Abstract
Background: Studies have shown that hypomethylating agents (HMAs), including 5-AZA and decitabine (Dac) are well-tolerated antileukemic agents (Kantarjian et al, JCO, 2012). Despite its myelosuppressive effect, Dac has low extramedullary toxicities, making it an attractive drug for allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT). Reports suggest that HMAs selectively upregulate tumor associated antigens (TAAs) on malignant cells without expression in healthy tissue (Cruijsen, 2016). We previously reported on a series of 20 patients (pts) in a phase I study of 5-day Dac plus mini fludarabine and busulfan (DacMiniFluBu) in elderly or medically infirm pts (Baker et al, Blood, 2012). In the current analysis, we compared updated results from our DacFluBu study with a historical MiniFluBu control group in pts with MDS or AML.
Methods: Pts were evaluated to assess engraftment, toxicity, disease response, PFS and OS. Pts received Dac 20 mg/m2/day on days (d) -15 to -11, Flu 30 mg/m2/day, on d -7 to -3 and Bu 130 mg/m2 on d -4 and -3. The control group received Flu 30 mg/m2 on d -6 to -2 and Bu 130 mg/m2 on d -3 and -2. Both groups received thymoglobulin 2 mg/kg IV on d -3, -2 and -1, followed by infusion of donor stem cells on d 0. Immunosuppression consisted of tacrolimus starting on d -2 and MTX 5 mg/m2 IV on d +1, 3, 6, and 11.
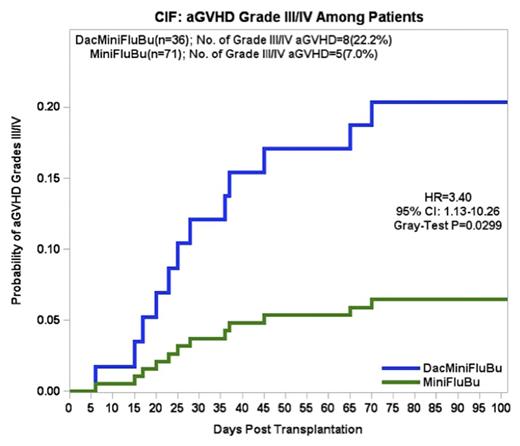
Results: 107 pts were analyzed between 5/2009 and 8/2015; 36 pts received DacMiniFluBu; 17 with MDS, and 19 with AML. 23 (64%) had unrelated donors (URD); 13 (36%) had sibling donors. 71 pts were included in the MiniFluBu control group for comparison; 33 with MDS, and 38 with AML. 53 (75%) had URD; 18 (25%) had sibling donors. Median age was 68.5 yrs compared to 66 yrs, respectively. Cohorts were comparable for gender, disease and graft source. The incidence of severe (gr III/IV) acute GVHD (aGvHD) was 22% compared to the control group of 6% (p=0.0195). Moderate or severe cGVHD was seen in 7 pts vs 22 in the control group (p=0.2535). The median follow-up in the DacMiniFluBu group was 262 d, OS was 35%, relapse incidence was 28%, and NRM at 6 mos was 22%. In the control group, the median follow-up was 424 d (p=0.2213), OS was 34%, relapse was 41%, and NRM was 15%. Median time to relapse in the study vs control group was 142 and 149 d (p=0.8722). There were 22 deaths after DacMiniFluBu and 43 after MiniFluBu (p=0.7382). 6 pts in the study group received DLI at a median of 170 d post HCT for either relapse (n=3) or falling chimerism (n=3) compared to 16 pts in the control group at a median of 183 d. Multivariate analysis was performed to estimate the cumulative incidence of severe aGvHD by regimen. Results showed that conditioning regimen (HR=3.98, 95% CI, p=0.0197), degree of match (HR=1.365, p=0.039) and non-hematologic (heme) gr IV events (HR= 4.266, p=0.029) were all significant independent factors predicting a higher incidence of severe aGvHD.
Conclusions: There were no significant differences in the cumulative incidences of relapse or survival between pts receiving DacMiniFluBu and MiniFluBu. However, the risk of severe aGvHD was 4 times greater in DacMiniFluBu recipients when controlling for infections, degree of match, and non-heme gr IV events. Findings were confirmed in univariate and multivariate analyses. This may be explained by the increased expression of TAAs in healthy tissues in response to Dac, which evoke T cell responses. This is the first report showing that adding Dac to the MiniFluBu regimen was an independent risk factor for severe aGvHD. Other findings in our analysis linking age, risk stratification, and degree of match to GvHD are consistent with prior reports. The differences between our results and those of other studies warrant larger validation analyses. Dac as part of a conditioning regimen should only be used in context of a clinical trial.
Skarbnik:Genentech: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Vesole:Amgen: Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Speakers Bureau. Goy:Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Acerta: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Research Funding; Johnson & Johnson: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; infinity: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Writing support, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.



This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal