit of normal.
IGHV mutation status and long-term PFS after FCR.
In the MDACC data set, the following pretreatment characteristics were associated with poor PFS after first-line FCR therapy: presence of del(17p) (hazard ratio [HR], 14.9; P < .0001) and unmutated IGHV (HR, 3.6; P = .04) (W. Wierda, MDACC, oral presentation, IWCLL meeting, September 2013). These 2 factors have also been identified by the GCLLSG to be associated with a worse PFS in patients receiving first-line FCR.14 Importantly, 60% of patients with mutated IGHV who received first-line FCR have remained free of disease progression beyond 10 years (compared with only 10% for patients with unmutated IGHV). These data point toward a possible future therapeutic strategy where the CIT approach would be reserved for patients with mutated IGHV.
Minimal residual disease (MRD) quantification and long-term outcomes.
Bottcher et al evaluated MRD by 4-color flow cytometry, with a sensitivity of at least 10−4, in both peripheral blood and bone marrow (BM) of patients enrolled on the GCLLSG CLL8 trial.32 MRD levels were characterized as low (<10−4), intermediate (≥10−4 to <10−2), or high (≥10−2). The low-level MRD equals “MRD negativity” according to the IWCLL criteria. At ∼3 months after completion of all treatment, there was a significantly higher proportion of patients with low-level MRD in the FCR arm compared with the FC arm (peripheral blood: 63% vs 35%, P < .0001; BM: 44% vs 28%, P = .0007). Achievement of low-level MRD was significantly associated with a longer PFS, irrespective of sample type, sample timing, or therapy received. In a multivariate model, MRD remained predictive for PFS and OS. The MDACC group reported outcomes for MRD assessment in BM after first-line FCR therapy in 237 patients.33 After course 3 and at final response assessment, 17% and 43% of patients were MRD negative (<10−4 by 4-color flow cytometry) in BM, respectively. In a multivariate model, mutated IGHV gene and trisomy 12 were independently associated with achievement of MRD-negative status. Similar to the results of the CLL8 trial, MRD negativity was independently associated with a significantly longer PFS and OS.
Intensive-CIT–ineligible patients (non-del(17p))
The current standard first-line treatment of this group of patients is CIT with chlorambucil and an anti-CD20 antibody.6 Hillmen et al reported results of a phase 2 study of the combination of chlorambucil and rituximab (National Cancer Research Institute CLL208 trial).34 A total of 100 patients were treated with a median age of 70 years. The ORR was 84%, with a CR rate of 10%. The median PFS was 24 months. Foa et al reported outcomes of 85 patients who received first-line treatment with chlorambucil and rituximab, followed by rituximab maintenance vs observation.35 The median age was 70 years. The ORR was 82%, with a CR rate of 17%. The median PFS was 35 months. There was a trend toward longer PFS for patients receiving rituximab maintenance.
Obinutuzumab is a humanized type II CD20 mAb with a glycoengineered Fc domain that leads to increased direct antibody-induced cell death, enhanced antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, and lower complement-dependent cytotoxicity than the type I CD20 mAb, rituximab.36,37 In preclinical studies, obinutuzumab was more effective than rituximab in B-cell depletion and inhibiting growth of human lymphomas in animal models.36,37 In the GCLLSG CLL11 trial, previously untreated patients with CLL with coexisting conditions (total CIRS score >6 and/or creatinine clearance 30-69 mL/min) were randomly assigned on a 1:2:2 basis to receive chlorambucil monotherapy, chlorambucil plus rituximab, or chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab.6,38 A total of 781 patients were enrolled, with a median age of 73 years. Treatment with obinutuzumab-chlorambucil, compared with rituximab-chlorambucil, resulted in a higher ORR (78.4% [CR 20.7% + PR 57.7%] vs 65.1% [CR 7% + PR 58.1%], P < .001) and a higher blood and BM MRD-negative rate. PFS was significantly longer with obinutuzumab-chlorambucil compared with that seen with rituximab-chlorambucil treatment (median PFS, 29.2 vs 15.4 months; P < .001).6,38 The OS was similar in the 2 arms. Infusion-related reactions and neutropenia were more common with obinutuzumab-chlorambucil than with rituximab-chlorambucil, but the risk of infection was not increased. In addition, obinutuzumab-chlorambucil arm led to an improved PFS (median PFS, 29.9 vs 11.1 months; P < .001) and OS (HR, 0.47; P = .0014) compared with that seen with chlorambucil monotherapy. In a recent update of this study, the rituximab-chlorambucil arm was also shown to be superior to chlorambucil monotherapy for both PFS (median PFS, 16.3 vs 11.1 months; P < .001) and OS (HR, 0.60; P = .02).38 The CLL11 trial establishes the combination of chlorambucil with a CD20 mAb as a standard of care for first-line therapy for older patients with CLL who have comorbidities. Based on the CLL11 trial data, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) approved obinutuzumab in combination with chlorambucil for patients with previously untreated CLL.
Ofatumumab, a type I CD20 mAb, has also been combined with chlorambucil as first-line treatment of patients with CLL who were deemed ineligible for FCR based regimens.39 In this phase 3 trial (COMPLEMENT-1 trial), 447 patients were randomized to receive chlorambucil ± ofatumumab. The combination of chlorambucil/ofatumumab led to a significantly improved ORR (82% vs 69%, P < .001) and PFS (median PFS, 22.4 months vs 13.1 months; P < .001).39 However, there was no difference in OS. Based on these results, the FDA and EMA approved the combination of ofatumumab and chlorambucil for first-line treatment of patients with CLL for whom fludarabine-based therapy is considered inappropriate
Patients with del(17p)
Patients with del(17p) or TP53 gene mutation have poor outcomes with conventional CIT regimens such as FCR, in part due to lack of wild-type p53 function, an important pathway for mediating cytotoxicity of purine analogs.13,14,40 In the GCLLSG CLL8 trial, only 1 of the 22 (5%) such patients treated on the FCR arm achieved a CR, with a median PFS of only 11.3 months.14 Similarly, in the GCLLSG first-line BR trial, none of the 8 patients with del(17p) achieved CR, and the median PFS was only 7.9 months.15 In a recent retrospective analysis, the MDACC group reported outcomes of 63 patients with del(17p) receiving first-line treatment (mainly FCR-based regimens) with a median PFS of only 14 months.41 Alemtuzumab, a humanized anti-CD52 mAb, acts via a p53-independent pathway and was thought to be an attractive strategy for patients with del(17p).42 Hillmen et al conducted a phase 3 randomized trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of intravenous alemtuzumab compared with chlorambucil in the first-line treatment of patients with CLL.43 In the subset of patients with del(17p) who were treated on the alemtuzumab arm, the median PFS was only 10.7 months, not dissimilar from the FCR first-line data.43 In an attempt to increase the efficacy of alemtuzumab, 2 recent studies evaluated the combination of alemtuzumab and corticosteroids. In the UK CLL206 trial, the use of alemtuzumab with high-dose pulse methylprednisolone as first-line treatment of patients with del(17p) (n = 17) resulted in a high ORR of 88% (CR, 65%), but the median PFS was only 18.3 months.44 The French/German CLL20 trial combined alemtuzumab with dexamethasone followed by consolidation either with alemtuzumab or with an allogeneic stem cell transplant.45 Forty-two patients with del(17p) received first-line therapy with alemtuzumab and dexamethasone in this trial, with an ORR of 97% (CR 21%) and a median PFS of 32.8 months. Consolidation with an allogeneic stem cell transplant may have contributed to the improved outcomes for this group of patients. However, due to the introduction of novel therapies (such as ibrutinib, detailed below), potential toxicities with alemtuzumab (eg, cytomegalovirus reactivation), and the withdrawal of alemtuzumab from the market (available only directly from the manufacturer), alemtuzumab has limited role in the management of patients with CLL.
Ibrutinib is an oral, selective, and irreversible inhibitor of BTK and is the current standard first-line therapy for patients with del(17p) (see “Novel therapies in the first-line setting” for details).
Patients who are frail and have significant comorbidities, making them ineligible for CIT
As mentioned previously, the median age at the time of first treatment of CLL is ∼76 to 77 years. Comorbid conditions and poor performance status can limit the ability of patients in this age group to receive CIT. For these patients, an anti-CD20 mAb therapy could be considered. All patients should be screened for del(17p), and if del(17p) is detected, treatment with ibrutinib should be offered.
Hainsworth et al reported outcomes with rituximab monotherapy as initial treatment in 44 patients (median age, 66 years) with CLL.46 Patients received 375 mg/m2 rituximab weekly for 4 consecutive weeks, and those without disease progression continued to receive identical 4-week rituximab courses at 6-month intervals, for a total of 4 courses. The ORR was 58%, with a CR of 9%. The median PFS was 18.6 months. Strati et al reported outcomes of 40 patients with CLL who received rituximab and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor as initial therapy.47 The median age was 73 years. The ORR was 59%, with a median PFS of 15 months. Flinn et al examined the role of ofatumumab monotherapy in the first-line setting in patients who were >65 years or in younger patients who had declined fludarabine-based treatment.48 A total of 77 patients were enrolled, with a median age of 72 years. Ofatumumab was given weekly for 8 weeks with an initial dose of 300 mg followed by either 2000 mg (cohort 1) or 1000 mg (cohort 2). Maintenance therapy with ofatumumab (every 2 months) for 2 years was also given. The ORRs for cohorts 1 and 2 were 55% (5% CR) and 36% (4% CR), respectively. The PFS at 15 months for cohort 1 was 74%. Flynn et al examined the role of obinutuzumab monotherapy in untreated patients with CLL (GAGE trial).49 A total of 80 patients (median age, 67 years) were treated at either the 2000-mg or 1000-mg dose level. The ORR was higher in the 2000-mg cohort (67% ORR, 21% CR/CRi) compared with the 1000-mg cohort (49% ORR, 5% CR/CRi).
Novel therapies in the first-line setting
Lenalidomide is an immunomodulatory drug with multiple effects on the tumor microenvironment and immune system, including downregulation of immune checkpoint PD-1 on T cells.50-53 Based on the encouraging results of lenalidomide in patients with relapsed/refractory CLL,54-56 the group at MDACC explored lenalidomide monotherapy as first-line therapy for patients with CLL.8,57 Treatment consisted of 5 mg lenalidomide daily continuously. After 2 28-day courses, the dose of lenalidomide could be escalated by 5 mg per cycle to the maximum daily dose of 25 mg. A total of 60 patients (≥65 years) were enrolled. The median age was 71 years (range, 66-85). The median daily dose received was 5 mg. The ORR was 65%, with a CR of 10%. The median time to best response was 25 months. The estimated 2-year PFS was 60%. Tumor flare, noted in 52% of the patients, was associated with an improved PFS. Chen et al treated 25 previously untreated patients with CLL in a single-arm phase 2 trial.58,59 The median age was 60 years (range, 33-78). The original study design used a starting lenalidomide dose of 10 mg daily (21 days out of a 28-day cycle). However, significant toxicities (tumor lysis and cytopenias) were noted in first 2 enrolled patients; the study was then amended to decrease the starting dose to 2.5 mg daily, with a target daily dose of 10 mg (dose escalation to 25 mg was permitted for nonresponders). The median daily dose received was 15 mg. In the original report, an ORR of 56% was noted, with no CR.58 In an updated analysis, the authors reported an improved ORR of 72%, with a CR of 20%.59 Similar to the MDACC study, the responses improve over time and the best response is often delayed; the median time to best response in this study was 18 months. The 3-year PFS and OS were 65% and 85%, respectively.59 Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia and thrombocytopenia were common (76% and 28%, respectively). The MDACC group recently reported preliminary results of the combination of lenalidomide and rituximab as first-line therapy for patients with CLL.60 The treatment consisted of 375 mg/m2 rituximab given weekly for 4 weeks then monthly during months 3 to 12 and 10 mg lenalidomide day by mouth from day 9 onwards continuously. Forty-eight patients were evaluable, with a median age of 66 years (range, 42-79). The ORR was 83% with a CR rate of 15%. ORR was similar for patients with mutated and unmutated IGHV gene, age ≥65 years and <65 years, or for various fluorescence in situ hybridization categories. The median PFS and OS were not reached at a median follow up of 11 months. Future studies, likely in combination with targeted agents, will further clarify the role of lenalidomide in the first-line treatment of CLL.
B-cell receptor (BCR) activation plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of CLL.61,62 BTK is a non–receptor tyrosine kinase of the Tec kinase family and plays a crucial role in BCR signaling.63 Ibrutinib is an oral, selective, and irreversible inhibitor of BTK. It forms a specific bond with the cysteine-481 of BTK.64 Ibrutinib has been extensively studied in patients with relapsed or refractory CLL with a very high ORR and improved PFS and OS compared with ofatumumab in a randomized phase 3 trial (RESONATE trial).2-4 Ibrutinib is FDA approved for patients with relapsed/refractory CLL and for patients with del(17p).3 There are limited data reported so far with ibrutinib in the first-line setting. O’Brien et al reported on the outcomes of 31 patients with CLL/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) who received ibrutinib monotherapy in the first-line setting.65 The median age was 71 years (range, 65–84). As this was a first-line trial, the frequency of del(17p) and del(11q) were low (6% and 3%, respectively). After a median follow-up of 35 months, an ORR of 84% was noted, with 23% attaining CR, 55% PR, and 6% partial response with lymphocytosis (PR-L).4 The 30-month PFS was 96%, and OS was 97%. It is important to note that most patients will develop lymphocytosis after initiating ibrutinib. This is an expected finding with ibrutinib and other BCR inhibitors, and it generally resolves over the course of 6 to 9 months with continued ibrutinib treatment. Development of lymphocytosis does not appear to be detrimental to long-term clinical outcomes.66
A recent study from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute reported on the outcomes of 35 patients with untreated CLL with del(17p) or TP53 mutation who received treatment with ibrutinib.67 The median age was 62 years (range, 33-82). An impressive ORR of 97% was noted, with 12% attaining CR, 70% PR, and 15% PR-L. The median time to CR was 48 weeks. The 2-year PFS was 91%. These data compare quite favorably to the median PFS of only 11 months noted with CIT in the first-line setting for patients with del(17p).14 In addition, in the relapsed setting, the median PFS for patients with 17p deletion with ibrutinib monotherapy is ∼28 months4 ; these data in the relapsed setting are much superior to those seen with CIT, even in the first-line setting for patients with del(17p). Based on these data, the FDA and EMA approved ibrutinib for all patients with del(17p). Ibrutinib is the current standard first-line therapy for patients with del(17p).
PI3K-δ is critical for activation, proliferation, and survival of B cells and is hyperactive in many B-cell malignancies, including CLL.68 Idelalisib is a potent and selective inhibitor of PI3K-δ and is approved by the FDA in combination with rituximab for patients with relapsed or refractory CLL where rituximab monotherapy would be considered appropriate.5 The idelalisib and rituximab combination is also approved for the first-line treatment of patients with del(17p) by the EMA, but not the FDA. As with ibrutinib, the majority of studies with idelalisib have been conducted in patients with relapsed or refractory CLL,5 and there are limited data in the first-line setting. In a recent report, idelalisib monotherapy (150 mg twice daily) was given as first-line therapy to older patients (≥65 years) with CLL/SLL.69 A total of 37 patients (median age, 70 years) were treated. Fourteen percent of the patient had del(17p). In the 27 evaluable patients, an ORR of 81% (all PR/PR-L) was noted. The most frequent grade ≥3 treatment-related AEs included rash 3%, diarrhea 3%, and pneumonia 5%. Pneumonitis was observed in 2 patients. Results from idelalisib in combination with rituximab in the first-line setting for older patients (≥65 years) with CLL/SLL have also been reported.70 A total of 64 patients were enrolled, with a median age of 71 years (range, 65-90). The ORR was 97%, with a CR rate of 19%. There were 9 patients with del(17p)/TP53 mutation, all of whom responded (3 CR and 6 PR). However, toxicities were common with this regimen; the important grade ≥3 AEs included diarrhea/colitis (42%), pneumonia (19%), rash (13%), and transaminitis (23%). In addition, pneumonitis developed in 2 patients, both grade 5, and 1 patient with diverticulitis developed bowel perforation. It is important to note that diarrhea/colitis is a late event with the median time to onset of grade ≥3 diarrhea/colitis of 9.5 months (range, 3-29). Toxicities observed with idelalisib may be immune mediated,71,72 and a more intact immune system in the first-line setting may have contributed to the increased toxicities.
Conclusions
As detailed above, the therapy for CLL is undergoing a major transformation at this time. Several of the novel targeted therapies have already gained FDA approval. Most of them are oral (hence ease of administration) with excellent response rates and acceptable toxicities. A major challenge at this time is how best to incorporate these novel therapies in the clinical care of our patients. Ibrutinib is approved for all patients with del(17p), including in the first-line setting. The combination of idelalisib and rituximab is approved for del(17p) in the first-line setting by the EMA. The combinations of obinutuzumab/chlorambucil and of ofatumumab/chlorambucil are approved for the first-line treatment of patients who are deemed unfit for CIT. There are several ongoing or planned phase 3 randomized trials with novel targeted therapies in the first-line setting (see Table 2). Additionally, there are several ongoing phase 2 trials with the combination of novel targeted agents in the first-line setting (such as ibrutinib plus FCR in younger patients [NCT02251548]; duvelisib, a PI3K-δ and PI3K-γ inhibitor, plus FCR in younger patients [NCT02158091]; ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab in older patients [NCT02315768]; ABT-199, a Bcl-2 antagonist in patients with del(17p) [NCT01889186]; and lenalidomide plus obinutuzumab [NCT02371590]). These trials will further clarify the role of targeted therapies as initial therapy of CLL.
Ongoing or planned phase 3 trials in the first-line setting for CLL
| Trial name . | Trial number . | Patient population . | Trial design . |
|---|---|---|---|
| RESONATE-2 | NCT01722487 | ≥65 y; no del(17p) | Ibrutinib vs chlorambucil |
| PCYC-1130-CA | NCT02264574 | ≥18 y | Ibrutinib/obinutuzumab vs chlorambucil/obinutuzumab |
| ECOG-E1912 | NCT02048813 | 18-70 y; no del(17p) | IR vs FCR |
| UK NCRI CLL10 | — | — | IR vs FCR |
| ALLIANCE A041202 | NCT01886872 | ≥65 y | Ibrutinib vs IR vs BR |
| GS-US-312-0118 | NCT01980875 | ≥18 y | Idelalisib/obinutuzumab vs chlorambucil/obinutuzumab |
| GS-US-312-0123 | NCT01980888 | ≥18 y | BR ± idelalisib |
| Trial name . | Trial number . | Patient population . | Trial design . |
|---|---|---|---|
| RESONATE-2 | NCT01722487 | ≥65 y; no del(17p) | Ibrutinib vs chlorambucil |
| PCYC-1130-CA | NCT02264574 | ≥18 y | Ibrutinib/obinutuzumab vs chlorambucil/obinutuzumab |
| ECOG-E1912 | NCT02048813 | 18-70 y; no del(17p) | IR vs FCR |
| UK NCRI CLL10 | — | — | IR vs FCR |
| ALLIANCE A041202 | NCT01886872 | ≥65 y | Ibrutinib vs IR vs BR |
| GS-US-312-0118 | NCT01980875 | ≥18 y | Idelalisib/obinutuzumab vs chlorambucil/obinutuzumab |
| GS-US-312-0123 | NCT01980888 | ≥18 y | BR ± idelalisib |
IR, ibrutinib and rituximab; NCRI, National Cancer Research Institute.
Authorship
Contribution: N.J. and S.O.B. planned the review, conducted the literature search, and wrote the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: N.J. has served as a consultant to Pharmacyclics and Novartis and has received research support from Pharmacyclics, BMS, Genentech/Roche, and Infinity. S.O.B. has served as a consultant to Amgen, Celgene, and GSK and has received research support from Pharmacyclics, Acerta, TG Therapeutics, Regeneron, ProNAi, and Infinity.
Correspondence: Susan O’Brien, Chao Family Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of California Irvine Medical Center, 101 The City Dr, Building 56, Room 216L, Orange, CA 92868; e-mail: obrien@uci.edu.