Abstract
The therapeutic benefits of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) for hematologic malignancies are primarily derived from an anti-leukemia effect that is mediated by T cells in donor grafts. Unfortunately, these T cells also mediate graft-versus-host disease (GvHD), the major complication of allo-HSCT.
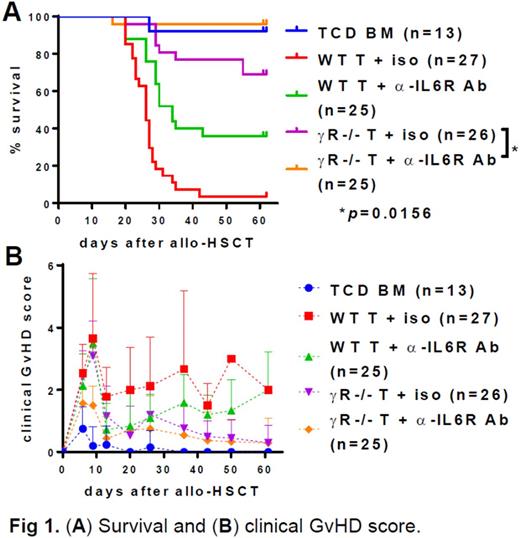
We have previously published that in vivo administration of JAK1/JAK2 inhibitors to murine allo-HSCT recipients of interferon gamma receptor deficient (IFNγR-/-) T cells results in 100% survival in a fully MHC-mismatched B6 to Balb/c allo-HSCT model (Choi et al., 2014, PLoS ONE). Since the infusion of IFNγR-/- T cells alone is associated with only ~70% survival, we hypothesize that JAK1/JAK2 inhibitors have either additional off-target effects or are inhibiting other non-IFNγR signaling pathways which are themselves dependent on JAK1/JAK2. The major other cytokine receptor signaling pathway mediated via both JAK1 and JAK2 is the interleukin 6 receptor (IL6R) signaling pathway. Thus, it is possible that JAK1/JAK2 inhibitors also block signaling through IL6R in addition to IFNγR. In addition, Alam et al. have recently reported that single nucleotide polymorphisms of donor IFNγ and IL6 are closely linked to gastrointestinal GvHD in patients (2015, BMT). Therefore, we examined if blockade of both IFNγR and IL6R signaling results in complete elimination of GvHD after a fully MHC-mismatched allo-HSCT in which B6 (H-2b) T cell-depleted bone marrow cells (5x106) along with B6 pan T cells (5x105) are intravenously injected into lethally irradiated Balb/c mice (H-2d). As shown in Fig. 1, we have found that blocking both IFNγR (IFNγR-/- T cells) and IL6R (α-IL6R Ab) signaling dramatically reduces GvHD and results in >95% survival. In addition, we found that blocking both IFNγR and IL6R signaling significantly increased regulatory T cells (Tregs) in peripheral blood (23.2% Foxp3+ in CD4+ T cells (n=17) vs 2.5% in WT T cell control (n=16) at day 27 after allo-HSCT), suggesting that increase in Tregs might be a potential mechanism underlying the reduced GvHD after dual blockade of IFNγR and IL6R signaling.
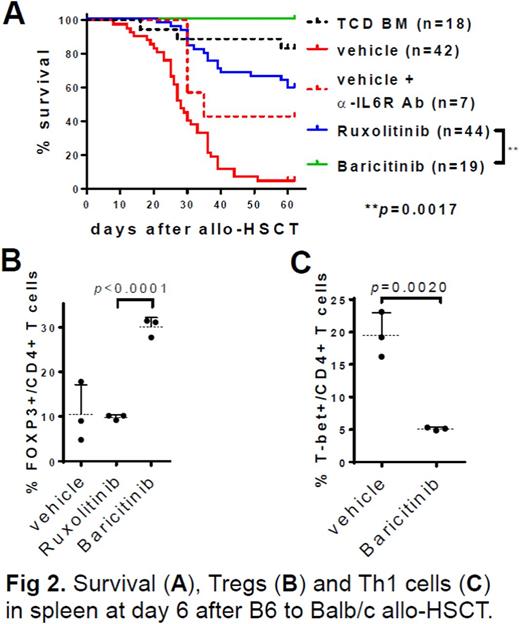
Baricitinib is a potent and balanced JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor currently being clinically developed by Eli Lilly for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. We hypothesize that baricitinib will optimally block both IFNγR and IL6R signaling pathways and prevent GvHD. We found that that baricitinib is a potent suppressor of GvHD in B6 to Balb/c allo-HSCT models (100% survival), superior to ruxolitinib and similar to blockade of both IFNγR and IL6R signaling (Fig. 2A). Baricitinib increases Tregs in vivo (Fig. 2B) and reduces the ratio of IL5 (Th2 cytokine) to IL2 (cytokine for Treg induction) in plasma (p=0.0046), a potential diagnostic marker for GvHD (Fujii et al., 2006, Int J Mol Med), significantly better than ruxolitinib. Lastly, we found that baricitinib inhibits the expression of T-bet (Fig. 2C), which is the master transcription factor of Th1 cells, that are primary effector T cells in inducing GvHD. These data suggest that the suppression of GvHD by baricitinib results from increased Tregs and decreased Th1 and Th2 cells.
We next examined if the prevention of GvHD by baricitinib is dependent on natural regulatory T cells (Tregs) in donor grafts. Tregs were depleted from donor pan T cells before allo-HSCT (B6 to Balb/c). We found that in vivo administration of baricitinib resulted in 70% survival (0% control, p<0.0001; 100% Treg-replete T cells + baricitinib. In addition, based on clinical GvHD score when recipients of Treg-replete T cells were compared with those of Treg-deplete T cells, the beneficial effect of Tregs in the donor grafts for the prevention of GvHD was observed only for the first two weeks after allo-HSCT (p≤0.01).
Lastly, we examined whether baricitinib can cure ongoing GvHD by administering baricitinib starting at day 10 after allo-HSCT when GvHD is established (B6 to Balb/c). We found that baricitinib treatment results in a significant reduction of GvHD and 100% survival (10% control, p<0.0001).
All of these data suggest that pharmacologic co-blockade of IFNγR and IL6R pathways is a promising therapeutic strategy to prevent and effectively treat established GvHD. The inhibitory effect of baricitinib, ruxolitinib, and blockade of IFNγR and IL6R on JAK-STAT signaling using JAK/STAT phosphorylation antibody arrays is currently being investigated and will be presented.
DiPersio:Incyte Corporation: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal